Abstract
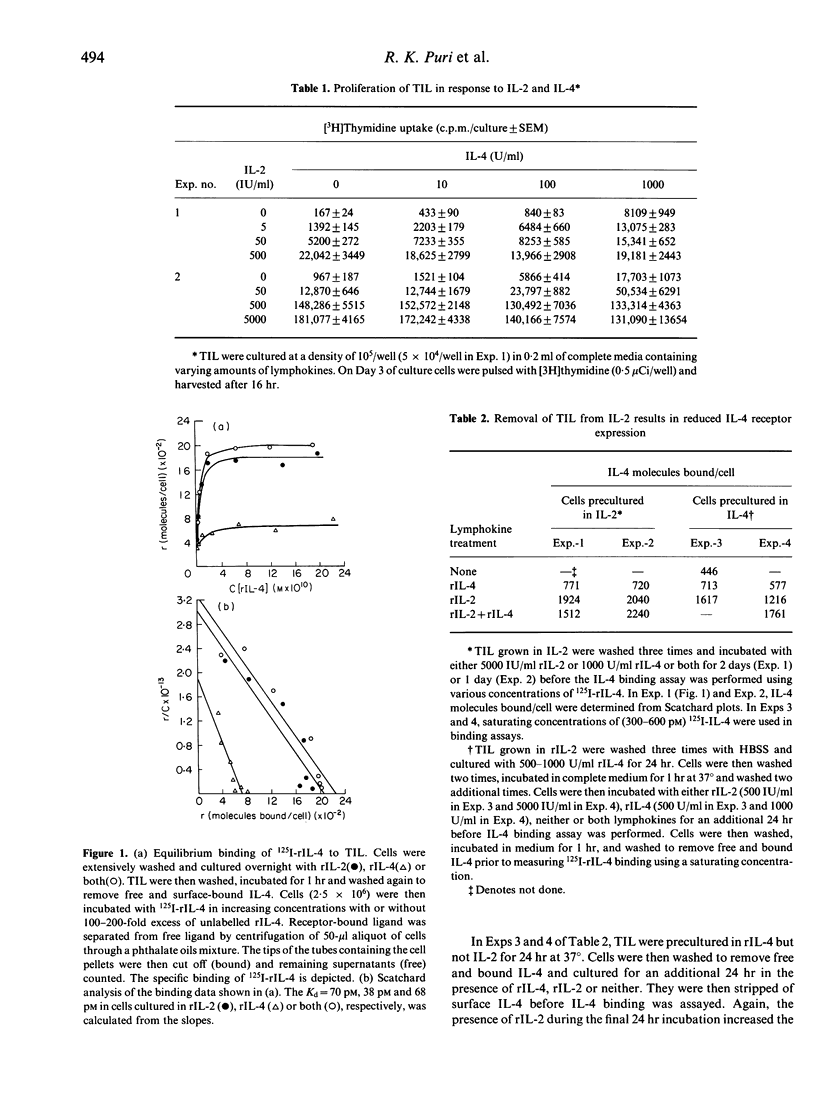
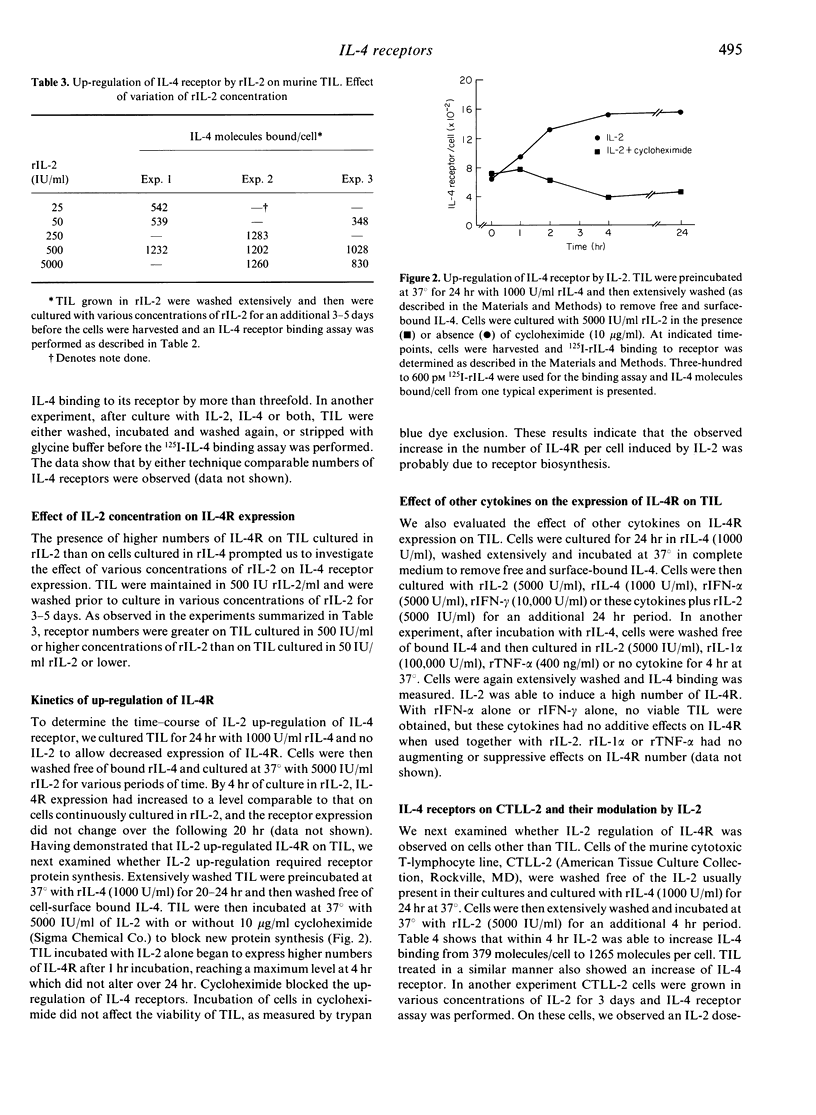
Since interleukin-2 (IL-2) and IL-4 act in concert to support the development of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and the generation of antigen-specific tumour infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL), we investigated the interaction of these cytokines with an established TIL line. TIL proliferated in an additive fashion in response to suboptimal concentrations of IL-2 and various concentrations of IL-4. TIL possessed high-affinity IL-4 receptors whether cultured in recombinant IL-2 (rIL-2) or rIL-4, but cells cultured in rIL-2 had higher numbers of IL-4 receptors than cells cultured in rIL-4. When TIL were cultured in increasing concentrations of rIL-2, a dose-dependent enhancement in IL-4 receptor number was observed. The maximum induction of IL-4 receptor expression was achieved by 4 hr of incubation with rIL-2 and was completely blocked by cycloheximide. Other cytokines, such as rIL-1, recombinant tumour necrosis factor (rTNF), recombinant interferon-alpha (rIFN-alpha) and rIFN-gamma, had no effect on IL-4 receptor number. rIL-2 also up-regulated IL-4 receptors on CTLL-2, a murine CTL line. These data indicate that high-affinity IL-4 receptors exist on murine TIL and they can be up-regulated by IL-2. Our observation that IL-2 up-regulates IL-4 receptor may help explain the additive effects of these lymphokines on the proliferation of TIL and other cell lines. It may also help explain their co-operative effects on the generation of antigen-specific TIL and the differentiation of CTL.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fernandez-Botran R., Sanders V. M., Mosmann T. R., Vitetta E. S. Lymphokine-mediated regulation of the proliferative response of clones of T helper 1 and T helper 2 cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):543–558. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Botran R., Sanders V. M., Vitetta E. S. Interactions between receptors for interleukin 2 and interleukin 4 on lines of helper T cells (HT-2) and B lymphoma cells (BCL1). J Exp Med. 1989 Feb 1;169(2):379–391. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrini S., Biassoni R., Moretta A., Bruzzone M., Nicolin A., Moretta L. Clonal analysis of T lymphocytes isolated from ovarian carcinoma ascitic fluid. Phenotypic and functional characterization of T-cell clones capable of lysing autologous carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1985 Sep 15;36(3):337–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbloom D. S., Hoover D. L., Wahl L. M. The characteristics of binding of human recombinant interferon-gamma to its receptor on human monocytes and human monocyte-like cell lines. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foxwell B. M., Woerly G., Ryffel B. Identification of interleukin 4 receptor-associated proteins and expression of both high- and low-affinity binding on human lymphoid cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Sep;19(9):1637–1641. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horohov D. W., Crim J. A., Smith P. L., Siegel J. P. IL-4 (B cell-stimulatory factor 1) regulates multiple aspects of influenza virus-specific cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4217–4223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Farrar J., Hilfiker M., Johnson B., Takatsu K., Hamaoka T., Paul W. E. Identification of a T cell-derived b cell growth factor distinct from interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):914–923. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson G. H., Heinemann D., Symes M. O., Williamson R. C. Differential immune reactivity of tumour-intrinsic and peripheral-blood lymphocytes against autoplastic colorectal carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 1981 Sep;44(3):396–402. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1981.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Platsoucas C. D., Balch C. M. Autologous tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the infiltrate of human metastatic melanomas. Activation by interleukin 2 and autologous tumor cells, and involvement of the T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1419–1441. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami Y., Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T. Interleukin 4 promotes the growth of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes cytotoxic for human autologous melanoma. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2183–2191. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Castle B. E., Christiansen J., Schreurs J., Rennick D., Arai N., Hoy P., Takebe Y., Howard M. Expression of high affinity receptors for murine interleukin 4 (BSF-1) on hemopoietic and nonhemopoietic cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):456–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muul L. M., Spiess P. J., Director E. P., Rosenberg S. A. Identification of specific cytolytic immune responses against autologous tumor in humans bearing malignant melanoma. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):989–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara J., Paul W. E. Up-regulation of interleukin 4/B-cell stimulatory factor 1 receptor expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8221–8225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park L. S., Friend D., Grabstein K., Urdal D. L. Characterization of the high-affinity cell-surface receptor for murine B-cell-stimulating factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1669–1673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A. Adoptive immunotherapy of cancer using lymphokine activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2. Important Adv Oncol. 1986:55–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T., Muul L. M., Chang A. E., Avis F. P., Leitman S., Linehan W. M., Robertson C. N., Lee R. E., Rubin J. T. A progress report on the treatment of 157 patients with advanced cancer using lymphokine-activated killer cells and interleukin-2 or high-dose interleukin-2 alone. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 9;316(15):889–897. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704093161501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Packard B. S., Aebersold P. M., Solomon D., Topalian S. L., Toy S. T., Simon P., Lotze M. T., Yang J. C., Seipp C. A. Use of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and interleukin-2 in the immunotherapy of patients with metastatic melanoma. A preliminary report. N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 22;319(25):1676–1680. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812223192527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Spiess P., Lafreniere R. A new approach to the adoptive immunotherapy of cancer with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1318–1321. doi: 10.1126/science.3489291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess P. J., Yang J. C., Rosenberg S. A. In vivo antitumor activity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes expanded in recombinant interleukin-2. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987 Nov;79(5):1067–1075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vose B. M., Gallagher P., Moore M., Schofield P. F. Specific and non-specific lymphocyte cytotoxicity in colon carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1981 Dec;44(6):846–855. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1981.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


