Abstract
Lewis rats immunized with myelin basic protein (MBP) in Freund's complete adjuvant (FCA) suffer from a single episode of paralysis from which they recover spontaneously. Subsequent to recovery, further episodes of paralysis cannot normally be induced by reimmunization with MBP in FCA. It is well established that serum, obtained from rats in the refractory state, can suppress the induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) when given to animals from the time of immunization with MBP in FCA. Here it is shown that treatment with some such sera from Day 7 after immunization also suppressed the disease. However, not all convalescent sera were suppressive, indicating that rats immunized with MBP in FCA could become refractory to EAE without assayable levels of suppressive activity in their sera. In the context of this result it was notable that a correlation was found between the level of antibody specific for the encephalitogenic peptide in sera and the ability to suppress EAE. An inverse relationship was also shown between the amount of anti-encephalitogenic peptide antibody produced after immunization and the severity of EAE induced. Spleen cells from animals treated with Lewis anti-MBP serum after immunization with MBP in FCA could be activated to transfer EAE by in vitro culture with MBP despite the absence of any clinical signs in the donor animals, i.e. the serum inhibited the expansion or differentiation of these cells rather than preventing their priming or bringing about clonal deletion.
Full text
PDF

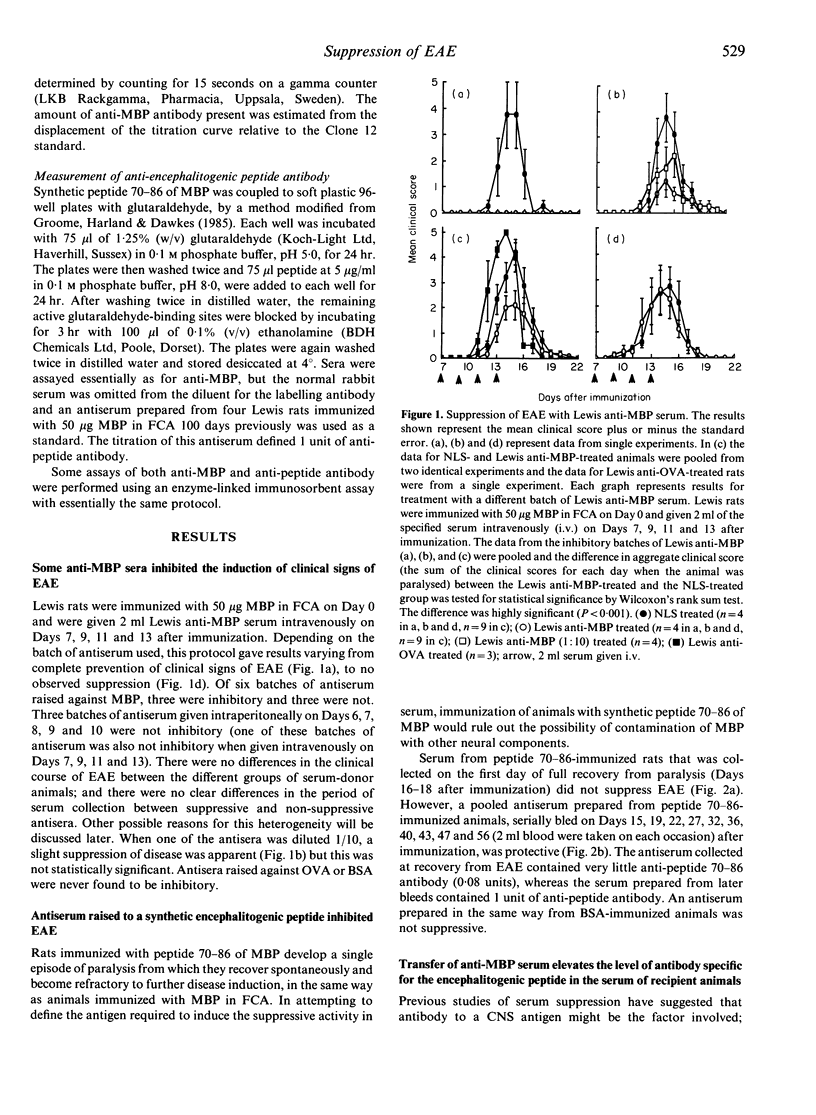
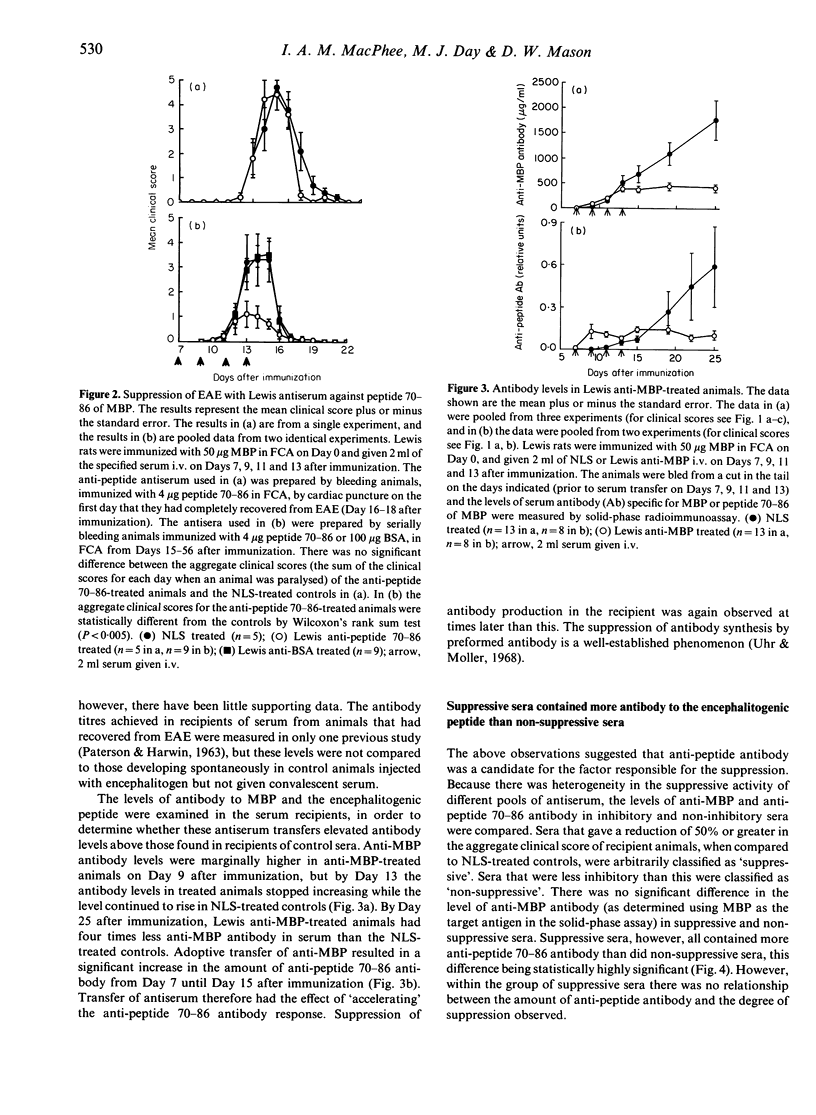
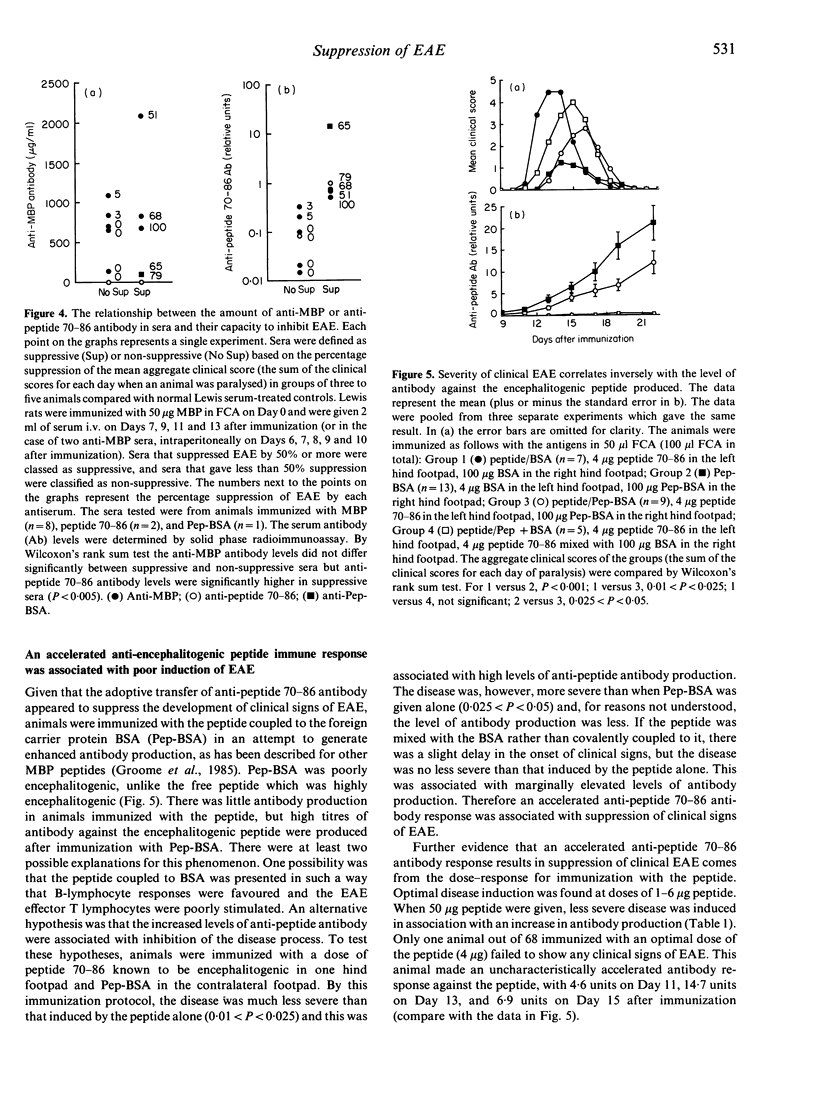
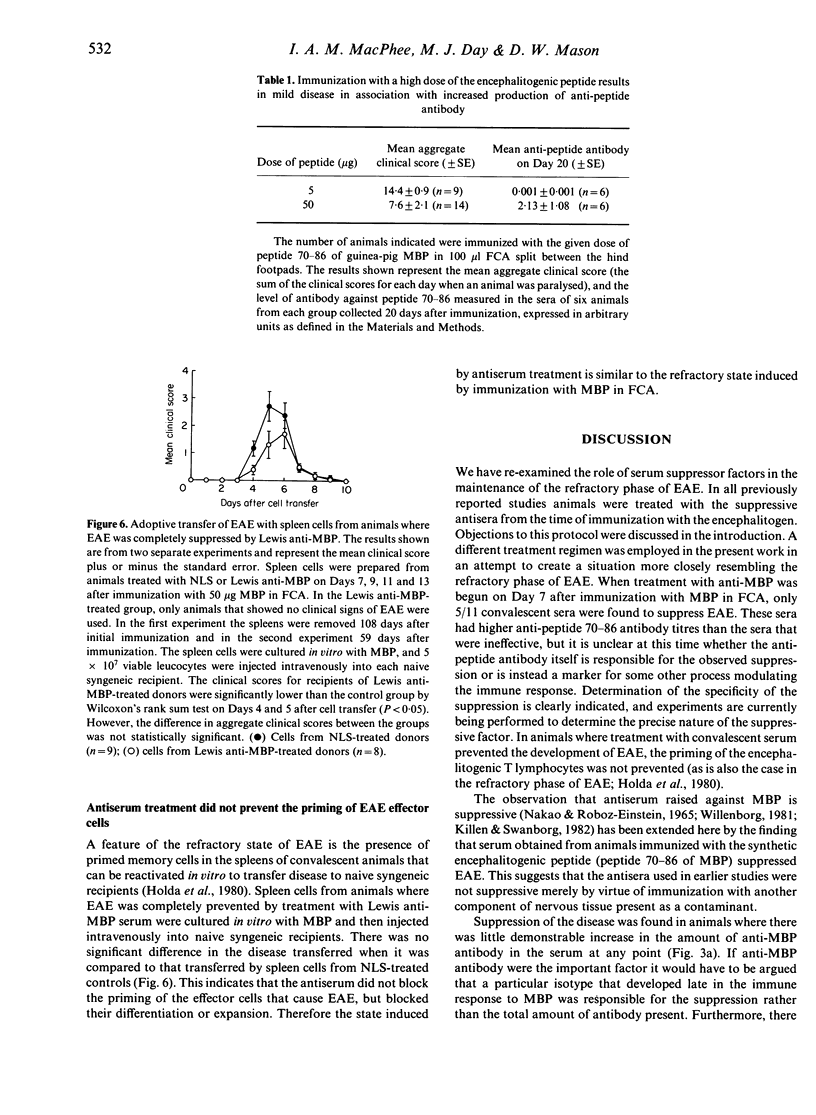


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner T., Ovadia H., Evron S., Mizrachi R., Abramsky O. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: passive transfer of resistance during lactation. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Oct;12(4):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostoff S. W., Mason D. W. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: successful treatment in vivo with a monoclonal antibody that recognizes T helper cells. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1938–1942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrt P., Ada G. L. An in vitro reaction between labelled flagellin or haemocyanin and lymphocyte-like cells from normal animals. Immunology. 1969 Oct;17(4):503–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. H., Fritz R. B., Chou F. C., Kibler R. F. The immune response of Lewis rats to peptide 68-88 of guinea pig myelin basic protein. I. T cell determinants. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1540–1543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin G., Engers H. D. Inhibition of antigen-induced T-cell clone proliferation by antigen-specific antibodies. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):547–548. doi: 10.1038/308547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellerman K. E., Powers J. M., Brostoff S. W. A suppressor T-lymphocyte cell line for autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):265–267. doi: 10.1038/331265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groome N. P., Dawkes A., Gales M., Hruby S., Alvord E. C., Jr Region-specific immunoassays for human myelin basic protein. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Oct;12(4):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinrichs D. J., Roberts C. M., Waxman F. J. Regulation of paralytic experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats: susceptibility to active and passive disease reinduction. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1857–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holda J. H., Welch A. M., Swanborg R. H. Autoimmune effector cells. I. Transfer of experimental encephalomyelitis with lymphoid cells cultured with antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):657–659. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell M. D., Winters S. T., Olee T., Powell H. C., Carlo D. J., Brostoff S. W. Vaccination against experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with T cell receptor peptides. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):668–670. doi: 10.1126/science.2814489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. A. Protection of rats from experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with antiserum to guinea-pig spinal cord. Immunology. 1974 Apr;26(4):703–711. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killen J. A., Swanborg R. H. Regulation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Part 4. Further characterization of postrecovery suppressor cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1982 Oct;3(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(82)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Zanders E. D., Lake P., Webster R. G., Eckels D. D., Woody J. N., Green N., Lerner R. A., Feldmann M. Inhibition of T cell proliferation by antibodies to synthetic peptides. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Feb;14(2):153–157. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R., Steinetz B. Effects of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis on thymus and adrenal: relation to remission and relapse. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Nov;165(2):218–224. doi: 10.3181/00379727-165-40961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee I. A., Antoni F. A., Mason D. W. Spontaneous recovery of rats from experimental allergic encephalomyelitis is dependent on regulation of the immune system by endogenous adrenal corticosteroids. J Exp Med. 1989 Feb 1;169(2):431–445. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee I. A., Mason D. W. Studies on the refractoriness to reinduction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats that have recovered from one episode of the disease. J Neuroimmunol. 1990 Apr;27(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(90)90131-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlin D. E., Blank S. E., Kibler R. F. Recurrent experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):712–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minagawa H., Takenaka A., Itoyama Y., Mori R. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. A model of predictable relapse by cyclophosphamide. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Apr;78(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris P. J. Suppression of rejection of organ allografts by alloantibody. Immunol Rev. 1980;49:93–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00428.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAO A., ROBOZ-EINSTEIN E. CHEMICAL AND IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES WITH A DIALYZABLE ENCEPHALITOGENIC COMPOUND FROM BOVINE SPINAL CORD. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:171–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATERSON P. Y., HARWIN S. M. Suppression of allergic encephalomyelitis in rats by means of antibrain serum. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:755–774. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesoa S. A., Hayosh N. S., Swanborg R. H. Regulation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Part 5. Role of the recipient in suppressor cell induction. J Neuroimmunol. 1984 Dec;7(2-3):131–135. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(84)80013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polman C. H., Matthaei I., de Groot C. J., Koetsier J. C., Sminia T., Dijkstra C. D. Low-dose cyclosporin A induces relapsing remitting experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Feb;17(3):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J. O., Whitaker J. N., Vasu R. I., Metzger D. W. Multiple epitopes in a dodecapeptide of myelin basic protein determined by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2426–2431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin S., Kibler R. F., Morrison D. C. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats: inhibition by bacterial lipopolysaccharides and acquired resistance to reinduction by challenge with myelin basic protein. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):16–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richert J. R., Driscoll B. F., Kies M. W., Alvord E. C., Jr Adoptive transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: incubation of rat spleen cells with specific antigen. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):494–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick J. D. Long-term depletion of CD8+ T cells in vivo in the rat: no observed role for CD8+ (cytotoxic/suppressor) cells in the immunoregulation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):495–502. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick J., Brostoff S., Mason D. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the absence of a classical delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. Severe paralytic disease correlates with the presence of interleukin 2 receptor-positive cells infiltrating the central nervous system. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1058–1075. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. A., Rumjanek V. M. Transfer of protection against allergic encephalomyelitis from mother to offspring. Immunology. 1984 Jan;51(1):201–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W., Möller G. Regulatory effect of antibody on the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1968;8:81–127. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60465-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbark A. A., Hashim G., Offner H. Immunization with a synthetic T-cell receptor V-region peptide protects against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):541–544. doi: 10.1038/341541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch A. M., Holda J. H., Swanborg R. H. Regulation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. II. Appearance of suppressor cells during the remission phase of the disease. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):186–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willenborg D. O. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat: studies on the mechanism of recovery from disease and acquired resistance to reinduction. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1145–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willenborg D. O. Total body irradiation allows reinduction of allergic encephalomyelitis in convalescent Lewis rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;68(3):247–251. doi: 10.1159/000233106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. W., Vandenbark A. A., Jacobs M. P., Offner H., Raus J. C. Murine monoclonal anti-myelin basic protein (MBP) antibodies inhibit proliferation and cytotoxicity of MBP-specific human T cell clones. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Sep;24(1-2):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


