Abstract
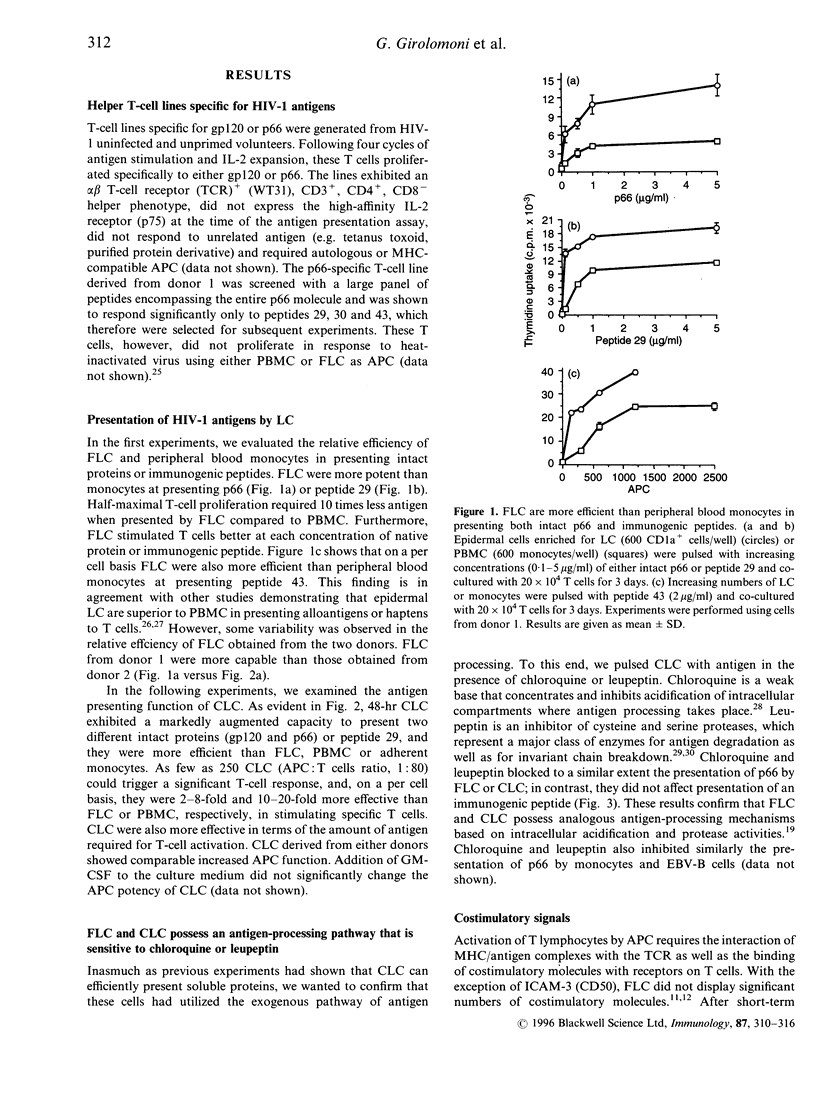
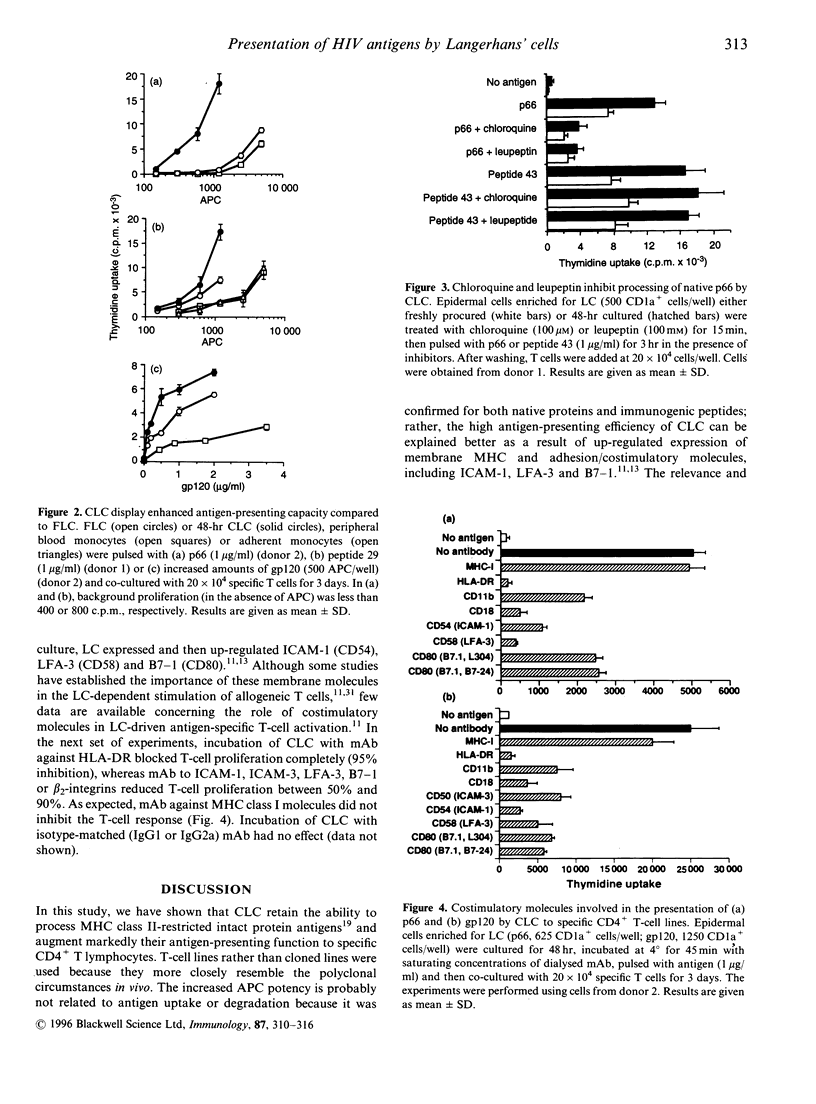
Cultured Langerhans' cells (CLC) exhibit enhanced antigen-presenting function compared to freshly isolated LC (FLC), but they are commonly believed to be inefficient at processing intact proteins. In this study, FLC and CLC from normal, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) seronegative volunteers were compared for their ability to present the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120 or reverse transcriptase (p66) antigens to autologous, specific CD4+ T cell lines. Epidermal cell suspensions enriched for LC were prepared from suction blister roofs. FLC stimulated T cells at lower antigen concentrations compared to unfractionated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). CLC were more potent on a per cell basis than FLC, PBMC or adherent monocytes at presenting native gp120, native p66 or immunogenic peptides. CLC were also more efficient than FLC or PBMC in terms of the amount of antigen required for T-cell activation. Chloroquine and leupeptin inhibited presentation of intact p66, but not of an immunodominant peptide, by FLC or CLC, thus indicating that both cells utilize antigen-processing mechanisms that are based on intracellular acidification and protease activity. Incubation of CLC with monoclonal antibodies against HLA-DR, CD11b, CD18, CD50, CD54, CD58 or CD80, but not anti-major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I), inhibited antigen-specific T-cell proliferation to varying degrees. We conclude that human CLC retain the ability to process and present protein antigens potently to CD4+ T cells. Thus, CLC have the capacity to participate actively in the generation and maintenance of T-helper cell immunity to viral antigens during HIV-1 infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba S., Katz S. I. The ability of cultured Langerhans cells to process and present protein antigens is MHC-dependent. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2479–2487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker D., Reske-Kunz A. B., Knop J., Reske K. Biochemical properties of MHC class II molecules endogenously synthesized and expressed by mouse Langerhans cells. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1213–1220. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. G., McLachlan S. M., Britton S. Cyclosporin A promotes spontaneous outgrowth in vitro of Epstein-Barr virus-induced B-cell lines. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):300–301. doi: 10.1038/289300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blauvelt A., Clerici M., Lucey D. R., Steinberg S. M., Yarchoan R., Walker R., Shearer G. M., Katz S. I. Functional studies of epidermal Langerhans cells and blood monocytes in HIV-infected persons. J Immunol. 1995 Apr 1;154(7):3506–3515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caux C., Dezutter-Dambuyant C., Schmitt D., Banchereau J. GM-CSF and TNF-alpha cooperate in the generation of dendritic Langerhans cells. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):258–261. doi: 10.1038/360258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. J., Katz S. I. Cultured human Langerhans cells process and present intact protein antigens. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Sep;99(3):331–336. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12616663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft M., Duncan D. D., Swain S. L. Response of naive antigen-specific CD4+ T cells in vitro: characteristics and antigen-presenting cell requirements. J Exp Med. 1992 Nov 1;176(5):1431–1437. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai R., Grammer S. F., Streilein J. W. Fresh and cultured Langerhans cells display differential capacities to activate hapten-specific T cells. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):59–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Reid P. A., Lanzavecchia A., Watts C. Processed antigen binds to newly synthesized MHC class II molecules in antigen-specific B lymphocytes. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90575-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enk A. H., Angeloni V. L., Udey M. C., Katz S. I. An essential role for Langerhans cell-derived IL-1 beta in the initiation of primary immune responses in skin. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):3698–3704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannetti A., Zambruno G., Cimarelli A., Marconi A., Negroni M., Girolomoni G., Bertazzoni U. Direct detection of HIV-1 RNA in epidermal Langerhans cells of HIV-infected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1993 Apr;6(4):329–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolomoni G., Cruz P. D., Jr, Bergstresser P. R. Internalization and acidification of surface HLA-DR molecules by epidermal Langerhans cells: a paradigm for antigen processing. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jun;94(6):753–760. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolomoni G., Simon J. C., Bergstresser P. R., Cruz P. D., Jr Freshly isolated spleen dendritic cells and epidermal Langerhans cells undergo similar phenotypic and functional changes during short-term culture. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2820–2826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolomoni G., Stone D. K., Bergstresser P. R., Cruz P. D., Jr Vacuolar acidification and bafilomycin-sensitive proton translocating ATPase in human epidermal Langerhans cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 May;96(5):735–741. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12470970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolomoni G., Zambruno G., Manca V., Bergstresser P. R., Cruz P. D., Jr Spleen dendritic cells exhibit altered morphology and increased allostimulatory capacity after short-term culture. Exp Dermatol. 1992 Oct;1(3):129–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1992.tb00004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolomoni G., Zambruno G., Manfredini R., Zacchi V., Ferrari S., Cossarizza A., Giannetti A. Expression of B7 costimulatory molecule in cultured human epidermal Langerhans cells is regulated at the mRNA level. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Jul;103(1):54–59. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12389619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G., Oliver J., Bilyk N., McMenamin C., McMenamin P. G., Kraal G., Thepen T. Downregulation of the antigen presenting cell function(s) of pulmonary dendritic cells in vivo by resident alveolar macrophages. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):397–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleijmeer M. J., Oorschot V. M., Geuze H. J. Human resident langerhans cells display a lysosomal compartment enriched in MHC class II. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Oct;103(4):516–523. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12395666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch F., Heufler C., Kämpgen E., Schneeweiss D., Böck G., Schuler G. Tumor necrosis factor alpha maintains the viability of murine epidermal Langerhans cells in culture, but in contrast to granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, without inducing their functional maturation. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):159–171. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch F., Trockenbacher B., Kämpgen E., Grauer O., Stössel H., Livingstone A. M., Schuler G., Romani N. Antigen processing in populations of mature murine dendritic cells is caused by subsets of incompletely matured cells. J Immunol. 1995 Jul 1;155(1):93–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämpgen E., Koch N., Koch F., Stöger P., Heufler C., Schuler G., Romani N. Class II major histocompatibility complex molecules of murine dendritic cells: synthesis, sialylation of invariant chain, and antigen processing capacity are down-regulated upon culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3014–3018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D., Constant S., Pasqualini T., Flavell R., Bottomly K. Role of dendritic cells in the priming of CD4+ T lymphocytes to peptide antigen in vivo. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):6742–6750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manca F., Fenoglio D., Valle M. T., Li Pira G., Kunkl A., Ferraris A., Saverino D., Lancia F., Mortara L., Lozzi L. Human CD4+ T cells can discriminate the molecular and structural context of T epitopes of HIV gp120 and HIV p66. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995 Jul 1;9(3):227–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manca F., Habeshaw J. A., Dalgleish A. G., Fenoglio D., Li Pira G., Sercarz E. E. Role of flanking variable sequences in antigenicity of consensus regions of HIV gp120 for recognition by specific human T helper clones. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jan;23(1):269–274. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manca F., Habeshaw J., Dalgleish A. The naive repertoire of human T helper cells specific for gp120, the envelope glycoprotein of HIV. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 15;146(6):1964–1971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manca F., Walker L., Newell A., Celada F., Habeshaw J. A., Dalgleish A. G. Inhibitory activity of HIV envelope gp120 dominates over its antigenicity for human T cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Apr;88(1):17–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowicz S., Engleman E. G. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor promotes differentiation and survival of human peripheral blood dendritic cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):955–961. doi: 10.1172/JCI114525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll H. Epidermal Langerhans cells are critical for immunoregulation of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Immunol Today. 1993 Aug;14(8):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90138-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mommaas A. M., Mulder A. A., Out C. J., Girolomoni G., Koerten H. K., Vermeer B. J., Koning F. Distribution of HLA class II molecules in epidermal Langerhans cells in situ. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Feb;25(2):520–525. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Doherty U., Steinman R. M., Peng M., Cameron P. U., Gezelter S., Kopeloff I., Swiggard W. J., Pope M., Bhardwaj N. Dendritic cells freshly isolated from human blood express CD4 and mature into typical immunostimulatory dendritic cells after culture in monocyte-conditioned medium. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):1067–1076. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paglia P., Girolomoni G., Robbiati F., Granucci F., Ricciardi-Castagnoli P. Immortalized dendritic cell line fully competent in antigen presentation initiates primary T cell responses in vivo. J Exp Med. 1993 Dec 1;178(6):1893–1901. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.6.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinet V., Vergelli M., Martin R., Bakke O., Long E. O. Antigen presentation mediated by recycling of surface HLA-DR molecules. Nature. 1995 Jun 15;375(6532):603–606. doi: 10.1038/375603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puré E., Inaba K., Crowley M. T., Tardelli L., Witmer-Pack M. D., Ruberti G., Fathman G., Steinman R. M. Antigen processing by epidermal Langerhans cells correlates with the level of biosynthesis of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules and expression of invariant chain. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1459–1469. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappersberger K., Gartner S., Schenk P., Stingl G., Groh V., Tschachler E., Mann D. L., Wolff K., Konrad K., Popovic M. Langerhans' cells are an actual site of HIV-1 replication. Intervirology. 1988;29(4):185–194. doi: 10.1159/000150045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid C. D., Stackpoole A., Meager A., Tikerpae J. Interactions of tumor necrosis factor with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and other cytokines in the regulation of dendritic cell growth in vitro from early bipotent CD34+ progenitors in human bone marrow. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 15;149(8):2681–2688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Res P., Kapsenberg M. L., Bos J. D., Stiekema F. The crucial role of human dendritic antigen-presenting cell subsets in nickel-specific T-cell proliferation. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 May;88(5):550–554. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12470142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Teletski C. L., Stang E., Bakke O., Long E. O. Cell surface HLA-DR-invariant chain complexes are targeted to endosomes by rapid internalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8581–8585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani N., Gruner S., Brang D., Kämpgen E., Lenz A., Trockenbacher B., Konwalinka G., Fritsch P. O., Steinman R. M., Schuler G. Proliferating dendritic cell progenitors in human blood. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):83–93. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani N., Koide S., Crowley M., Witmer-Pack M., Livingstone A. M., Fathman C. G., Inaba K., Steinman R. M. Presentation of exogenous protein antigens by dendritic cells to T cell clones. Intact protein is presented best by immature, epidermal Langerhans cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):1169–1178. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani N., Schuler G. The immunologic properties of epidermal Langerhans cells as a part of the dendritic cell system. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1992;13(3-4):265–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00200527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallusto F., Lanzavecchia A. Efficient presentation of soluble antigen by cultured human dendritic cells is maintained by granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor plus interleukin 4 and downregulated by tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1109–1118. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. C., Cruz P. D., Jr, Tigelaar R. E., Sontheimer R. D., Bergstresser P. R. Adhesion molecules CD11a, CD18, and ICAM-1 on human epidermal Langerhans cells serve a functional role in the activation of alloreactive T cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Jan;96(1):148–151. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12515946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer R. D. The mixed epidermal cell-lymphocyte reaction. I. Human epidermal cells elicit a greater allogeneic lymphocyte response than do autologous peripheral blood lymphoid cells. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2612–2614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stössel H., Koch F., Kämpgen E., Stöger P., Lenz A., Heufler C., Romani N., Schuler G. Disappearance of certain acidic organelles (endosomes and Langerhans cell granules) accompanies loss of antigen processing capacity upon culture of epidermal Langerhans cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1471–1482. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen M. B., Rongen H. A., Bos J. D. Function of adhesion molecules lymphocyte function-associated antigen-3 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human epidermal Langerhans cells in antigen-specific T cell activation. J Immunol. 1994 Apr 1;152(7):3400–3409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R., Davis L. S., Lipsky P. E. Isolation and characterization of human peripheral blood dendritic cells. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):821–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidard L., Rock K. L., Benacerraf B. Heterogeneity in antigen processing by different types of antigen-presenting cells. Effect of cell culture on antigen processing ability. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):1905–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambruno G., Cossarizza A., Zacchi V., Ottani D., Luppi A. M., Giannetti A., Girolomoni G. Functional intercellular adhesion molecule-3 is expressed by freshly isolated epidermal Langerhans cells and is not regulated during culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Aug;105(2):215–219. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12317494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


