Abstract
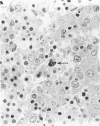
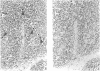
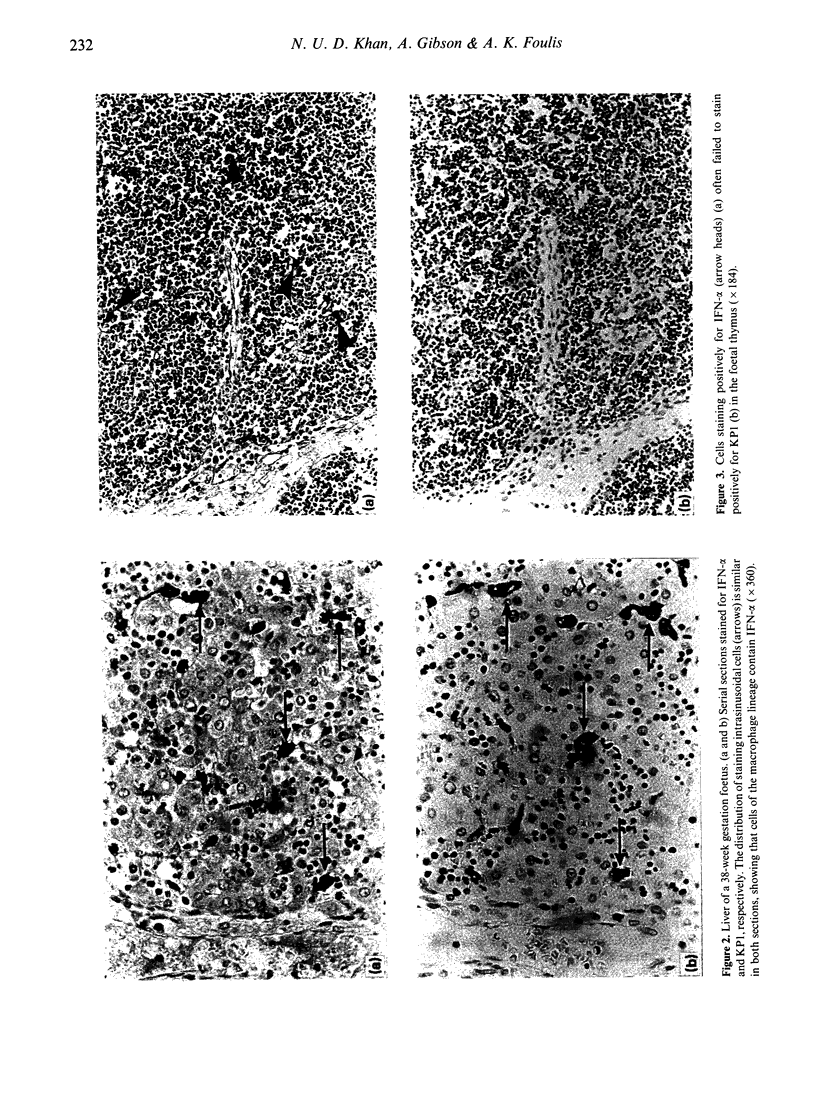
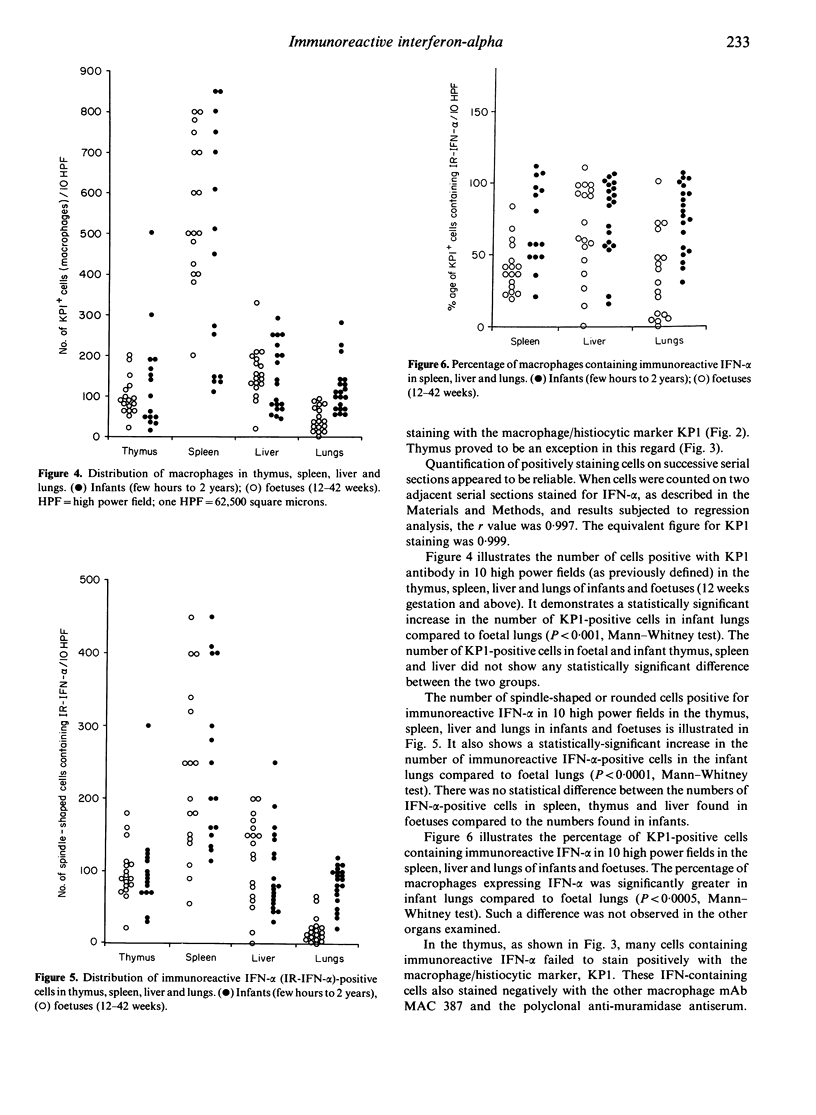
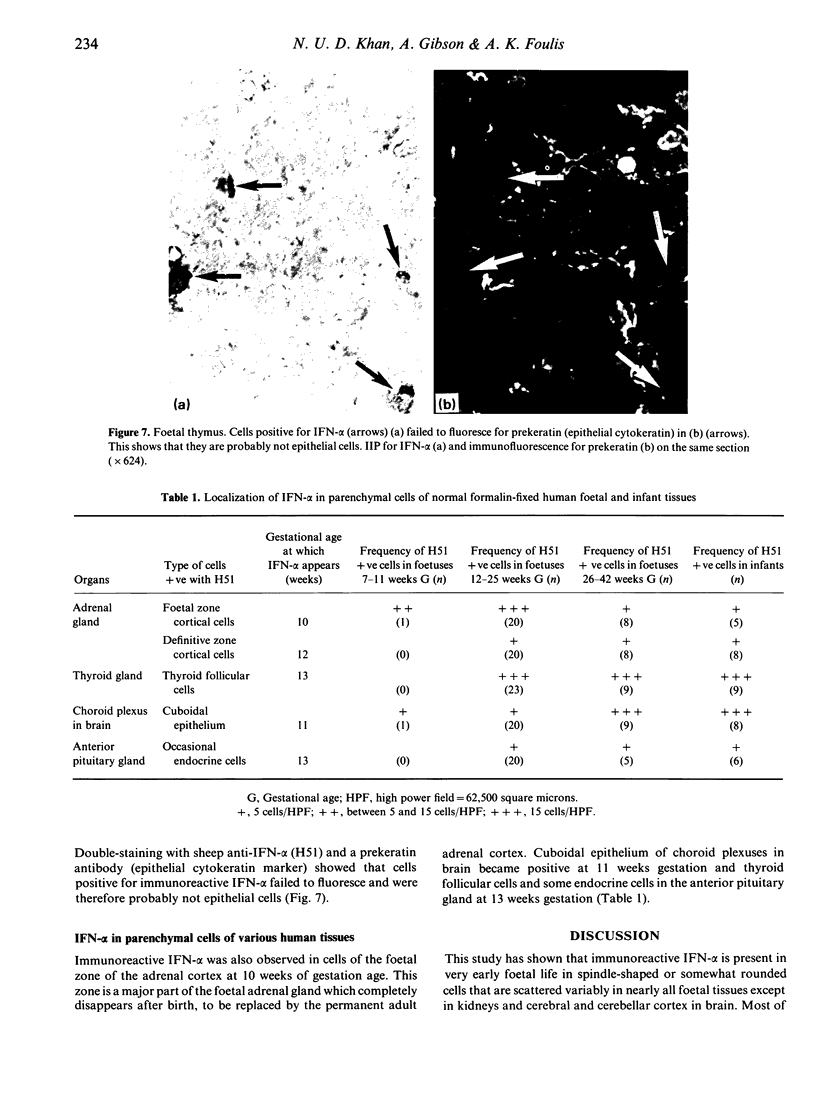
Human foetal and infant tissues were studied to test the hypothesis that microbes have a role in switching on interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) synthesis. Foetal tissues were essentially 'germ free', while the infants had been exposed to a normal microbial environment in life. IFN-alpha was first seen at 9 weeks gestation in macrophages in the liver and thereafter was seen in macrophages in most other organs. When infant lungs were compared with foetal lungs, a statistically significant increase in the number of macrophages and the percentage of these cells expressing IFN-alpha was noted in the infant lungs. No such change was observed in spleen, liver and thymus following birth. These findings suggest that there is a basal production of IFN-alpha by macrophages that is not dependent on microbial products, but that such products can enhance synthesis of this cytokine.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bocci V., Muscettola M., Paulesu L., Grasso G. The physiological interferon response. II. Interferon is present in lymph but not in plasma of healthy rabbits. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jan;65(Pt 1):101–108. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-1-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chard T., Craig P. H., Menabawey M., Lee C. Alpha interferon in human pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1986 Nov;93(11):1145–1149. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1986.tb08635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzvonyár J., Ruzicska G., Deseö G., Csaba B. Distribution of P32-labeled coli endotoxin in the tissues of pregnant rabbits and of their fetuses. Preliminary report. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1970 Mar;106(5):721–725. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(70)90397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulis A. K., Farquharson M. A., Meager A. Immunoreactive alpha-interferon in insulin-secreting beta cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1987 Dec 19;2(8573):1423–1427. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Robert N., Buffet-Janvresse C., Rivière Y., Hovanessian A. G. Continuous production of interferon in normal mice: effect of anti-interferon globulin, sex, age, strain and environment on the levels of 2-5A synthetase and p67K kinase. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):711–718. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Augmented induction of interferons during Listeria monocytogenes infection. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):960–969. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho-Yen D. O., Carrington D. Alpha-interferon responses in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with suspected meningitis. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jan;40(1):83–86. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howatson A. G., Farquharson M., Meager A., McNicol A. M., Foulis A. K. Localization of alpha-interferon in the human feto-placental unit. J Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;119(3):531–534. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1190531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan N. U., Pulford K. A., Farquharson M. A., Howatson A., Stewart C., Jackson R., McNicol A. M., Foulis A. K. The distribution of immunoreactive interferon-alpha in normal human tissues. Immunology. 1989 Feb;66(2):201–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior C., Haslam P. L. Interferon in lungs. Lancet. 1989 Jun 10;1(8650):1333–1333. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92731-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulford K. A., Rigney E. M., Micklem K. J., Jones M., Stross W. P., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. KP1: a new monoclonal antibody that detects a monocyte/macrophage associated antigen in routinely processed tissue sections. J Clin Pathol. 1989 Apr;42(4):414–421. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.4.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozawa S., Chihara K., Shiozawa K., Fujita T., Ikegami H., Koyama S., Kurimoto M. A sensitive radioimmunoassay for alpha-interferon: circulating alpha-interferon-like substance in the plasma of healthy individuals and rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Oct;66(1):77–87. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G., Streuli M., Gresser I., Gugenheim J., Blanchard B., Guymarho J., Vignaux F., Gigou M. Interferon messenger RNA is produced constitutively in the organs of normal individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5038–5042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoumbos N. C., Gascon P., Djeu J. Y., Young N. S. Interferon is a mediator of hematopoietic suppression in aplastic anemia in vitro and possibly in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):188–192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maeyer E., Fauve R. M., de Maeyer-Guignard J. Production d'interféron au niveau du macrophage. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 Mar;120(3):438–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]