Abstract
ABA-1 is an approximately 14,000 molecular weight (MW) allergen which is among the most abundant proteins synthesized by the nematode parasite Ascaris. IgG and IgE responses to it are major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-restricted in rodents and have only been found to occur in rats of the RT1u haplotype and mice of the H-2s haplotype. Humans infected with the parasite vary substantially in their immune response to the allergen, but the genetic basis for this unknown. H-2 recombinant mice were used to identify the region within the MHC controlling antibody responses to the allergen. IgG antibody to immunoaffinity purified ABA-1 was assayed by radio-immunoassay and IgE by passive cutaneous anaphylaxis. This showed that the restriction element is the I-A molecule and that there was some evidence for I-E modulation of the level of response.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler J., Miller J. N., Johnson P., Orr T. S. Characterisation of an allergen extracted from Ascaris suum. Determination of the molecular weight, isoelectric point, amino acid and carbohydrate content of the native allergen. Immunochemistry. 1973 Dec;10(12):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxevanis C. N., Nagy Z. A., Klein J. A novel type of T-T cell interaction removes the requirement for I-B region in the H-2 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3809–3813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
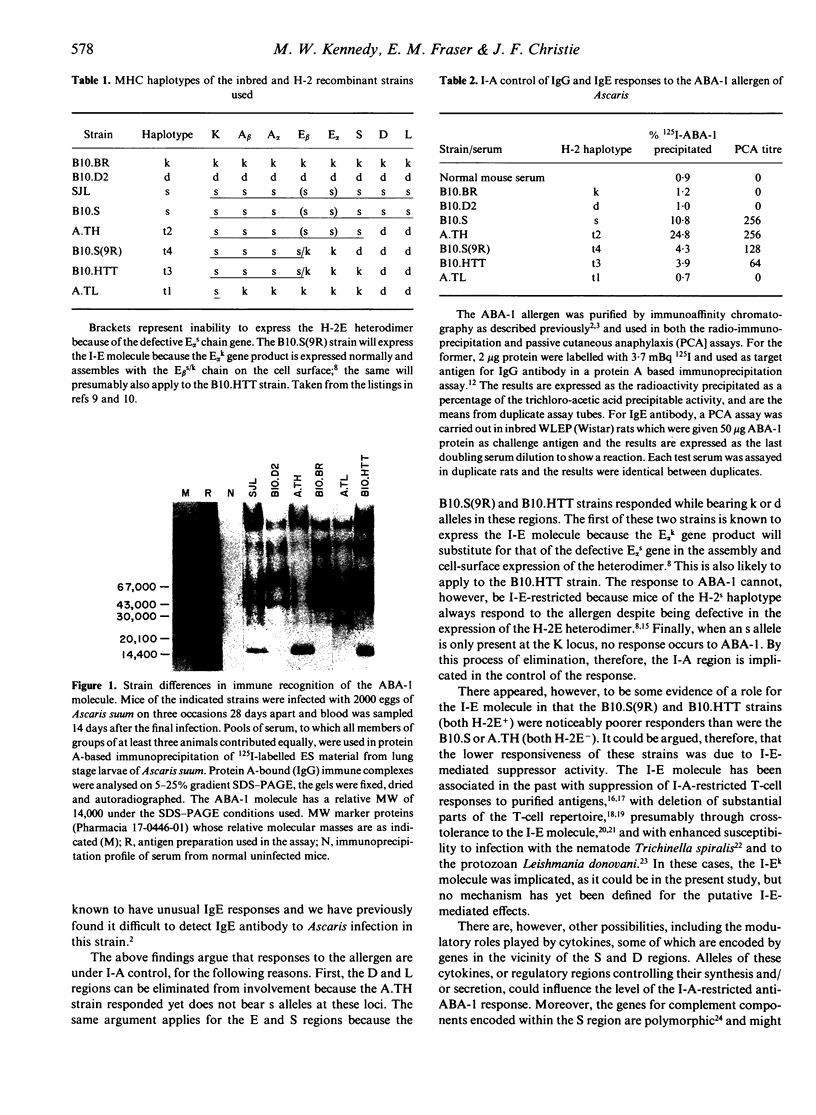
- Christie J. F., Dunbar B., Davidson I., Kennedy M. W. N-terminal amino acid sequence identity between a major allergen of Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum, and MHC-restricted IgE responses to it. Immunology. 1990 Apr;69(4):596–602. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haswell-Elkins M. R., Kennedy M. W., Maizels R. M., Elkins D. B., Anderson R. M. The antibody recognition profiles of humans naturally infected with Ascaris lumbricoides. Parasite Immunol. 1989 Nov;11(6):615–627. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1989.tb00925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P., Murphy D. B., McDevitt H. O. Variable synthesis and expression of E alpha and Ae (E beta) Ia polypeptide chains in mice of different H-2 haplotypes. Immunogenetics. 1981;12(3-4):321–337. doi: 10.1007/BF01561674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Roehm N., Marrack P. T cell tolerance by clonal elimination in the thymus. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90568-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W. Genetic control of the immune repertoire in nematode infections. Parasitol Today. 1989 Oct;5(10):316–324. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(89)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Gordon A. M., Tomlinson L. A., Qureshi F. Genetic (major histocompatibility complex?) control of the antibody repertoire to the secreted antigens of Ascaris. Parasite Immunol. 1987 Mar;9(2):269–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1987.tb00506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Qureshi F., Fraser E. M., Haswell-Elkins M. R., Elkins D. B., Smith H. V. Antigenic relationships between the surface-exposed, secreted and somatic materials of the nematode parasites Ascaris lumbricoides, Ascaris suum, and Toxocara canis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Mar;75(3):493–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Qureshi F., Haswell-Elkins M., Elkins D. B. Homology and heterology between the secreted antigens of the parasitic larval stages of Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jan;67(1):20–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Qureshi F. Stage-specific secreted antigens of the parasitic larval stages of the nematode Ascaris. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):515–522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Tomlinson L. A., Fraser E. M., Christie J. F. The specificity of the antibody response to internal antigens of Ascaris: heterogeneity in infected humans, and MHC (H-2) control of the repertoire in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 May;80(2):219–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F., David C. S. H-2 haplotypes, genes and antigens: second listing. II. The H-2 complex. Immunogenetics. 1983;17(6):553–596. doi: 10.1007/BF00366126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzinger P. A one-receptor view of T-cell behaviour. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):497–501. doi: 10.1038/292497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGibbon A. M., Christie J. F., Kennedy M. W., Lee T. D. Identification of the major Ascaris allergen and its purification to homogeneity by high-performance liquid chromatography. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Mar;39(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90055-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Jones P. P., Loken M. R., McDevitt H. O. Interaction between I region loci influences the expression of a cell surface Ia antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5404–5408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira D. B., Blackwell N., Virchis A. E., Axelrod R. A. T helper and T suppressor cells are restricted by the A and E molecules, respectively, in the F antigen system. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(2):169–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00563514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittner C., Schneider P. M. Complexity of MHC class III genes and complement polymorphism. Immunol Today. 1989 Dec;10(12):401–403. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. T-lymphocyte recognition of antigen in association with gene products of the major histocompatibility complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:237–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson L. A., Christie J. F., Fraser E. M., McLaughlin D., McIntosh A. E., Kennedy M. W. MHC restriction of the antibody repertoire to secretory antigens, and a major allergen, of the nematode parasite Ascaris. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2349–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]