Abstract
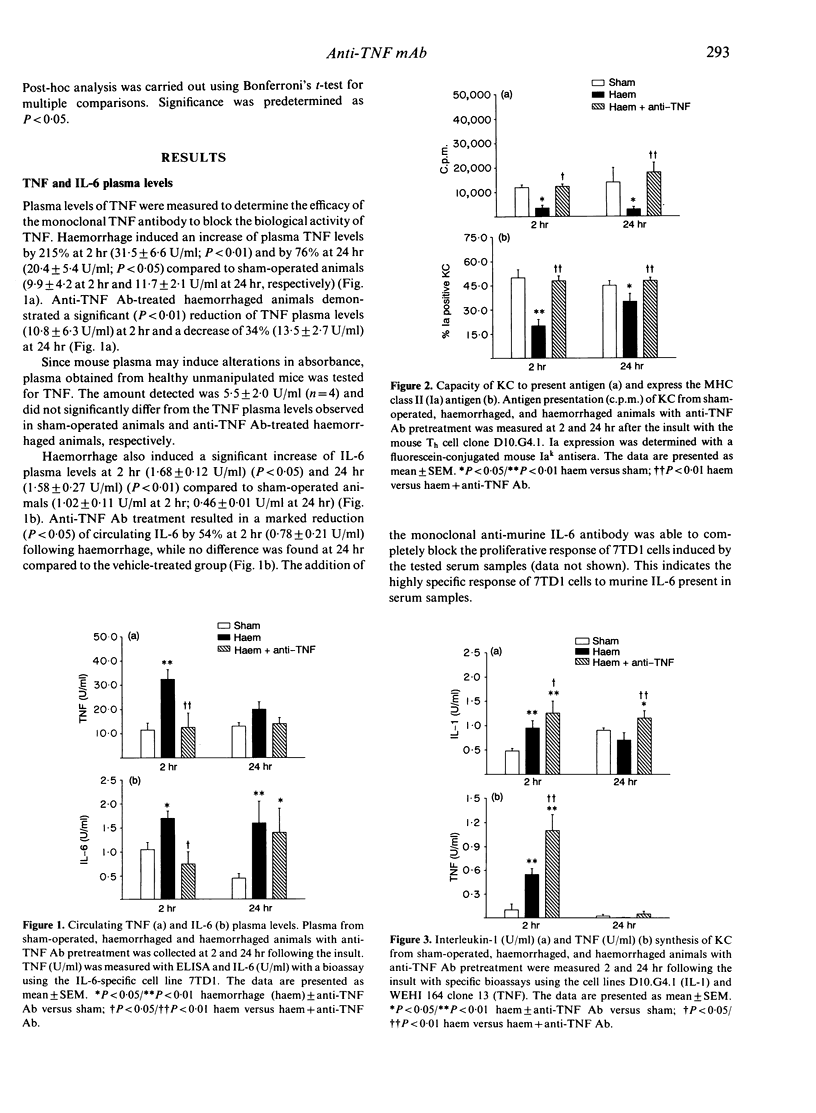
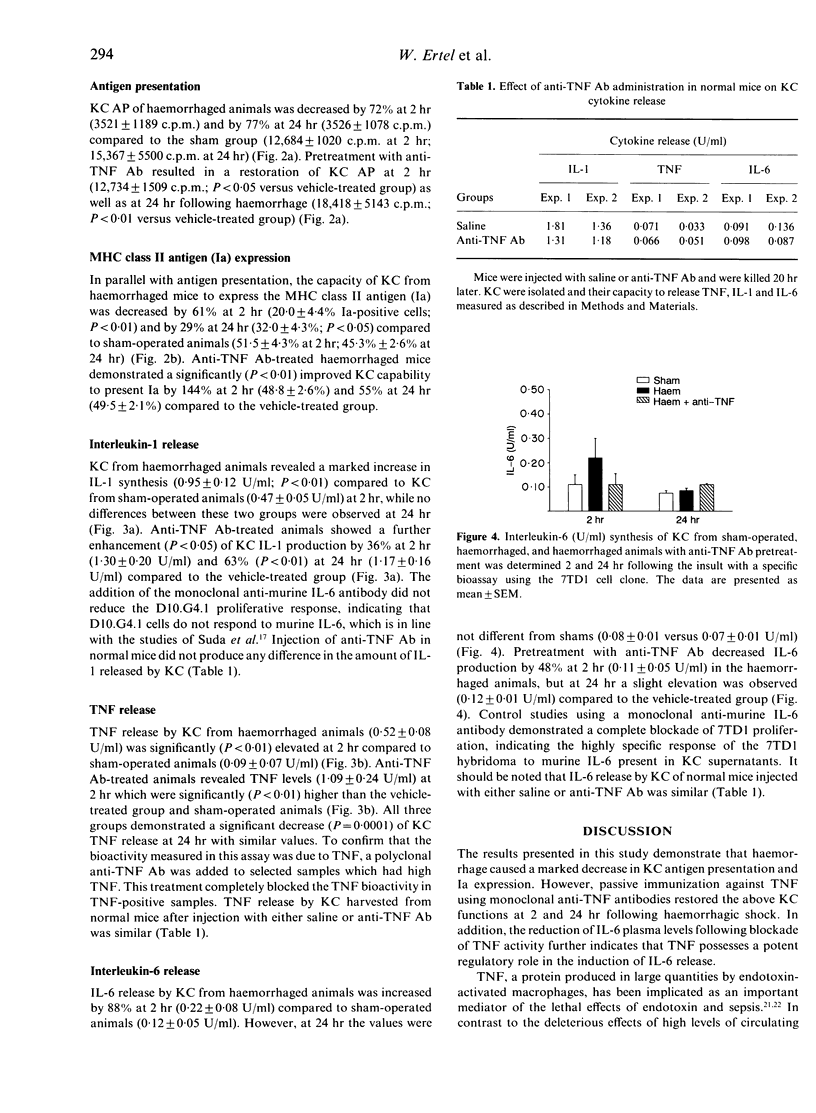
Kupffer cells (KC), by virtue of their ability to present antigen (AP) and express major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II antigen (Ia), play a pivotal role in the host defence system against invading micro-organisms. Although haemorrhagic shock depresses the above KC functions, it is not known whether increased KC tumour necrosis factor (TNF) production and elevated TNF plasma levels following haemorrhage are responsible for it. To study this, C3H/HeN mice were pretreated intraperitoneally with either anti-murine TNF antibody (anti-TNF Ab) or saline. Twenty hours later mice were bled and maintained at a mean blood pressure of 35 mmHg for 60 min followed by adequate fluid resuscitation. Two and 24 hr later, plasma was collected and KC were isolated. AP was measured by co-culturing KC with the D10.G4.1 Th cell clone. Ia expression was determined by direct immunofluorescence. Interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6 and TNF levels in KC supernatants and plasma were measured with bioassays or ELISA. Haemorrhage increased circulating TNF levels by 215% at 2 hr and by 76% at 24 hr (P less than 0.05), which was prevented by pretreatment with anti-TNF Ab. Haemorrhage-induced increase of circulating IL-6 was abolished (P less than 0.05) at 2 hr but not at 24 hr in the anti-TNF Ab group. The suppression of KC AP (P less than 0.05) and Ia expression (P less than 0.05) due to haemorrhage was attenuated (P less than 0.05) in anti-TNF Ab-treated mice at 2 and 24 hr and KC IL-1 and TNF synthesis was further (P less than 0.01) increased. These results indicate that TNF plays a critical role in the initiation and regulation of KC AP, Ia expression, and cytokine production following haemorrhage.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayala A., Perrin M. M., Chaudry I. H. Defective macrophage antigen presentation following haemorrhage is associated with the loss of MHC class II (Ia) antigens. Immunology. 1990 May;70(1):33–39. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayala A., Perrin M. M., Meldrum D. R., Ertel W., Chaudry I. H. Hemorrhage induces an increase in serum TNF which is not associated with elevated levels of endotoxin. Cytokine. 1990 May;2(3):170–174. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90012-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachwich P. R., Chensue S. W., Larrick J. W., Kunkel S. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates interleukin-1 and prostaglandin E2 production in resting macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):94–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90881-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. J., Lee S. H. Effects of interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on the expression of an Ia antigen on a murine macrophage cell line. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2853–2856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudry I. H., Ayala A., Ertel W., Stephan R. N. Hemorrhage and resuscitation: immunological aspects. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):R663–R678. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.259.4.R663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Tracey K. J., Moldawer L. L., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. B., Kenney J. S., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Allison A. C., Lowry S. F. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatanaga T., Hwang C. D., Kohr W., Cappuccini F., Lucci J. A., 3rd, Jeffes E. W., Lentz R., Tomich J., Yamamoto R. S., Granger G. A. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor (soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor) for tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin obtained from the serum ultrafiltrates of human cancer patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8781–8784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw L. B., Tekamp-Olson P., Chang A. C., Lee P. A., Taylor F. B., Jr, Murray C. K., Peer G. T., Emerson T. E., Jr, Passey R. B., Kuo G. C. Survival of primates in LD100 septic shock following therapy with antibody to tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha). Circ Shock. 1990 Mar;30(3):279–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman M., Weinberg J. B. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces increased hydrogen peroxide production and Fc receptor expression, but not increased Ia antigen expression by peritoneal macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Dec;42(6):704–707. doi: 10.1002/jlb.42.6.704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M. M., Perera P. Y., Vogel S. N. Examination of macrophage cell surface antigen regulation by rIFN-gamma and IFN-alpha/beta utilizing digital imaging by a novel laser detection system. Anchored cell analysis station (ACAS) 470. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Sep 29;123(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90024-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jablons D. M., Mulé J. J., McIntosh J. K., Sehgal P. B., May L. T., Huang C. M., Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T. IL-6/IFN-beta-2 as a circulating hormone. Induction by cytokine administration in humans. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1542–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Porcelli S., Tite J., Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Both a monoclonal antibody and antisera specific for determinants unique to individual cloned helper T cell lines can substitute for antigen and antigen-presenting cells in the activation of T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):836–856. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Phan S. H. Prostaglandins as endogenous mediators of interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Spengler M., May M. A., Spengler R., Larrick J., Remick D. Prostaglandin E2 regulates macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5380–5384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. H., Malangoni M. A., Sonnenfeld G. Immune enhancement by tumor necrosis factor-alpha improves antibiotic efficacy after hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma. 1989 Jul;29(7):967–971. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198907000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malangoni M. A., Livingston D. H., Sonnenfeld G., Polk H. C., Jr Interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Use in gram-negative infection after shock. Arch Surg. 1990 Apr;125(4):444–446. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1990.01410160030005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R., Epstein L. B. Tumour necrosis factor as immunomodulator and mediator of monocyte cytotoxicity induced by itself, gamma-interferon and interleukin-1. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):86–89. doi: 10.1038/323086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteu F., Nathan C. Shedding of tumor necrosis factor receptors by activated human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):599–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., Strieter R. M., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Nguyen D., Eskandari M., Kunkel S. L. In vivo dynamics of murine tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression. Kinetics of dexamethasone-induced suppression. Lab Invest. 1989 Jun;60(6):766–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush B. F., Jr, Sori A. J., Murphy T. F., Smith S., Flanagan J. J., Jr, Machiedo G. W. Endotoxemia and bacteremia during hemorrhagic shock. The link between trauma and sepsis? Ann Surg. 1988 May;207(5):549–554. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198805000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler R., Mancilla J., Endres S., Ghorbani R., Clark S. C., Dinarello C. A. Correlations and interactions in the production of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in human blood mononuclear cells: IL-6 suppresses IL-1 and TNF. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):40–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard B. C., Fraker D. L., Norton J. A. Prevention and treatment of endotoxin and sepsis lethality with recombinant human tumor necrosis factor. Surgery. 1989 Aug;106(2):156–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephan R. N., Kupper T. S., Geha A. S., Baue A. E., Chaudry I. H. Hemorrhage without tissue trauma produces immunosuppression and enhances susceptibility to sepsis. Arch Surg. 1987 Jan;122(1):62–68. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1987.01400130068010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Hodgkin P., Lee F., Zlotnik A. Biological activity of recombinant murine interleukin-6 in interleukin-1 T cell assays. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jun 21;120(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Cayphas S., Vink A., Uyttenhove C., Coulie P. G., Rubira M. R., Simpson R. J. Purification and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of a T-cell-derived lymphokine with growth factor activity for B-cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9679–9683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


