Abstract
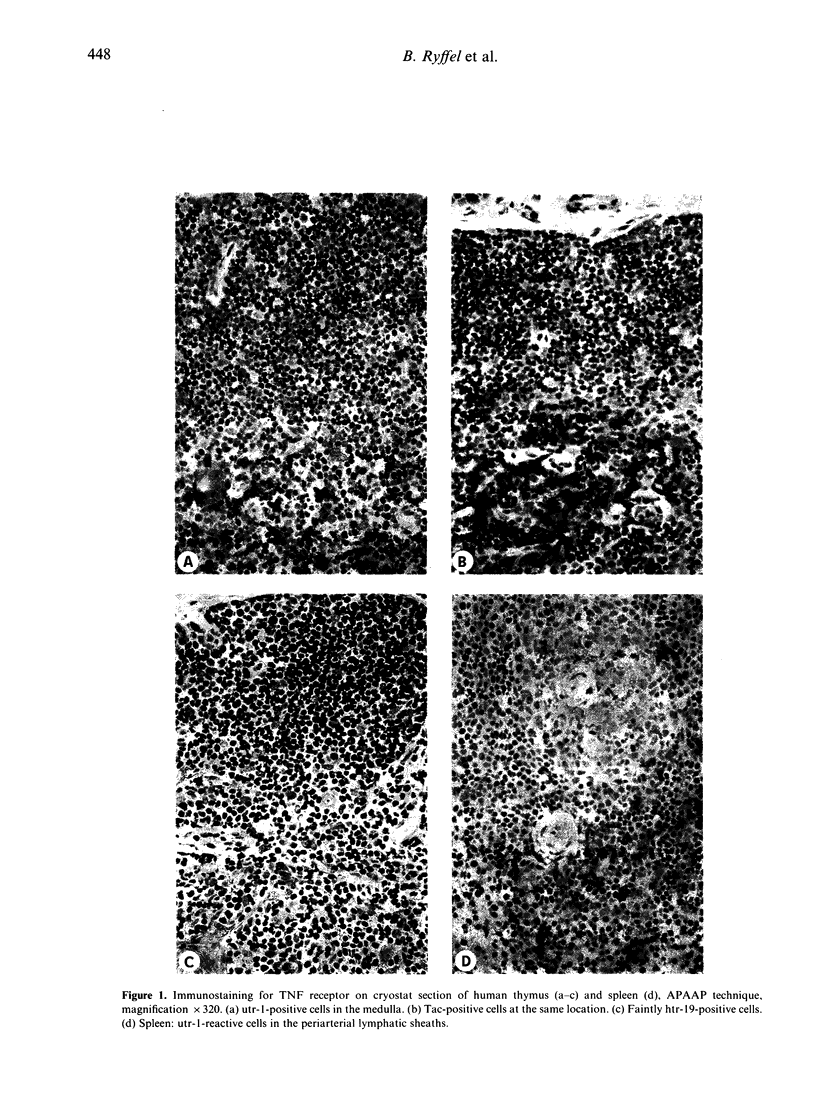
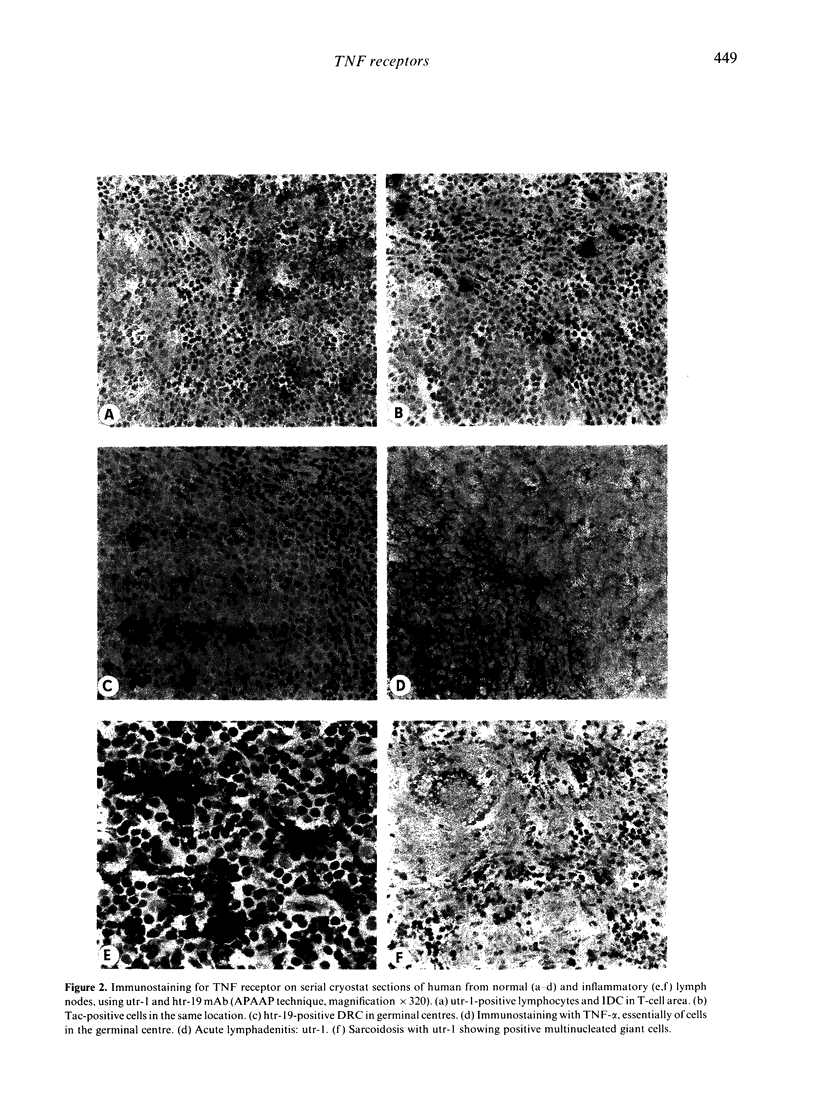
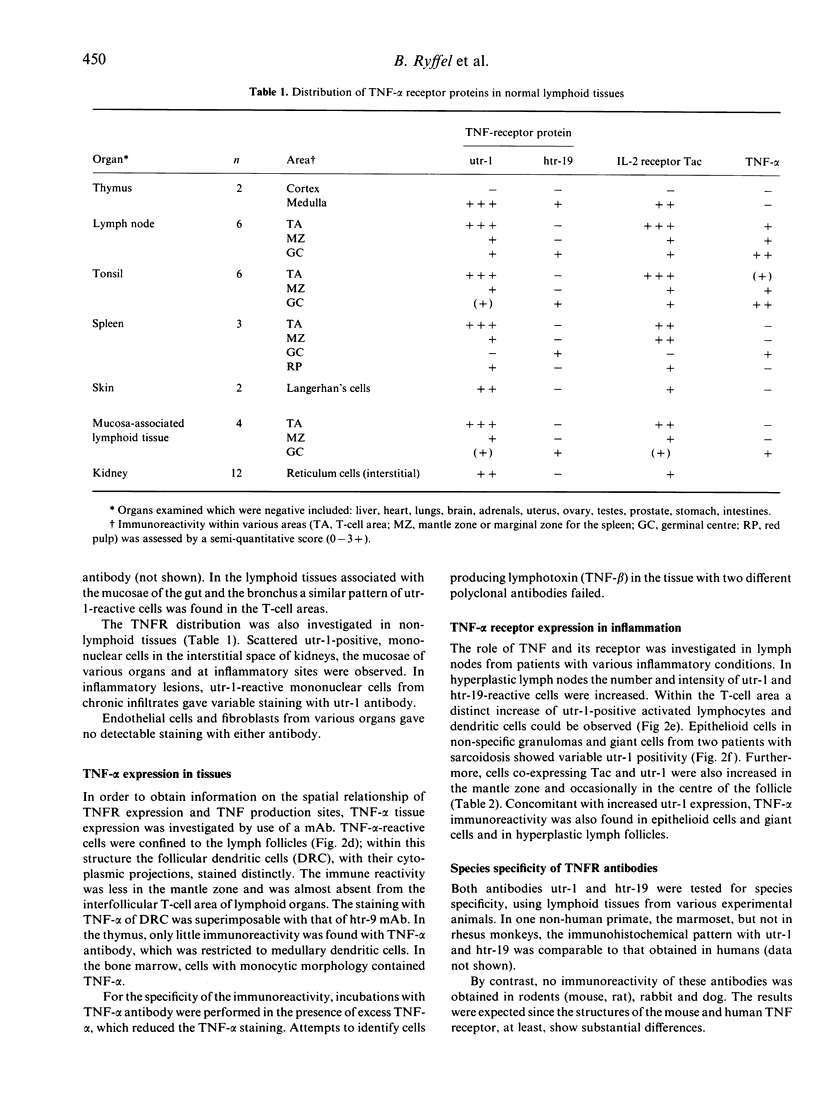
The nature and location of cells responding to tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) were investigated in situ by immunohistochemistry using monoclonal antibodies (mAb) directed against the p75 and p55 proteins of the TNF receptor. Receptor expression was found in the thymus and secondary lymphoid tissues. In the thymus the p75 receptor was confined to medullary lymphoblasts and dendritic cells, which co-stain with the Tac protein of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor. In lymph nodes and other secondary lymphoid tissues, the p75 receptor was expressed on activated lymphocytes and interdigitating reticulum cells of the T-cell area, whereas the p55 receptor was confined to the germinal centre dendritic reticulum cells (DRC), which is the main site of TNF-alpha production. TNF receptor (TNFR) proteins were up-regulated in reactive hyperplasia together with increased TNF-alpha expression. Surprisingly, no TNFR was detectable on non-lymphoid tissues. The species specificity of these TNFR antibodies was high: whereas the antibodies cross-reacted with epitopes in non-human primates, no immunoreactivity was detected in lower animal species, e.g. dog, rabbit and rodents. The data presented suggest that TNF-alpha, which is produced by germinal centre DRC, might regulate an in vivo immune response through autocrine and paracrine pathways, e.g. through the p55 and p75 receptor proteins, which are expressed at different sites of the lymphoid tissue.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amino N., Linn E. S., Pysher T. J., Mier R., Moore G. E., DeGroot L. J. Human lymphotoxin obtained from established lymphoid lines: purification characteristics and inhibition by anti-immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1334–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockhaus M., Schoenfeld H. J., Schlaeger E. J., Hunziker W., Lesslauer W., Loetscher H. Identification of two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3127–3131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Otterness I. G., Higashi G. I., Forsch C. S., Kunkel S. L. Monokine production by hypersensitivity (Schistosoma mansoni egg) and foreign body (Sephadex bead)-type granuloma macrophages. Evidence for sequential production of IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1281–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor increases mRNA levels and surface expression of HLA-A,B antigens in vascular endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):446–450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembic Z., Loetscher H., Gubler U., Pan Y. C., Lahm H. W., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Lesslauer W. Two human TNF receptors have similar extracellular, but distinct intracellular, domain sequences. Cytokine. 1990 Jul;2(4):231–237. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90022-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann H. P., Remy R., Brockhaus M., van Loon A. P. Two different cell types have different major receptors for human tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha). J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14927–14934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura K., Spriggs D., Kufe D. Expression of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human monocytes and internalization of receptor bound ligand. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 1;139(9):2989–2992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Miller A., Fauci A. S. Effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha on mitogen-activated human B cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):786–791. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhweide R., Van Damme J., Ceuppens J. L. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 6 synergistically induce T cell growth. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1019–1025. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. X., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 cause a rapid and transient stimulation of c-fos and c-myc mRNA levels in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11908–11911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Pan Y. C., Lahm H. W., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Tabuchi H., Lesslauer W. Molecular cloning and expression of the human 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90815-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall J. L., Yun K., Funamoto S., Parry B. R. In vivo immunohistochemical identification of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin in human lymphoid tissue. Am J Pathol. 1989 Sep;135(3):421–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Grau G. E., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor and immunopathology. Immunol Res. 1991;10(2):122–140. doi: 10.1007/BF02918160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S. Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis award lecture. Cytokine-mediated activation of vascular endothelium. Physiology and pathology. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):426–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Bombara M. P., Aiyer R. A., Rice G. G., Palladino M. A., Jr Tumor necrosis factor-alpha as a proliferative signal for an IL-2-dependent T cell line: strict species specificity of action. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1203–1208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Stoppacciaro A., Pomponi D., Boraschi D., Santoni A., Tagliabue A., Uccini S., Baroni C. D. Immunoreactivity for IL-1 beta and TNF alpha in human lymphoid and nonlymphoid tissues. Am J Pathol. 1989 Nov;135(5):889–897. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Lewis M., Koller K. J., Lee A., Rice G. C., Wong G. H., Gatanaga T., Granger G. A., Lentz R., Raab H. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90816-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheurich P., Thoma B., Ucer U., Pfizenmaier K. Immunoregulatory activity of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha: induction of TNF receptors on human T cells and TNF-alpha-mediated enhancement of T cell responses. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1786–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Davis T., Anderson D., Solam L., Beckmann M. P., Jerzy R., Dower S. K., Cosman D., Goodwin R. G. A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1019–1023. doi: 10.1126/science.2160731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolpen A. H., Guinan E. C., Fiers W., Pober J. S. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor and immune interferon act singly and in combination to reorganize human vascular endothelial cell monolayers. Am J Pathol. 1986 Apr;123(1):16–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. S., Bjorndahl J. M., Wang C. Y., Kao H. T., Fu S. M. Production of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin by human T cell lines and peripheral blood T lymphocytes stimulated by phorbol myristate acetate and anti-CD3 antibody. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):937–953. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos G. C., Kinoshita T., Thyphronitis G., Patel A. D., Dickler H. B., Finkelman F. D. Interactions between murine B lymphocyte surface membrane molecules. Loaded but not free receptors for complement and the Fc portion of IgG co-cap independently with cross-linked surface Ig. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):239–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Lee T. H. Tumor necrosis factor. New insights into the molecular mechanisms of its multiple actions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7313–7316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner S. J., Libby P. Human vascular smooth muscle cells. Target for and source of tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):100–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]