Abstract
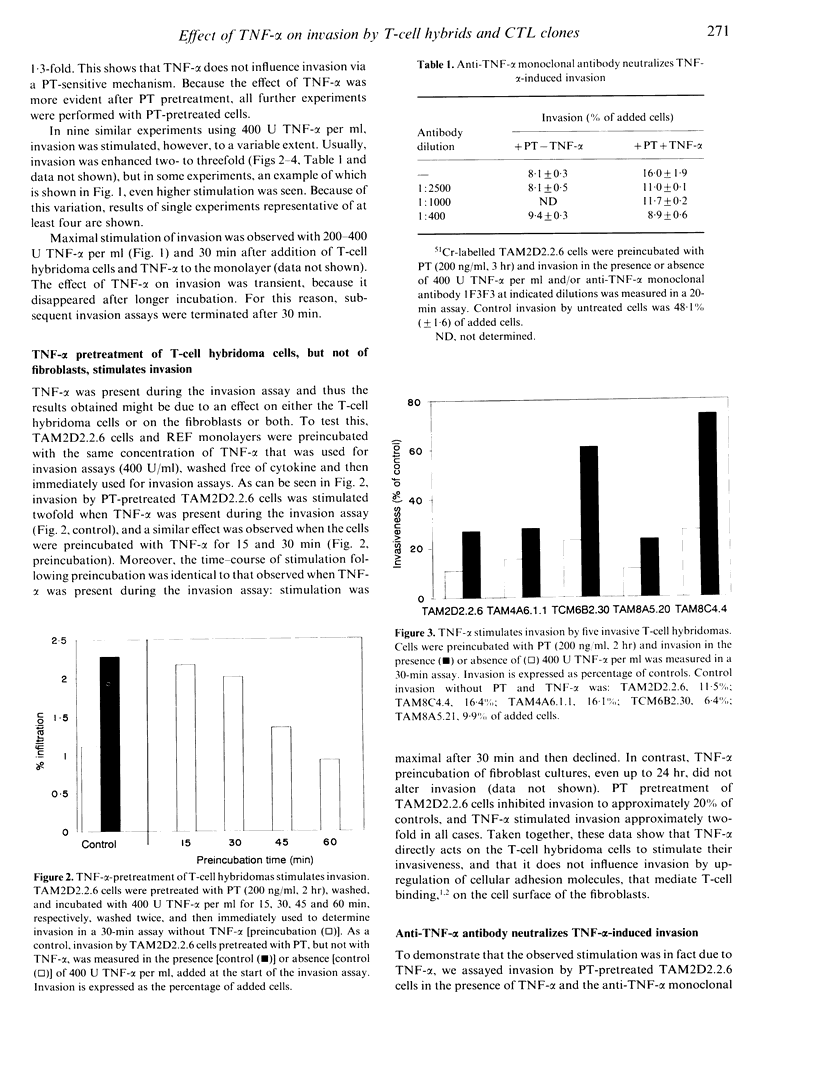
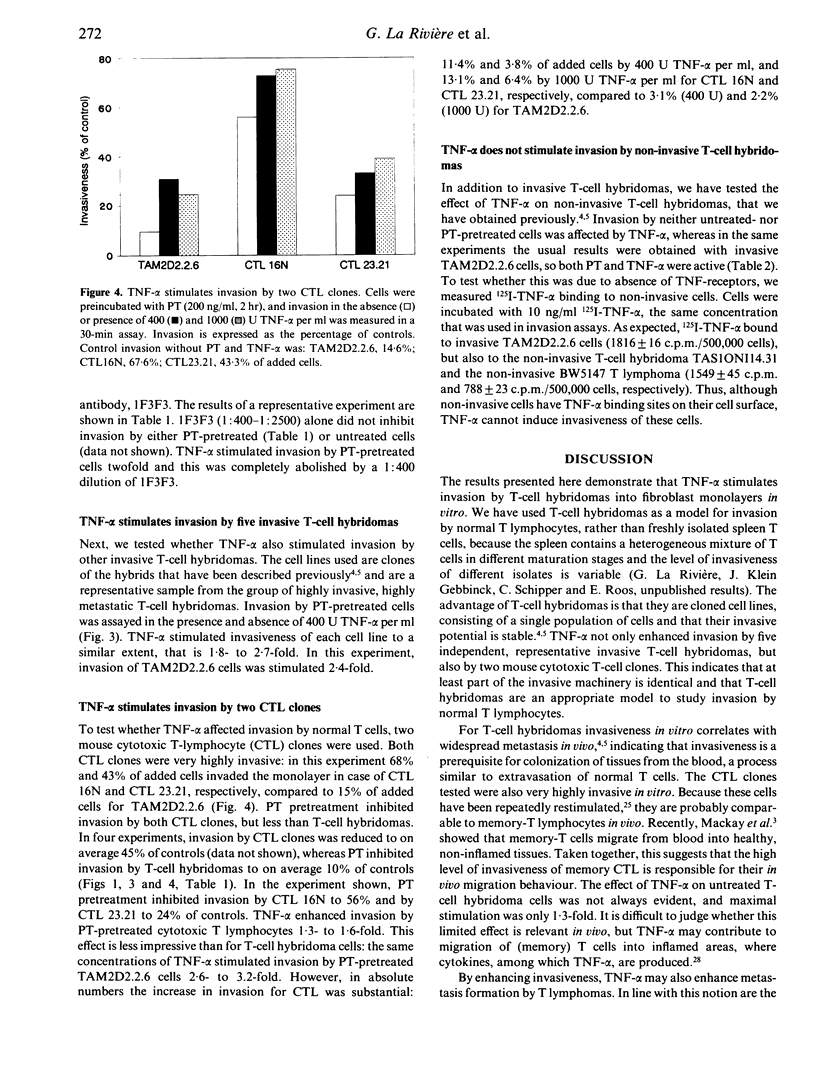
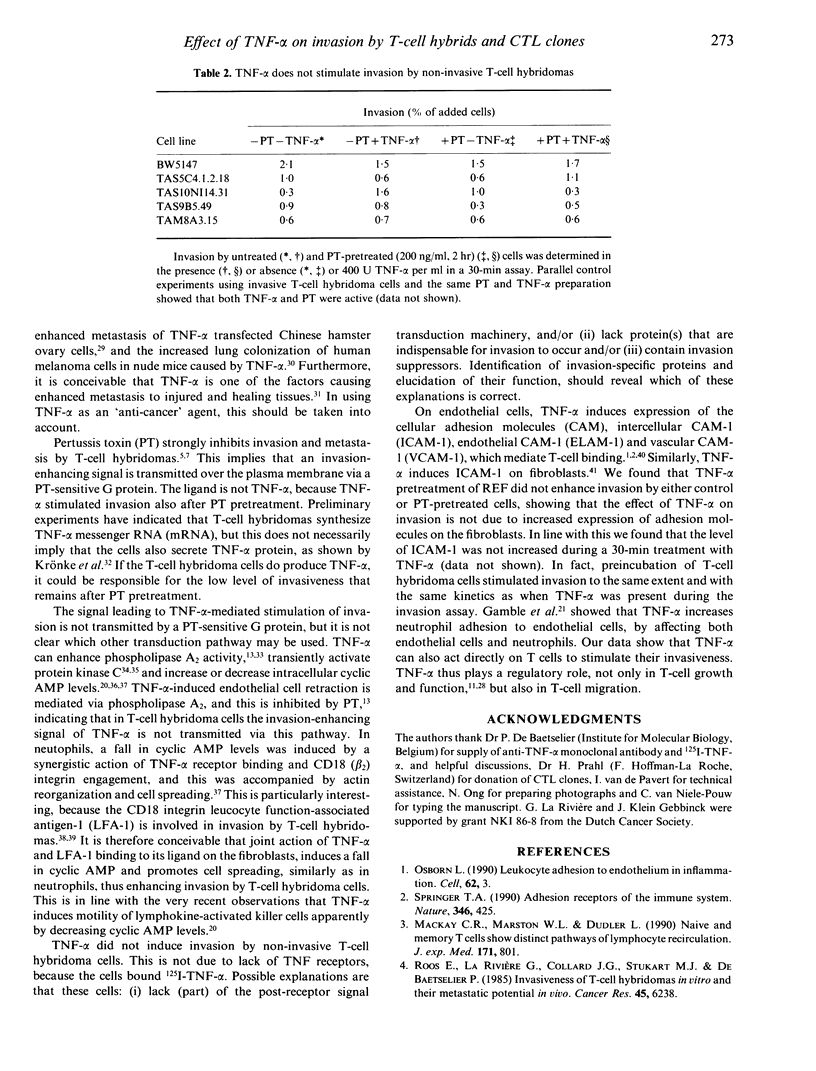
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) stimulated invasion by mouse T-cell hybridomas and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte clones into rat embryo fibroblast monolayers. The effect on these highly invasive cells was limited: invasion was stimulated maximally to 130% of controls. However, when cells were pretreated with pertussis toxin (PT), which inhibits invasion to +/- 20% of controls, a clearcut effect was observed: 400 U TNF-alpha per ml stimulated invasion usually two- to threefold, and sometimes even up to 10-fold. Therefore, experiments were done with PT-pretreated cells. Stimulation was dose dependent and maximal at 200-400 U TNF-alpha per ml. An anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody completely abolished TNF-alpha-induced invasion. The effect was maximal 30 min after addition of cells and TNF-alpha to the monolayer and then declined. TNF-alpha preincubation of T-cell hybridoma cells, but not of fibroblasts, had a similar stimulatory effect, which was also maximal after 30 min. This shows that TNF-alpha acts directly on the T-cell hybridoma cells. Invasive T-cell hybridomas colonize many tissues from the blood similarly as normal T cells. Our data thus suggest that TNF-alpha can stimulate migration of normal T lymphocytes into inflamed tissues and can promote metastasis of malignant T lymphomas. The signals involved are transmitted via a pertussis toxin-insensitive pathway.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J. S., Berger A. E., Ware C. F. Characterization of the receptor for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and lymphotoxin (LT) on human T lymphocytes. TNF and LT differ in their receptor binding properties and the induction of MHC class I proteins on a human CD4+ T cell hybridoma. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2582–2591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett J., Gerlach H., Nawroth P., Steinberg S., Godman G., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin increases permeability of endothelial cell monolayers by a mechanism involving regulatory G proteins. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1977–1991. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavender D., Saegusa Y., Ziff M. Stimulation of endothelial cell binding of lymphocytes by tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1855–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. A., Chen M. J., Crooke S. T., Bomalaski J. S. Tumour necrosis factor (cachectin) induces phospholipase A2 activity and synthesis of a phospholipase A2-activating protein in endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):125–132. doi: 10.1042/bj2500125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collard J. G., van de Poll M., Scheffer A., Roos E., Hopman A. H., Geurts van Kessel A. H., van Dongen J. J. Location of genes involved in invasion and metastasis on human chromosome 7. Cancer Res. 1987 Dec 15;47(24 Pt 1):6666–6670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuturi M. C., Murphy M., Costa-Giomi M. P., Weinmann R., Perussia B., Trinchieri G. Independent regulation of tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin production by human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1581–1594. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Pauli R., Opalka B. Antigen-dependent, H-2-restricted cytolytic and noncytolytic T cell lines with specificity for minor histocompatibility antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1982 May;12(5):365–373. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. R., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Vadas M. A. Stimulation of the adherence of neutrophils to umbilical vein endothelium by human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8667–8671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giavazzi R., Garofalo A., Bani M. R., Abbate M., Ghezzi P., Boraschi D., Mantovani A., Dejana E. Interleukin 1-induced augmentation of experimental metastases from a human melanoma in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 1;50(15):4771–4775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber N., Gopal T. V., Wilson D., Beall L. D., Polte T., Newman W. T cells bind to cytokine-activated endothelial cells via a novel, inducible sialoglycoprotein and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):819–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haliday E. M., Ramesha C. S., Ringold G. TNF induces c-fos via a novel pathway requiring conversion of arachidonic acid to a lipoxygenase metabolite. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):109–115. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura K., Sherman M. L., Spriggs D., Kufe D. Effect of tumor necrosis factor on GTP binding and GTPase activity in HL-60 and L929 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10247–10253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz T. B., Stoltz J. M. Stimulation of lymphocyte migration by endotoxin, tumor necrosis factor, and interferon. Cell Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;120(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Hensel G., Schlüter C., Scheurich P., Schütze S., Pfizenmaier K. Tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin gene expression in human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 1;48(19):5417–5421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane T. A., Lamkin G. E., Wancewicz E. V. Protein kinase C inhibitors block the enhanced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on endothelial cells activated by interleukin-1, lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1273–1281. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91587-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Marston W. L., Dudler L. Naive and memory T cells show distinct pathways of lymphocyte recirculation. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):801–817. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maghazachi A. A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is chemokinetic for lymphokine-activated killer cells: regulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Mar;49(3):302–308. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.3.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S. T., Naylor M. S., East N., Oliff A., Balkwill F. R. Cells secreting tumour necrosis factor show enhanced metastasis in nude mice. Eur J Cancer. 1990;26(10):1031–1034. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(90)90044-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. J., Van Epps D. E. In vivo neutrophil emigration in response to interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jan;45(1):62–68. doi: 10.1002/jlb.45.1.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming W. J., Bersani L., Mantovani A. Tumor necrosis factor is chemotactic for monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1469–1474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P., Alexander P., Senior P. V., Fleming J., Kirkham N., Taylor I. Mechanisms of organ selective tumour growth by bloodborne cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 1988 Jan;57(1):19–31. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Sanchez E. Tumor necrosis factor and CD11/CD18 (beta 2) integrins act synergistically to lower cAMP in human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2171–2181. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedwin G. E., Svedersky L. P., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Goeddel D. V. Effect of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and mitogens on the production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2492–2497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L. Leukocyte adhesion to endothelium in inflammation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90230-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos E., La Rivière G., Collard J. G., Stukart M. J., De Baetselier P. Invasiveness of T-cell hybridomas in vitro and their metastatic potential in vivo. Cancer Res. 1985 Dec;45(12 Pt 1):6238–6243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos E., Roossien F. F. Involvement of leukocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) in the invasion of hepatocyte cultures by lymphoma and T-cell hybridoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):553–559. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos E., Van de Pavert I. V. Inhibition of lymphoma invasion and liver metastasis formation by pertussis toxin. Cancer Res. 1987 Oct 15;47(20):5439–5444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roossien F. F., de Rijk D., Bikker A., Roos E. Involvement of LFA-1 in lymphoma invasion and metastasis demonstrated with LFA-1-deficient mutants. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1979–1985. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein R., Czajkowski M., O'Neill M. M., Marlin S. D., Mainolfi E., Merluzzi V. J. Induction of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 on primary and continuous cell lines by pro-inflammatory cytokines. Regulation by pharmacologic agents and neutralizing antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1665–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheurich P., Thoma B., Ucer U., Pfizenmaier K. Immunoregulatory activity of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha: induction of TNF receptors on human T cells and TNF-alpha-mediated enhancement of T cell responses. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1786–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Nottrott S., Pfizenmaier K., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor signal transduction. Cell-type-specific activation and translocation of protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2604–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornhill M. H., Kyan-Aung U., Lee T. H., Haskard D. O. T cells and neutrophils exhibit differential adhesion to cytokine-stimulated endothelial cells. Immunology. 1990 Feb;69(2):287–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verschueren H., Dekegel D., De Baetselier P. Development of a monolayer invasion assay for the discrimination and isolation of metastatic lymphoma cells. Invasion Metastasis. 1987;7(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. M., Walter S., Mantovani A. Re-evaluation of the chemotactic activity of tumour necrosis factor for monocytes. Immunology. 1990 Nov;71(3):364–367. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Lin J. X., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Enhancement of cAMP levels and of protein kinase activity by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 in human fibroblasts: role in the induction of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6802–6805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- la Rivière G., Schipper C. A., Collard J. G., Roos E. Invasiveness in hepatocyte and fibroblast monolayers and metastatic potential of T-cell hybridomas in mice. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 15;48(12):3405–3410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


