Abstract
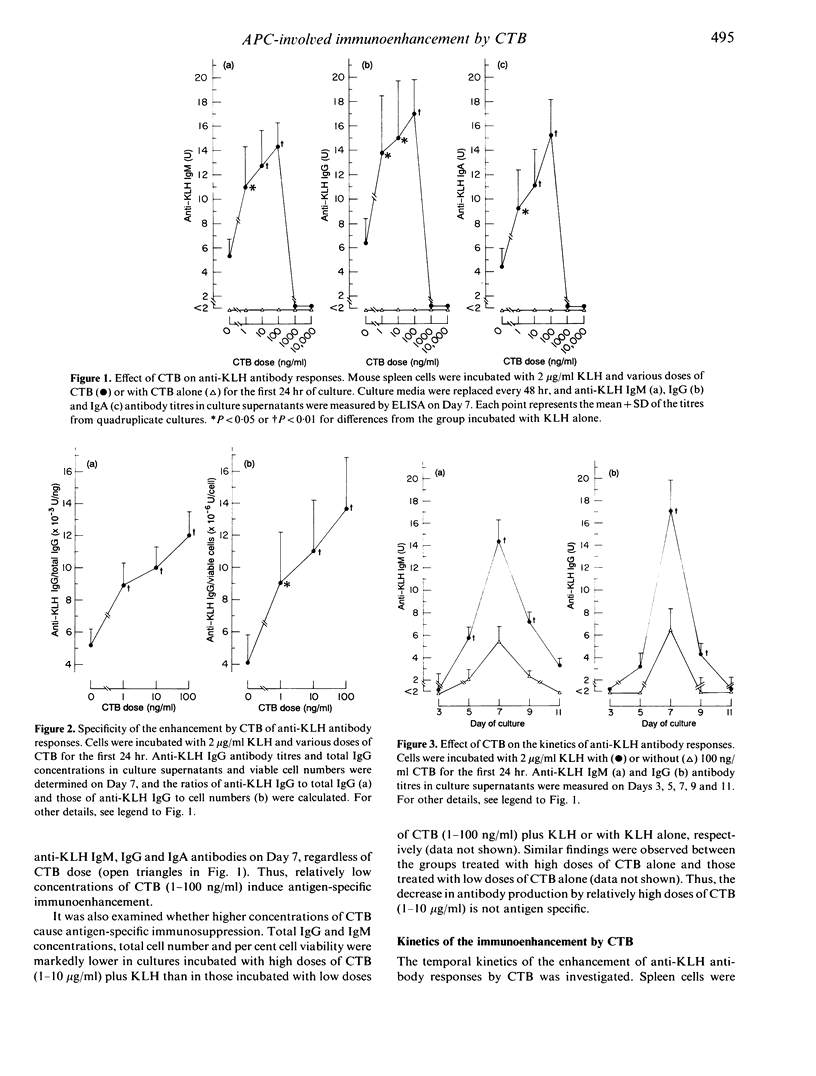
The enhancing effect of cholera toxin B subunit (CTB) on primary antibody responses to keyhole limpet haemocyanin (KLH) and the cellular basis of the effect were investigated, using in vitro cultures of mouse spleen cells. CTB (1-100 ng/ml) enhanced anti-KLH IgM, IgG and IgA antibody responses in a dose-dependent manner, when added to the cultures with KLH. This immunoenhancement was antigen specific, but not due to either polyclonal activation of the spleen cells or antigenic cross-reactivity between CTB and KLH. CTB did not affect the kinetics of the anti-KLH antibody responses. Early (Days 0-1) addition of CTB to the cultures enhanced the anti-KLH antibody production, whereas late (Days 5-7) addition of CTB did not. Addition of CTB with KLH to splenic adherent cells (SAC) resulted in a dose-dependent enhancement of the anti-KLH antibody responses, when the SAC were reconstituted with unimmunized non-adherent cells. Moreover, CTB enhanced IL-1 secretion from SAC incubated with KLH. These results suggest that CTB enhances the primary anti-KLH antibody responses in vitro by acting on early events in the responses, and that antigen-presenting cells play a major role in the enhancement.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bromander A., Holmgren J., Lycke N. Cholera toxin stimulates IL-1 production and enhances antigen presentation by macrophages in vitro. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):2908–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchiel S. W., Melmon K. L. Augmentation of the in vitro humoral immune response by pharmacologic agents. I: An explanation for the differential enhancement of humoral immunity via agents that elevate cAMP. Immunopharmacology. 1979 Mar;1(2):137–150. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(79)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. S., Strober W. Cholera holotoxin and its B subunit enhance Peyer's patch B cell responses induced by orally administered influenza virus: disproportionate cholera toxin enhancement of the IgA B cell response. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):433–436. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. J., Wilson A. D., Williams N. A., Stokes C. R. Mucosal priming of T-lymphocyte responses to fed protein antigens using cholera toxin as an adjuvant. Immunology. 1991 Mar;72(3):323–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook R. G., Stavitsky A. B., Schoenberg M. D. Regulation of the in vitro early anamnestic antibody response by exogenous cholera enterotoxin and cyclic AMP. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):426–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denizot F., Lang R. Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J Immunol Methods. 1986 May 22;89(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Generalized systemic and mucosal immunity in mice after mucosal stimulation with cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2736–2741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W., Lefkowitz J. A lavage technique allowing repeated measurement of IgA antibody in mouse intestinal secretions. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 24;67(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90089-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Mizel S. B. T-Cell lymphoma model for the analysis of interleukin 1-mediated T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1133–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi Y., Kurata H., Funato H., Nagamine T., Aizawa C., Tamura S., Shimada K., Kurata T. Comparison of intranasal inoculation of influenza HA vaccine combined with cholera toxin B subunit with oral or parenteral vaccination. Vaccine. 1990 Jun;8(3):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90053-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi Y., Tamura S. I., Suzuki Y., Nagamine T., Aizawa C., Shimada K., Kurata T. H-2-unrestricted adjuvant effect of cholera toxin B subunit on murine antibody responses to influenza virus haemagglutinin. Immunology. 1991 Mar;72(3):329–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodes R. J., Singer A. Cellular and genetic control of antibody responses in vitro. I. Cellular requirements for the generation of genetically controlled primary IgM responses to soluble antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Dec;7(12):892–897. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Actions of cholera toxin and the prevention and treatment of cholera. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):413–417. doi: 10.1038/292413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka M., Braun W., Matsumoto T. Cyclic AMP and immune responses. I. Influence of poly A:U and cAMP on antibody formation in vitro. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1027–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai K., Itoh K., Hinuma S., Tada M. Pretreatment of plastic Petri dishes with fetal calf serum. A simple method for macrophage isolation. J Immunol Methods. 1979;29(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Holmgren J. Strong adjuvant properties of cholera toxin on gut mucosal immune responses to orally presented antigens. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):301–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. J., Halsey J. F. Cholera toxin B subunit as a carrier protein to stimulate a mucosal immune response. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1818–1824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Burns D. L., Hsia J. A., Hewlett E. L., Guerrant R. L., Vaughan M. NIH conference. Cyclic nucleotides: mediators of bacterial toxin action in disease. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Nov;101(5):653–666. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-5-653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrup R. S., Fauci A. S. Adjuvant effect of cholera enterotoxin on the immune response of the mouse to sheep red blood cells. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):672–673. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S. I., Samegai Y., Kurata H., Kikuta K., Nagamine T., Aizawa C., Kurata T. Enhancement of protective antibody responses by cholera toxin B subunit inoculated intranasally with influenza vaccine. Vaccine. 1989 Jun;7(3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(89)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Samegai Y., Kurata H., Nagamine T., Aizawa C., Kurata T. Protection against influenza virus infection by vaccine inoculated intranasally with cholera toxin B subunit. Vaccine. 1988 Oct;6(5):409–413. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(88)90140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh H. S., Paetkau V. Biphasic effect of cyclic AMP on an immune response. Nature. 1974 Aug 9;250(5466):505–507. doi: 10.1038/250505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. D., Clarke C. J., Stokes C. R. Whole cholera toxin and B subunit act synergistically as an adjuvant for the mucosal immune response of mice to keyhole limpet haemocyanin. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Apr;31(4):443–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. D., Stokes C. R., Bourne F. J. Adjuvant effect of cholera toxin on the mucosal immune response to soluble proteins. Differences between mouse strains and protein antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jun;29(6):739–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woogen S. D., Ealding W., Elson C. O. Inhibition of murine lymphocyte proliferation by the B subunit of cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3764–3770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heyningen S. Cholera toxin. Biosci Rep. 1982 Mar;2(3):135–146. doi: 10.1007/BF01116376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


