Abstract
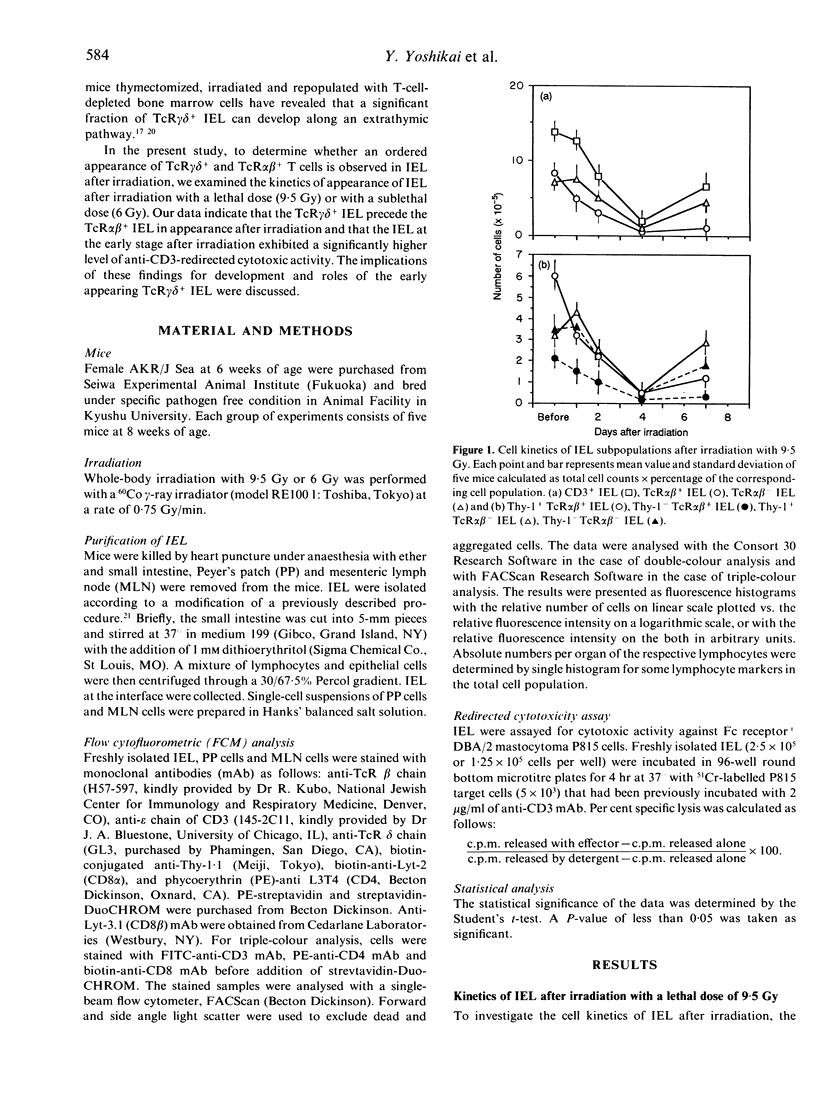
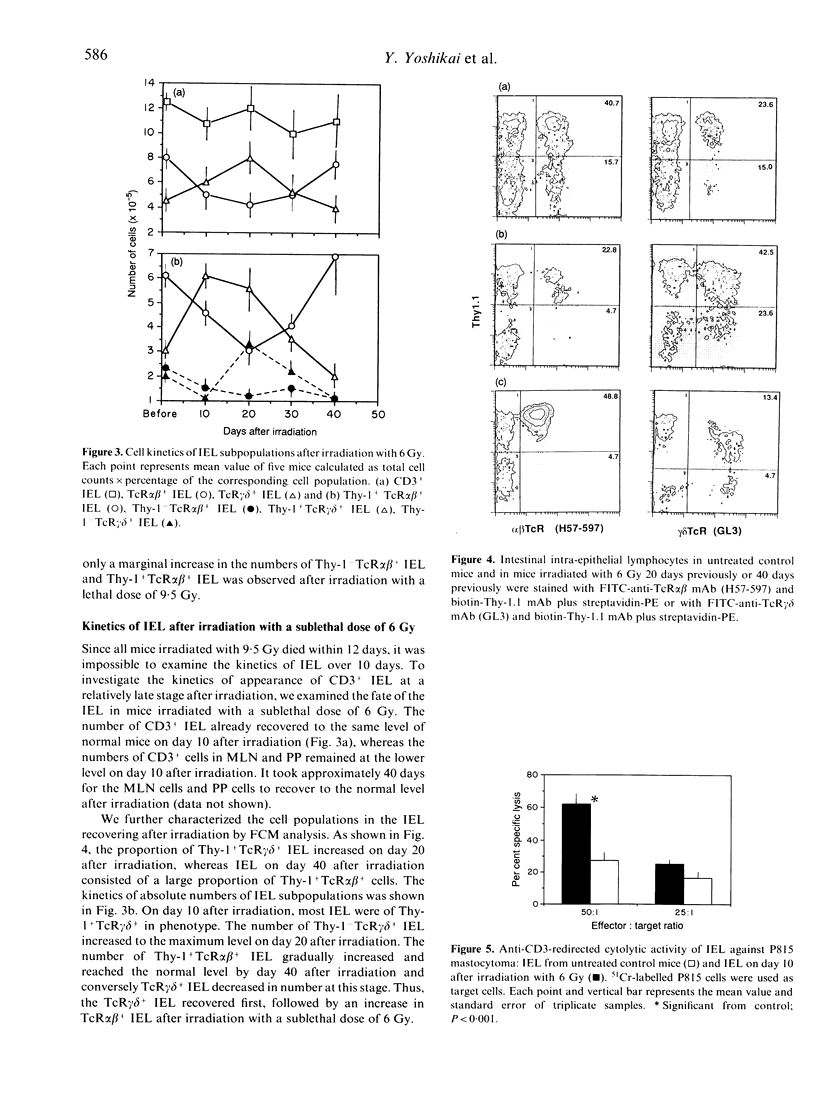
We have previously reported that T-cell receptor (TcR) gamma delta-bearing T cells precede TcR alpha beta-bearing T cells in appearance in the thymus after whole-body irradiation. In the present study, the kinetics of appearance of intestinal intra-epithelial lymphocytes (IEL) was examined in mice after whole-body irradiation with a lethal dose of 9.5 Gy or with a sublethal dose of 6 Gy. The number of CD3+ IEL decreased to the lowest value 4 days after irradiation with 9.5 Gy, and thereafter increased to half as many as the normal level by day 7. Thy-1+TcR alpha beta- IEL and Thy-TcR alpha beta- IEL recovered considerably by day 7 after the irradiation, whereas Thy-1+TcR alpha beta+ IEL and Thy-1+TcR alpha beta+ IEL hardly recovered at this stage. All mice died within 12 days after irradiation with a lethal dose of 9.5 Gy. On the other hand, when irradiation dose was decreased to 6 Gy, all mice survived beyond 40 days after irradiation. The number of CD3+ IEL recovered to the normal level by 10 days after irradiation with 6 Gy. Consistently with the results in mice irradiated with a lethal dose, the first cells to increase in IEL of mice irradiated with a sublethal dose were TcR gamma delta+ IEL expressing Thy-1 antigen. The number of Thy-1+TcR gamma delta+ IEL increased to approximately two-fold as many as that in normal mice by day 10, while TcR alpha beta+ IEL began to increase in number from day 20 after irradiation and recovered to the normal level by day 40 after irradiation. Thus, sequential appearance of TcR gamma delta+ and TcR alpha beta+ IEL was evident after irradiation, similar to that seen in the thymus after irradiation. The IEL on day 10 after a sublethal irradiation, which is composed mainly of Thy-1+TcR gamma delta+ IEL, exhibited a strong cytolytic activity against P815 in the presence of anti-CD3 mAb, suggesting that the early appearing Thy-1+TcR gamma delta+ IEL may play important roles in epithelial immunity at an early stage after irradiation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. P., Lanier L. L. Structure, function, and serology of the T-cell antigen receptor complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:503–540. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.002443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. E., Howarth J. L., Stone R. S. Acute response of germ-free and conventional mice to ionizing radiation. Arch Pathol. 1968 Dec;86(6):676–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandeira A., Itohara S., Bonneville M., Burlen-Defranoux O., Mota-Santos T., Coutinho A., Tonegawa S. Extrathymic origin of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes bearing T-cell antigen receptor gamma delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandeira A., Mota-Santos T., Itohara S., Degermann S., Heusser C., Tonegawa S., Coutinho A. Localization of gamma/delta T cells to the intestinal epithelium is independent of normal microbial colonization. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):239–244. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born W., Hall L., Dallas A., Boymel J., Shinnick T., Young D., Brennan P., O'Brien R. Recognition of a peptide antigen by heat shock--reactive gamma delta T lymphocytes. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.1695022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. B., Strominger J. L., Krangel M. S. The gamma delta T cell receptor. Adv Immunol. 1988;43:133–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerf-Bensussan N., Quaroni A., Kurnick J. T., Bhan A. K. Intraepithelial lymphocytes modulate Ia expression by intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2244–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Mucosal defenses against Salmonella infection in the mouse. J Infect Dis. 1979 May;139(5):503–510. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.5.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes B. J., Pardoll D. M. Molecular and cellular events of T cell development. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:207–264. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60643-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman T., Lefrancois L. Intraepithelial lymphocytes. Anatomical site, not T cell receptor form, dictates phenotype and function. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1569–1581. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman T., Lefrançois L. Expression of the gamma-delta T-cell receptor on intestinal CD8+ intraepithelial lymphocytes. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):855–858. doi: 10.1038/333855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Grand D., Cerf-Bensussan N., Malissen B., Malassis-Seris M., Briottet C., Vassalli P. Two gut intraepithelial CD8+ lymphocyte populations with different T cell receptors: a role for the gut epithelium in T cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):471–481. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa K., Sado T., Kubo S., Kamisaku H., Hitomi K., Utsuyama M. Intrathymic T cell differentiation in radiation bone marrow chimeras and its role in T cell emigration to the spleen. An immunohistochemical study. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3615–3624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Koning F., Coligan J. E., De Bruyn J., Strober S. Isolation of CD4- CD8- mycobacteria-reactive T lymphocyte clones from rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):226–229. doi: 10.1038/339226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huiskamp R., van Ewijk W. Repopulation of the mouse thymus after sublethal fission neutron irradiation. I. Sequential appearance of thymocyte subpopulations. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2161–2169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadish J. L., Basch R. S. Thymic regeneration after lethal irradiation evidence for an intra-thymic radioresistant T cell precursor. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):452–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishihara K., Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Tomooka S., Nomoto K. "Radioresistant" intrathymic T cell precursors express T cell receptor C gamma 4- and C delta-specific gene messages. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):841–847. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancois L., Goodman T. In vivo modulation of cytolytic activity and Thy-1 expression in TCR-gamma delta+ intraepithelial lymphocytes. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1716–1718. doi: 10.1126/science.2564701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER C. P., HAMMOND C. W., TOMPKINS M. The incidence of bacteremia in mice subjected to total body x-radiation. Science. 1950 May 19;111(2890):540–541. doi: 10.1126/science.111.2890.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki G., Yoshikai Y., Kishihara K., Nomoto K. Expression of T cell antigen receptor genes in the thymus of irradiated mice after bone marrow transplantation. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):384–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley R. L., Styre D., Klein J. R. Differentiation and functional maturation of bone marrow-derived intestinal epithelial T cells expressing membrane T cell receptor in athymic radiation chimeras. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1369–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onoue M., Uchida K., Yokokura T., Takahashi T., Mutai M. Effect of intestinal microflora on the survival time of mice exposed to lethal whole-body gamma irradiation. Radiat Res. 1981 Dec;88(3):533–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott D. M., Tait C., MacKenzie S., Mowat A. M., Davies M. D., Micklem H. S. Analysis of the effector functions of different populations of mucosal lymphocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:307–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penit C., Ezine S. Cell proliferation and thymocyte subset reconstitution in sublethally irradiated mice: compared kinetics of endogenous and intrathymically transferred progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajasekar R., Sim G. K., Augustin A. Self heat shock and gamma delta T-cell reactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1767–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha B., Vassalli P., Guy-Grand D. The V beta repertoire of mouse gut homodimeric alpha CD8+ intraepithelial T cell receptor alpha/beta + lymphocytes reveals a major extrathymic pathway of T cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):483–486. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada A., Takada Y., Huang C. C., Ambrus J. L. Biphasic pattern of thymus regeneration after whole-body irradiation. J Exp Med. 1969 Mar 1;129(3):445–457. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.3.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomooka S., Matsuzaki G., Kishihara K., Tanaka K., Yoshikai Y., Taniguchi K., Himeno K., Nomoto K. Sequential appearance of thymocyte subpopulations and T cell antigen receptor gene messages in the mouse thymus after sublethal irradiation. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):3986–3990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON B. R. SURVIVAL STUDIES OF WHOLE-BODY X-IRRADIATED GERMFREE (AXENIC) MICE. Radiat Res. 1963 Nov;20:477–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuuki H., Yoshikai Y., Kishihara K., Matsuzaki G., Ayukawa K., Nomoto K. The expression and sequences of T cell antigen receptor beta-chain genes in the thymus at an early stage after sublethal irradiation. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3683–3691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


