Abstract
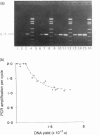
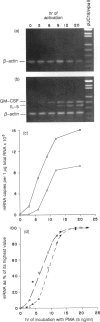
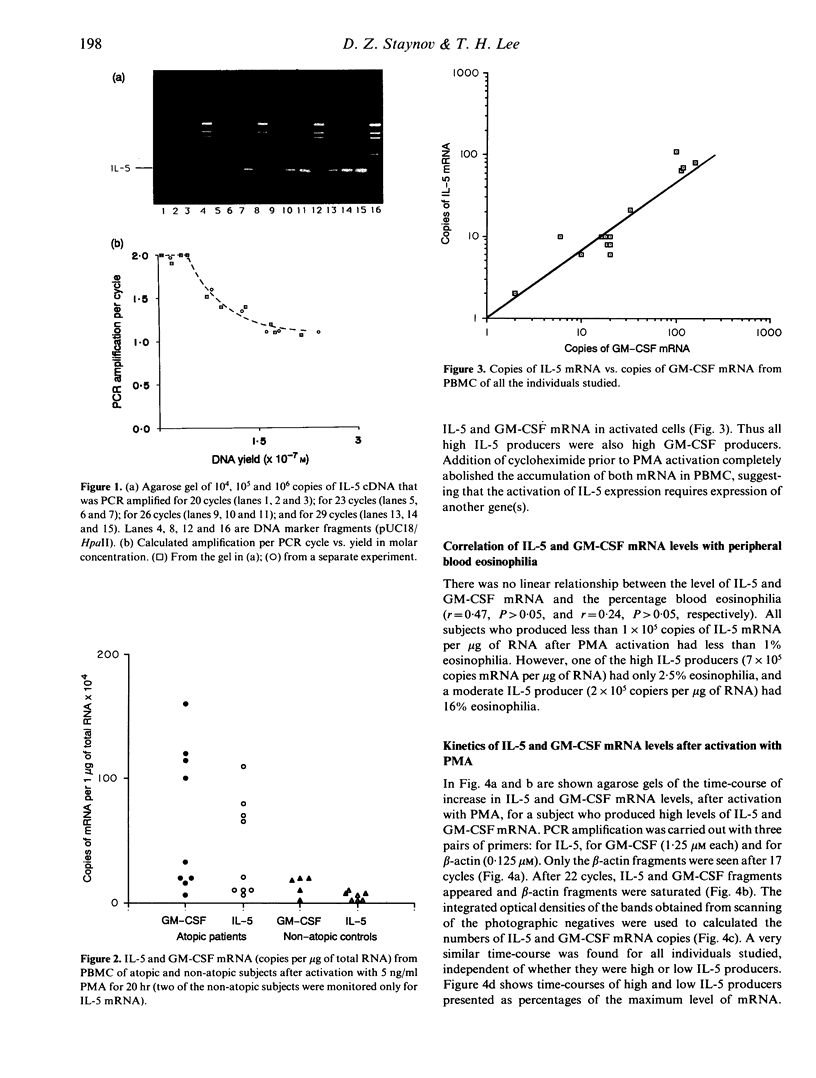
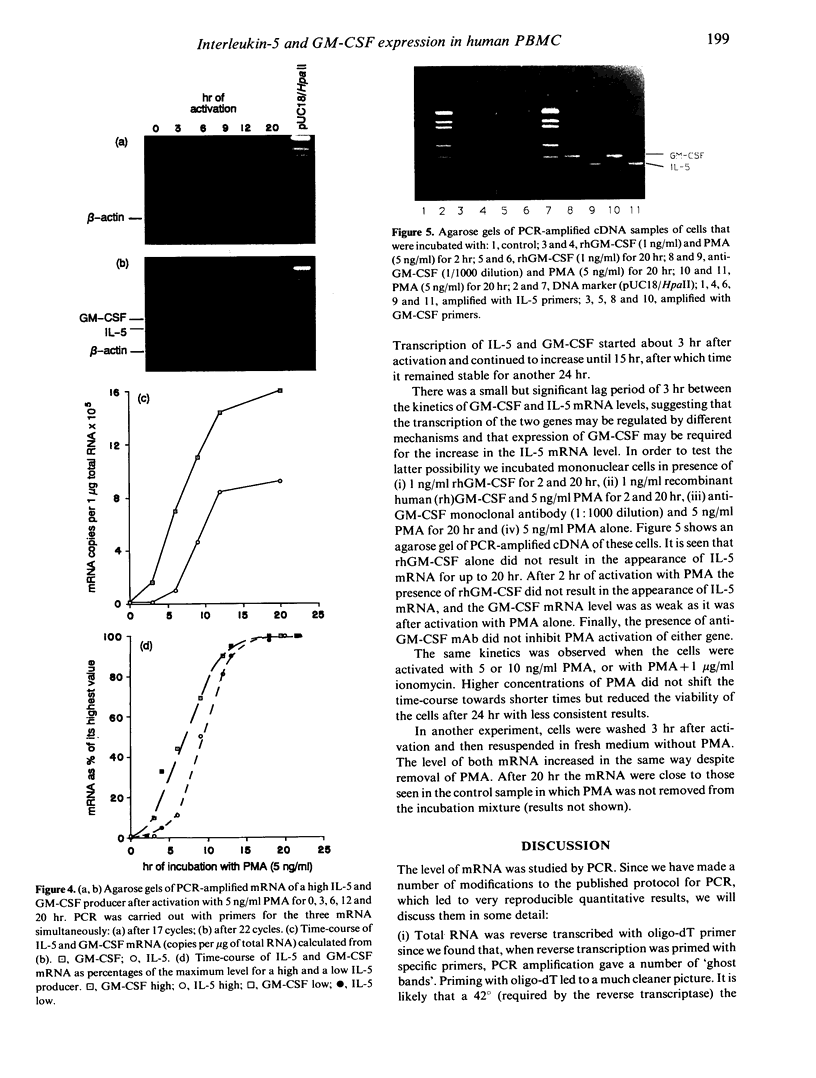
The expression of interleukin-5 (IL-5) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) was studied in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from atopic and non-atopic subjects after activation with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). The levels of IL-5 and GM-CSF mRNA were monitored by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). IL-5 and GM-CSF mRNA was undetectable in quiescent cells. Following PMA stimulation, some atopic patients showed considerably higher levels of IL-5 and GM-CSF mRNA expression than the non-atopic subjects, and there was a significant correlation between the levels of these two cytokines. It was found that activation of IL-5 expression in PBMC requires protein synthesis as does activation of GM-CSF expression, and that PMA is only required during the first few hours of activation. The kinetics of activation indicated that the level of both mRNA increased over 15 hr and remained constant for another 20 hr. The accumulation of IL-5 mRNA lagged about 3 hr behind GM-CSF mRNA accumulation, suggesting that the expression of these two genes is regulated separately. However, GM-CSF expression was not required for IL-5 activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohjanen P. R., Okajima M., Hodes R. J. Differential regulation of interleukin 4 and interleukin 5 gene expression: a comparison of T-cell gene induction by anti-CD3 antibody or by exogenous lymphokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5283–5287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke L. A., Hallsworth M. P., Litchfield T. M., Davidson R., Lee T. H. Identification of the major activity derived from cultured human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, which enhances eosinophil viability, as granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Aug;88(2):226–235. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90333-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell H. D., Tucker W. Q., Hort Y., Martinson M. E., Mayo G., Clutterbuck E. J., Sanderson C. J., Young I. G. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the gene encoding human eosinophil differentiation factor (interleukin 5). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6629–6633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. C., Kamen R. The human hematopoietic colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1229–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3296190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutterbuck E., Shields J. G., Gordon J., Smith S. H., Boyd A., Callard R. E., Campbell H. D., Young I. G., Sanderson C. J. Recombinant human interleukin 5 is an eosinophil differentiation factor but has no activity in standard human B cell growth factor assays. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1743–1750. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent L. A., Strath M., Mellor A. L., Sanderson C. J. Eosinophilia in transgenic mice expressing interleukin 5. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1425–1431. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enokihara H., Furusawa S., Nakakubo H., Kajitani H., Nagashima S., Saito K., Shishido H., Hitoshi Y., Takatsu K., Noma T. T cells from eosinophilic patients produce interleukin-5 with interleukin-2 stimulation. Blood. 1989 May 15;73(7):1809–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabstein K., Dower S., Gillis S., Urdal D., Larsen A. Expression of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and the IL 2 receptor by human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4503–4508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., Isobe M., Croce C. M., Golde D. W., Kaufman S. E., Gasson J. C. The human gene encoding GM-CSF is at 5q21-q32, the chromosome region deleted in the 5q- anomaly. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1282–1285. doi: 10.1126/science.2999978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kost T. A., Theodorakis N., Hughes S. H. The nucleotide sequence of the chick cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 10;11(23):8287–8301. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.23.8287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Sequential expression of genes involved in human T lymphocyte growth and differentiation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1593–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limaye A. P., Abrams J. S., Silver J. E., Ottesen E. A., Nutman T. B. Regulation of parasite-induced eosinophilia: selectively increased interleukin 5 production in helminth-infected patients. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):399–402. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. F., Rothenberg M. E., Petersen J., Weller P. F., Silberstein D., Sheffer A. L., Stevens R. L., Soberman R. J., Austen K. F. Interleukin 5 and phenotypically altered eosinophils in the blood of patients with the idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):343–348. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Hanley-Hyde J., Nordan R. P., Paul W. E. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):64–67. doi: 10.1038/339064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Hatake K., Dvorak A. M., Leiferman K. M., Donnenberg A. D., Arai N., Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Selective differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic cells induced by recombinant human interleukins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2288–2292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Mermod J. J., Vassalli P. Phagocytosis and inflammatory stimuli induce GM-CSF mRNA in macrophages through posttranscriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Heusser C. H., Moroni C. Production of the haemopoietic growth factors GM-CSF and interleukin-3 by mast cells in response to IgE receptor-mediated activation. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):150–152. doi: 10.1038/339150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Arai N., de Vries J., Spits H., Banchereau J., Zlotnik A., Rennick D., Howard M., Takebe Y., Miyatake S. Molecular biology of interleukin 4 and interleukin 5 genes and biology of their products that stimulate B cells, T cells and hemopoietic cells. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:137–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]