Abstract
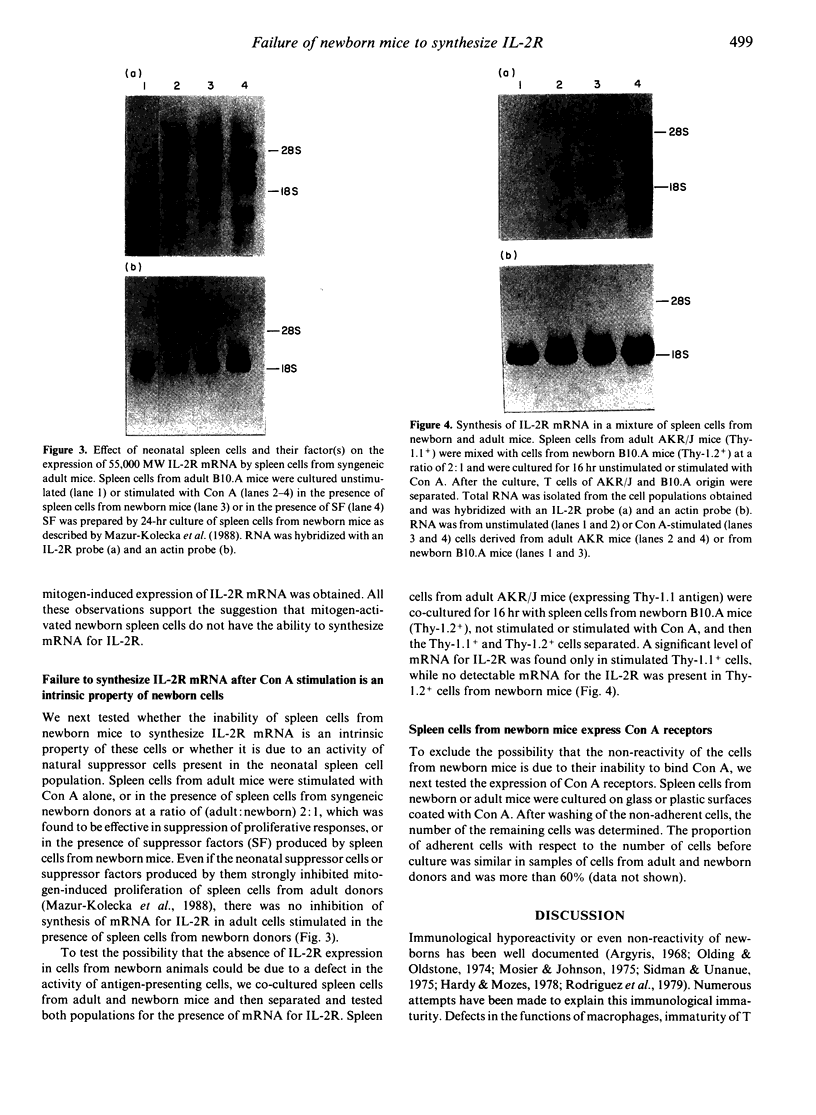
Spleen cells from newborn mice do not respond by proliferation to concanavalin A (Con A) or bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation. This non-reactivity cannot be reversed to a positive response by exogenous interleukin-2 (IL-2). The stimulation with Con A of spleen cells from newborn mice, in contrast to cells from adult animals, does not result in synthesis of mRNA for inducible 55,000 molecular weight (MW) IL-2 receptors (IL-2R). The failure of neonatal spleen cells to synthesize IL-2R mRNA is an intrinsic property of the cells themselves, and it is not due to activity of natural suppressor cells present in newborn animals. Since the expression of functional IL-2R represents one of the early and pivotal events in immune cell activation, we propose that the inability to synthesize IL-2R may be one of the primary reasons for the immunological immaturity of newborns.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argyris B. F., DeStefano M., Zamkoff K. W. Interleukin-2 production in the neonatal mouse. Transplantation. 1985 Sep;40(3):284–287. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198509000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argyris B. F. Role of macrophages in immunological maturation. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):459–467. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BILLINGHAM R. E., BRENT L., MEDAWAR P. B. Actively acquired tolerance of foreign cells. Nature. 1953 Oct 3;172(4379):603–606. doi: 10.1038/172603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. D., Diamond R. A., Rothenberg E. V. Changes in inducibility of IL-2 receptor alpha-chain and T cell-receptor expression during thymocyte differentiation in the mouse. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4121–4130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiscon M. Q., Golub E. S. Functional development of the interacting cells in the immune response. I. Development of T cell and B cell function. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1379–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamantstein T., Osawa H. The interleukin-2 receptor, its physiology and a new approach to a selective immunosuppressive therapy by anti-interleukin-2 receptor monoclonal antibodies. Immunol Rev. 1986 Aug;92:5–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy B., Mozes E. Expression of T cell suppressor activity in the immune response of newborn mice to a T-independent synthetic polypeptide. Immunology. 1978 Nov;35(5):757–762. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holán V., Lipoldová M., Takác M., Cerná J., Vancatová A., Cechová D., Veselský L., Hasek M. Establishment and characterization of a permanent T-cell line producing an antigen non-specific suppressor factor. Immunology. 1985 Oct;56(2):275–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holán V. Modulation of allotransplantation tolerance induction by interleukin-1 and interleukin-2. J Immunogenet. 1988 Oct-Dec;15(5-6):331–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka S. T., Stutman O. Analysis by limiting dilution of interleukin 2-producing T cells in murine ontogeny. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Nov;13(11):936–942. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830131113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake P., Clark E. A., Khorshidi M., Sunshine G. H. Production and characterization of cytotoxic Thy-1 antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. Detection of T cell subsets. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Nov;9(11):875–886. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830091109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipoldova M., Londei M., Grubeck-Loebenstein B., Feldmann M., Owen M. J. Analysis of T-cell receptor usage in activated T-cell clones from Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease. J Autoimmun. 1989 Feb;2(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipoldová M., Holán V. Expression of genes for interleukin-1 alpha and tumour necrosis factor-alpha in newborn mice. Immunology. 1990 May;70(1):136–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loertscher R., Strom T. B. Differential regulation of activation-associated receptor expression on CD4- and CD8-positive T lymphocytes by allosensitized suppressor T cells. Transplantation. 1989 Sep;48(3):473–478. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198909000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu C. Y., Calamai E. G., Unanue E. R. A defect in the antigen-presenting function of macrophages from neonatal mice. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):327–329. doi: 10.1038/282327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovský M., Medawar P., Hunt R., Palmer L., Doré C. A diet enriched in vitamin A acetate or in vivo administration of interleukin-2 can counteract a tolerogenic stimulus. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Feb 22;220(1221):439–445. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1984.0012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattes M. J., Tanimoto M., Pollack M. S., Maurer D. H. Preparing monolayers of non-adherent mammalian cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jul 15;61(2):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur-Kolecka B., Kubera M., Stedra J., Holán V., Skowron-Cendrzak A., Bubak-Satora M. Characteristics of the neonatal spleen cell subpopulation in mice which suppresses lymphocyte proliferative response to mitogen stimulation. Folia Biol (Krakow) 1988;36(1-2):127–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
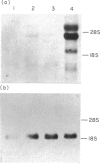
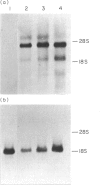
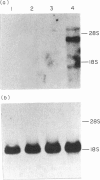
- Miller J., Malek T. R., Leonard W. J., Greene W. C., Shevach E. M., Germain R. N. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a mouse interleukin 2 receptor cDNA. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4212–4217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Oppenheim J. J., Rosenstreich D. L. Characterization of lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF) produced by the macrophage cell line, P388D1. I. Enhancement of LAF production by activated T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1497–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Johnson B. M. Ontogeny of mouse lymphocyte function. II. Development of the ability to produce antibody is modulated by T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):216–226. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murgita R. A., Hooper D. C., Stegagno M., Delovitch T. L., Wigzell H. Characterization of murine newborn inhibitory T lymphocytes: functional and phenotypic comparison with an adult T cell subset activated in vitro by alphafetoprotein. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Dec;11(12):957–964. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi M., Ishida Y., Honjo T. Expression of functional interleukin-2 receptors in human light chain/Tac transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):267–269. doi: 10.1038/331267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding L. B., Oldstone M. B. Lymphocytes from human newborns abrogate mitosis of their mother's lymphocytes. Nature. 1974 May 10;249(453):161–162. doi: 10.1038/249161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H. Expression and function of interleukin-2 receptors on immature thymocytes. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):101–103. doi: 10.1038/314101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez G., Andersson G., Wigzell H., Peck A. B. Non-T cell nature of the naturally occurring, spleen-associated suppressor cells present in the newborn mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Sep;9(9):737–746. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimuzu A., Kondo S., Takeda S., Yodoi J., Ishida N., Sabe H., Osawa H., Diamantstein T., Nikaido T., Honjo T. Nucleotide sequence of mouse IL-2 receptor cDNA and its comparison with the human IL-2 receptor sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1505–1516. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowron-Cendrzak A., Ptak W. Suprression of local graft-versus-host reactions by mouse fetal and newborn spleen cells. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jun;6(6):451–452. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A. The structure, function, and expression of interleukin-2 receptors on normal and malignant lymphocytes. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):727–732. doi: 10.1126/science.3008337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]