Abstract
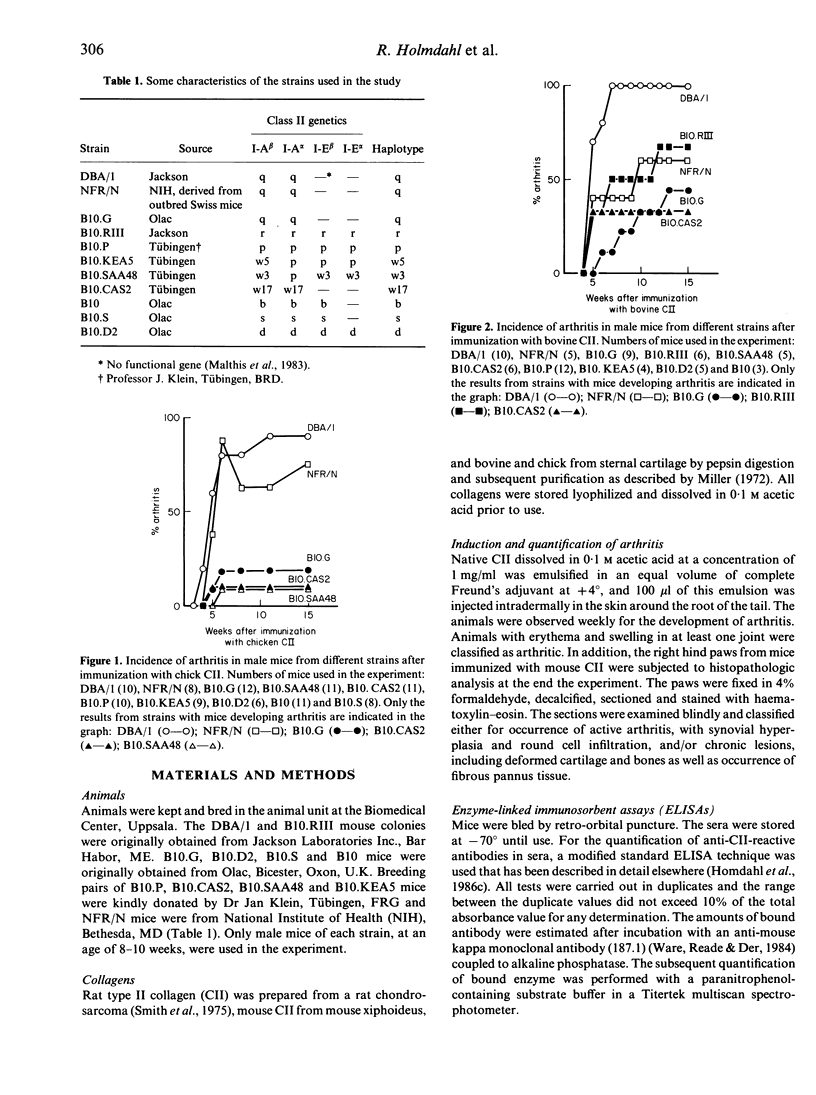
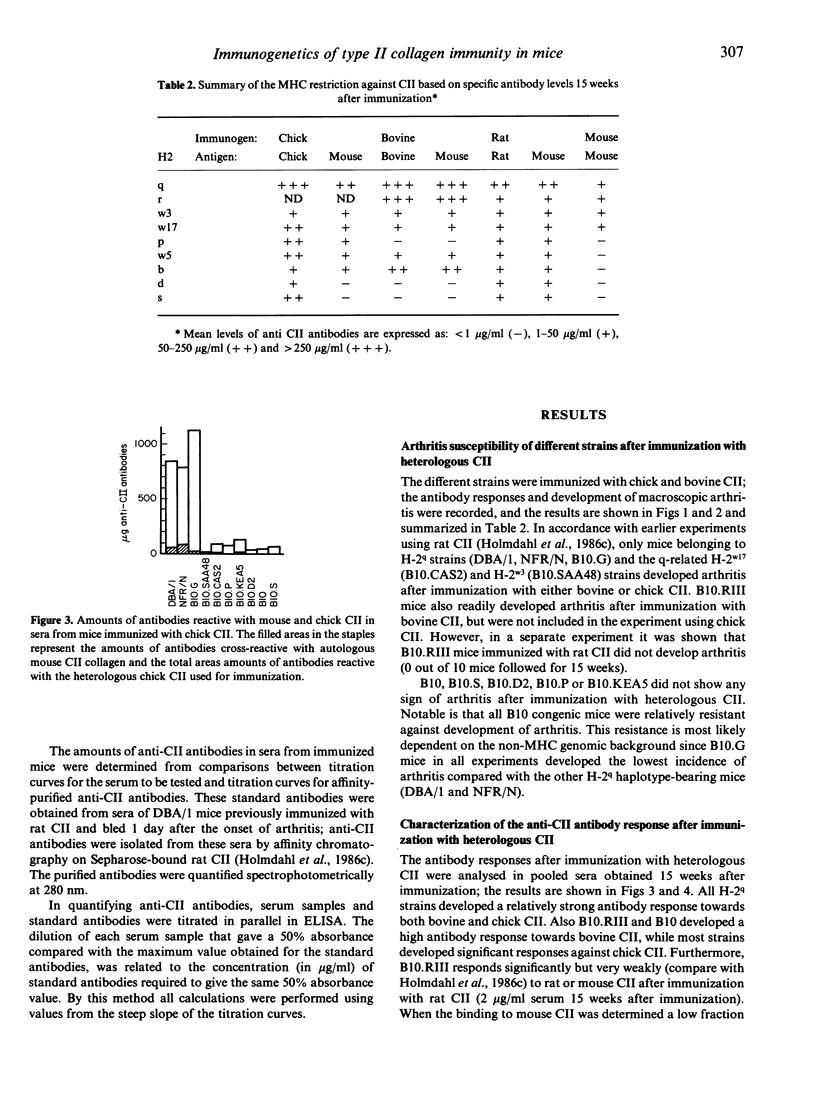
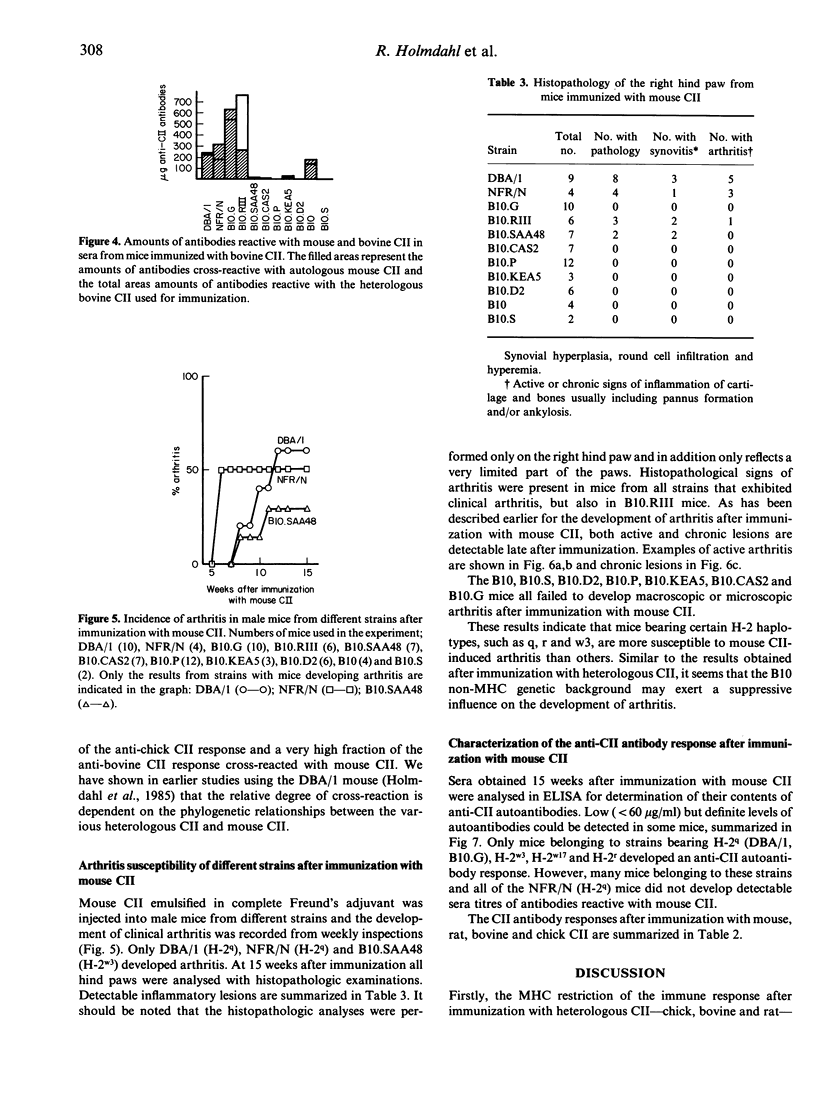
The MHC restriction of the antibody response and development of arthritis after immunization with autologous or heterologous type II collagens in mice have been investigated. Mice from three different H-2q-carrying strains (DBA/1, NFR/N and B10.G) with different non-MHC genes, as well as B10-congenic strains carrying wild type H-2q-related or H-2r haplotypes, were susceptible for collagen arthritis. All strains tested developed an antibody response cross-reacting with autologous type II collagen after immunization with heterologous type II collagen; H-2q predisposes for a high response against chick, rat and bovine type II collagen, H-2r and H-2b for a high response against bovine type II collagen. Only mouse strains with H-2q, H-2r, H-2w3 or H-2w17 were responders to mouse type II collagen, and only these strains developed arthritis after immunization with heterologous or autologous type II collagens. These findings indicate that the ability to mount an immune response against autologous type II collagen is a prerequisite for the susceptibility to collagen arthritis. A cross-reactive autoimmune response after immunization with various heterologous type II collagen may enhance further the development of arthritis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Courtenay J. S., Dallman M. J., Dayan A. D., Martin A., Mosedale B. Immunisation against heterologous type II collagen induces arthritis in mice. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):666–668. doi: 10.1038/283666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Andersson M., Tarkowski A. Origin of the autoreactive anti-type II collagen response. I. Frequency of specific and multispecific B cells in primed murine lymph nodes. Immunology. 1987 Jul;61(3):369–374. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jansson L., Andersson M. Female sex hormones suppress development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Dec;29(12):1501–1509. doi: 10.1002/art.1780291212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jansson L., Gullberg D., Rubin K., Forsberg P. O., Klareskog L. Incidence of arthritis and autoreactivity of anti-collagen antibodies after immunization of DBA/1 mice with heterologous and autologous collagen II. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Dec;62(3):639–646. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jansson L., Larsson E., Rubin K., Klareskog L. Homologous type II collagen induces chronic and progressive arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Jan;29(1):106–113. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F. Polymorphism of the mouse H-2 loci. Immunol Rev. 1981;60:23–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M., McDevitt H. O. Several mechanisms can account for defective E alpha gene expression in different mouse haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):273–277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Structural studies on cartilage collagen employing limited cleavage and solubilization with pepsin. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4903–4909. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck A. B., Darby B., Wakeland E. K. Variant class II molecules from H-2 haplotypes in wild mouse populations: functional characteristics of closely related class II gene products. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2432–2439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck A. B., Smith R. T., Jadus M. R. Heterogeneity of an anti-H-2 I-A response as determined by cloned T cell reactivity. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2067–2070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Sriram S., Cooper S. M. Prevention of type II collagen-induced arthritis by in vivo treatment with anti-L3T4. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1105–1110. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. D., Martin G. R., Miller E. J., Dorfman A., Swarm R. Nature of the collagen synthesized by a transplanted chondrosarcoma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jan;166(1):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Dixon F. J. Serum transfer of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):378–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakeland E. K., Klein J. Evidence for minor structural variations of class II genes in wild and inbred mice. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1280–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakeland E. K., Klein J. The histocompatibility-2 system in wild mice. XII. An immunochemical analysis of the anti-Ia antibodies in antisera produced against 13 B10.W lines. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1731–1736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware C. F., Reade J. L., Der L. C. A rat anti-mouse kappa chain specific monoclonal antibody, 187.1.10: purification, immunochemical properties and its utility as a general second-antibody reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 16;74(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90371-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson W. C., Townes A. S. Genetic susceptibility to murine collagen II autoimmune arthritis. Proposed relationship to the IgG2 autoantibody subclass response, complement C5, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and non-MHC loci. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1878–1891. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Luthra H. S., Griffiths M. M., Stuart J. M., Huse A., David C. S. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. IV. Variations in immunogenetic regulation provide evidence for multiple arthritogenic epitopes on the collagen molecule. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2443–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Luthra H. S., Stuart J. M., David C. S. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Major histocompatibility complex (I region) linkage and antibody correlates. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):688–700. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]