Abstract
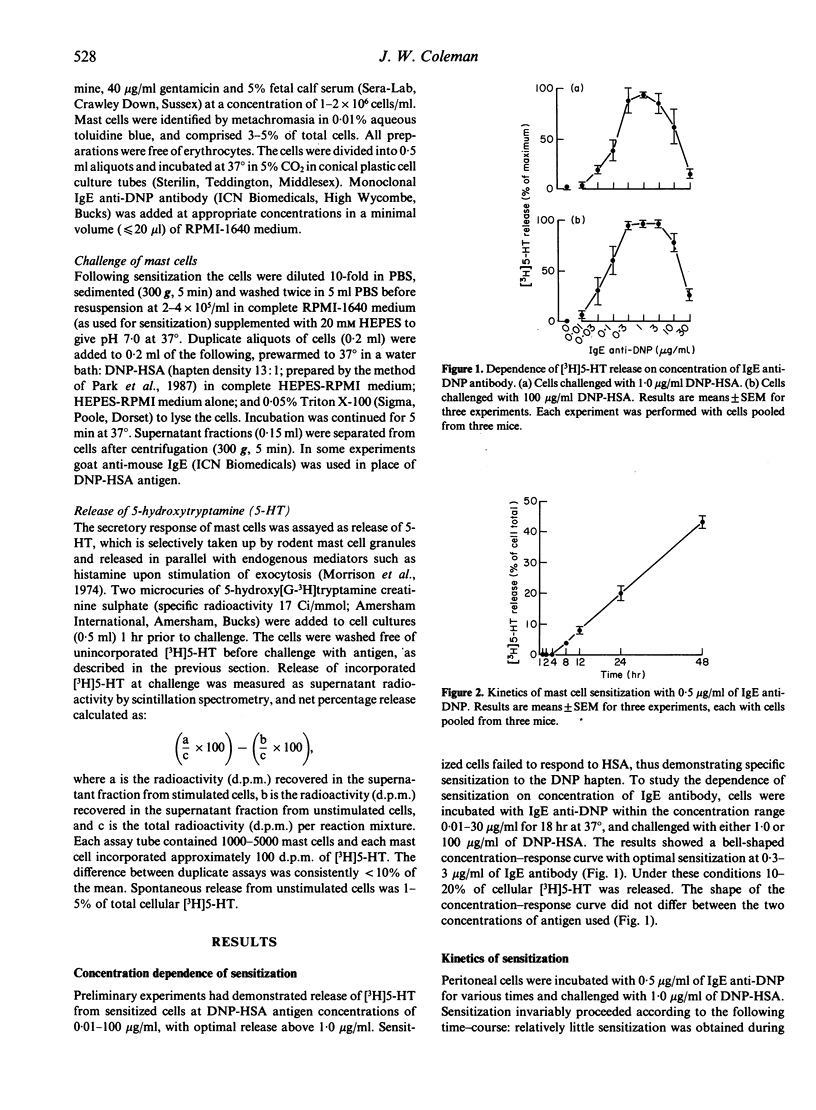
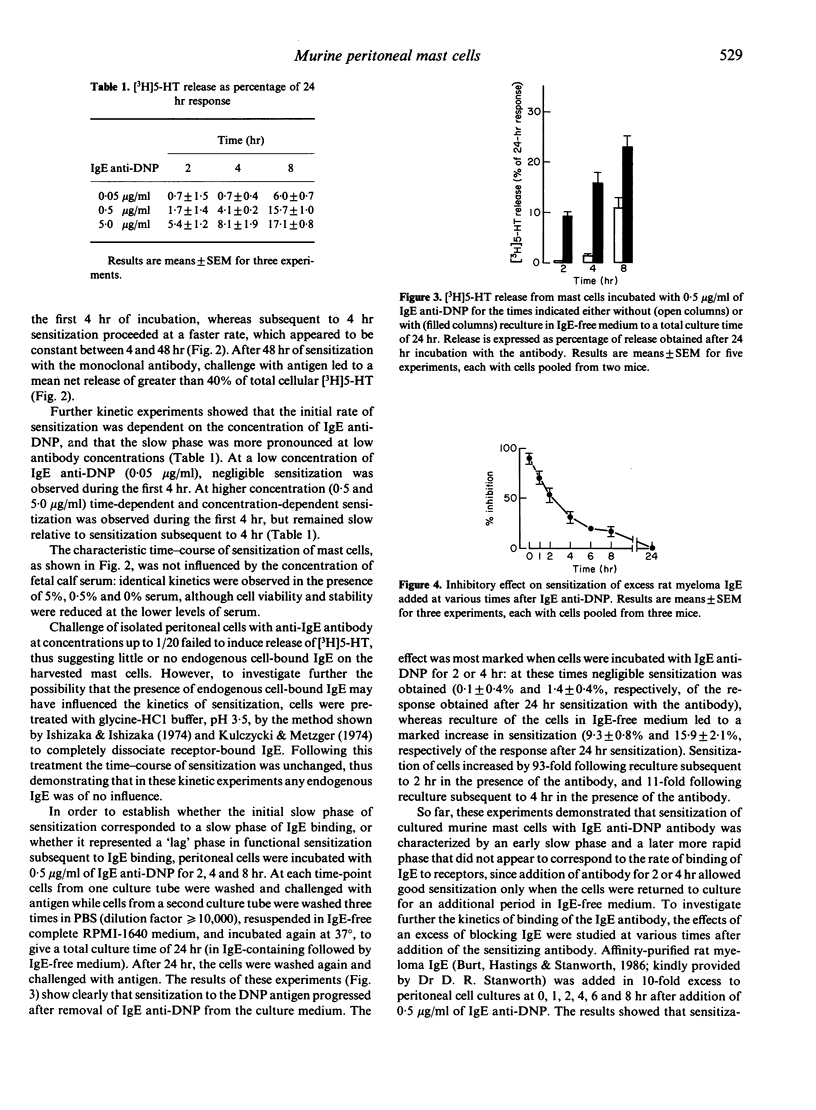
Incubation of murine peritoneal cells with monoclonal IgE anti-DNP antibody in vitro led to sensitization of mast cells, measured as release of 5-HT upon challenge with DNP-HSA antigen. Sensitization was maximal at 0.3-3.0 micrograms/ml of IgE anti-DNP and declined above and below this concentration range. In kinetic studies, the time-course of sensitization was clearly divisible into an early slow phase of approximately 4 hr, followed by a more rapid linear phase from 4 to 48 hr. The early slow phase was more pronounced at lower concentrations of IgE anti-DNP (within the range 0.05-5.0 micrograms/ml). The degree of sensitization obtained after incubation of peritoneal cells with IgE anti-DNP for fixed periods (2, 4 and 8 hr) was markedly increased when the cells were washed and recultured in IgE-free medium, thus demonstrating that sensitization proceeds subsequent to an early stage of binding of IgE to receptors. Sensitization with IgE anti-DNP was blocked by addition of excess rat myeloma IgE, but only to a marked extent (greater than 50%) when the blocking immunoglobulin was added during the first 2 hr, thus providing further evidence that the major part of binding of the IgE antibody took place during this early stage, that is, prior to the phase of greatest sensitization. These findings indicate a period of delay between binding of IgE to receptors and functional sensitization, measured as mediator release in response to antigen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burt D. S., Hastings G. Z., Stanworth D. R. Use of synthetic peptides in the production and characterization of antibodies directed against predetermined specificities in rat immunoglobulin E. Mol Immunol. 1986 Feb;23(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. W., Helm B. A., Stanworth D. R., Gould H. J. Inhibition of mast cell sensitization in vitro by a human immunoglobulin epsilon-chain fragment synthesized in Escherichia coli. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Sep;15(9):966–969. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad D. H., Bazin H., Sehon A. H., Froese A. Binding parameters of the interaction between rat IgE and rat mast cell receptors. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1688–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Mechanisms of reaginic hypersensitivity and IgE antibody response. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:109–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K. Mechanisms of passive sensitization. IV. Dissociation of IgE molecules from basophil receptors at acid pH. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1078–1084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Soto C. S., Ishizaka K. Mechanisms of passive sensitization. 3. Number of IgE molecules and their receptor sites on human basophil granulocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):500–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki A., Jr, Metzger H. The interaction of IgE with rat basophilic leukemia cells. II. Quantitative aspects of the binding reaction. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1676–1695. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza G., Metzger H. Distribution and valency of receptor for IgE on rodent mast cells and related tumour cells. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):548–550. doi: 10.1038/264548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H. The IgE-mast cell system as a paradigm for the study of antibody mechanisms. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:186–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01465.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Roser J. F., Henson P. M., Cochrane C. G. Activation of rat mast cells by low molecular weight stimuli. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):573–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. K., Tingle M. D., Grabowski P. S., Coleman J. W., Kitteringham N. R. Drug-protein conjugates--XI. Disposition and immunogenicity of dinitrofluorobenzene, a model compound for the investigation of drugs as haptens. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 1;36(5):591–599. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90707-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzansky J. J., Patterson R. Binding constants of IgE receptors on human blood basophils for IgE. Immunology. 1986 Jun;58(2):257–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Webb W. W., Elson E. L., Metzger H. Lateral motion and valence of Fc receptors on rat peritoneal mast cells. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):550–552. doi: 10.1038/264550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


