Abstract
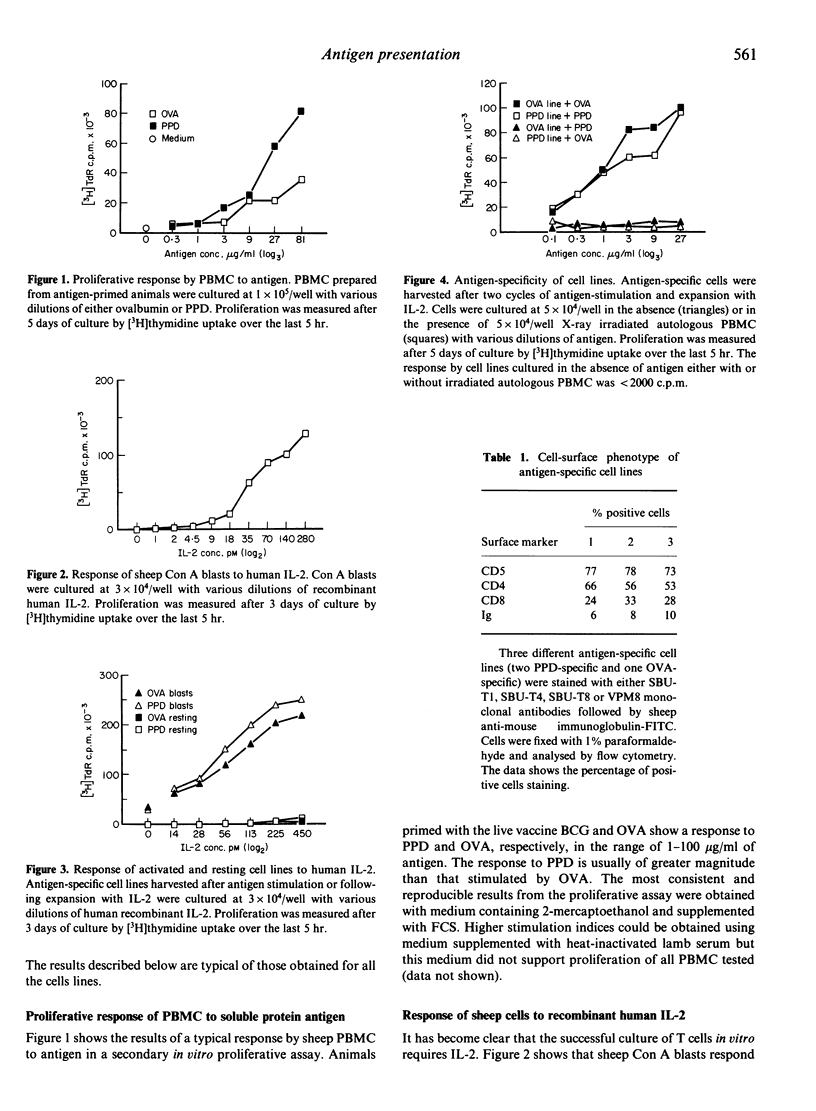
Antigen-specific sheep T-cell lines have been generated in vitro from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). PBMC prepared from antigen-primed animals were cultured in the presence of ovalbumin (OVA) or purified protein derivative (PPD). After 5 days of culture, activated antigen-specific cells were expanded by further culture in the presence of recombinant human interleukin-2 (IL-2). Cell lines generated after two cycles of antigen stimulation followed by expansion with IL-2 show a proliferative response to antigen only in the presence of autologous antigen-presenting cells (APC) and recognize only the antigen used in the original stimulation. An OVA-specific cell line was found to be capable of recognizing a synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acid residues 323-338 of OVA. The cell lines also responded by proliferation in an allogeneic mixed leucocyte reaction (MLR). Cell-surface phenotyping shows that the cell lines comprise both CD4- and CD8-positive cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen P. M., Unanue E. R. Differential requirements for antigen processing by macrophages for lysozyme-specific T cell hybridomas. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1077–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter B. J., Bach F. H. Lymphocyte reactivity in vitro. I. Cellular reconstitution of purified lymphocyte response. Cell Immunol. 1970 Jul;1(2):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Grey H. M. The interaction between protein-derived immunogenic peptides and Ia. Immunol Rev. 1987 Aug;98:115–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. Transient expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Consequences for T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1895–1911. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Berzofsky J. A. T-cell antigenic sites tend to be amphipathic structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7048–7052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL J. G., MORRIS B. The output of cells in lymph from the popliteal node of sheep. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1962 Oct;47:360–369. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1962.sp001620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefsmit E. C., Duijvestijn A. M., Kamperdijk E. W. Relation between langerhans cells, veiled cells, and interdigitating cells. Immunobiology. 1982 Apr;161(3-4):255–265. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(82)80081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba K., Steinman R. M. Resting and sensitized T lymphocytes exhibit distinct stimulatory (antigen-presenting cell) requirements for growth and lymphokine release. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1717–1735. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Skidmore B., White J., Marrack P. Antigen-inducible, H-2-restricted, interleukin-2-producing T cell hybridomas. Lack of independent antigen and H-2 recognition. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1198–1214. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A., Parodi B., Celada F. Activation of human B lymphocytes: frequency of antigen-specific B cells triggered by alloreactive or by antigen-specific T cell clones. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Sep;13(9):733–738. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Kimpton W. G., Brandon M. R., Cahill R. N. Lymphocyte subsets show marked differences in their distribution between blood and the afferent and efferent lymph of peripheral lymph nodes. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1755–1765. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Maddox J. F., Gogolin-Ewens K. J., Brandon M. R. Characterization of two sheep lymphocyte differentiation antigens, SBU-T1 and SBU-T6. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):729–737. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox J. F., Mackay C. R., Brandon M. R. Surface antigens, SBU-T4 and SBU-T8, of sheep T lymphocyte subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):739–748. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makoff A. J., Paynter C. A., Rowlands D. J., Boothroyd J. C. Comparison of the amino acid sequence of the major immunogen from three serotypes of foot and mouth disease virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8285–8295. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L., O'Malley B. W., Nisbet A. D., Fothergill J. E., Givol D., Fields S., Robertson M., Brownlee G. G. Sequence of chicken ovalbumin mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):723–728. doi: 10.1038/273723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C., Rusk C. M. Low and high affinity cellular receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for the level of Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1126–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H. T-lymphocyte recognition of antigen in association with gene products of the major histocompatibility complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:237–261. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger R. C., Oppenheim J. J. Synergistic interaction of macrophages and lymphocytes in antigen-induced transformation of lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Jul 1;132(1):44–65. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A., Buus S., Colon S., Smith J. A., Miles C., Grey H. M. Structural characteristics of an antigen required for its interaction with Ia and recognition by T cells. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):395–399. doi: 10.1038/328395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonkevitz R., Colon S., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Grey H. M. Antigen recognition by H-2-restricted T cells. II. A tryptic ovalbumin peptide that substitutes for processed antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2067–2074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonkevitz R., Kappler J., Marrack P., Grey H. Antigen recognition by H-2-restricted T cells. I. Cell-free antigen processing. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):303–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin 2. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:319–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts T. H., Brian A. A., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., McConnell H. M. Antigen presentation by supported planar membranes containing affinity-purified I-Ad. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7564–7568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts T. H., Gariépy J., Schoolnik G. K., McConnell H. M. T-cell activation by peptide antigen: effect of peptide sequence and method of antigen presentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5480–5484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


