Abstract
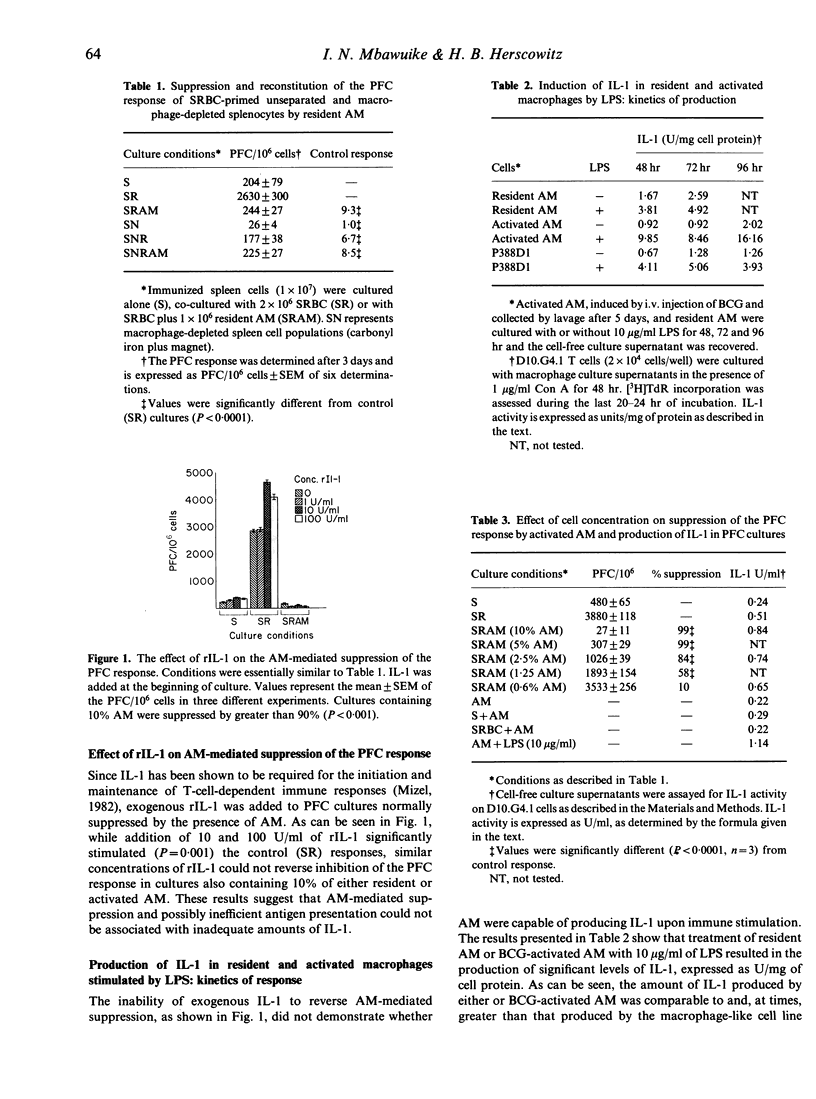
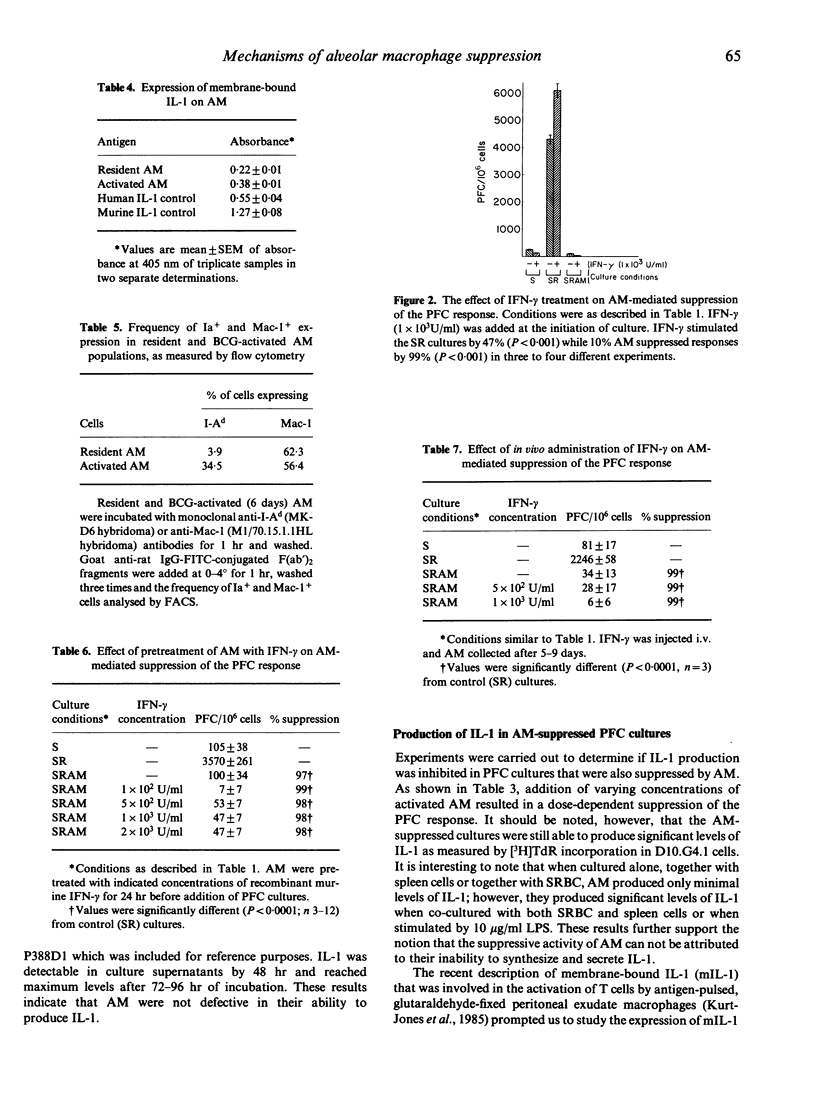
Murine alveolar macrophages (AM) have been shown to be inefficient at providing accessory function for initiation of the in vitro plaque-forming cell (PFC) response. In the present study AM, which were obtained either from untreated mice (resident AM) or mice injected i.v. with BCG (activated AM) potently suppressed the PFC response of spleen cells from animals previously primed with sheep erythrocytes (SRBC). Addition of AM at a concentration of 10% with respect to spleen cells resulted in greater than 90% suppression of the PFC response. In order to determine if inefficient antigen presentation was associated with AM-mediated suppression, the role of IL-1 and Ia antigen was studied. Addition of exogenous recombinant IL-1 (rIL-1) stimulated the PFC response in control cultures, but had no effect on AM-mediated suppression. Resident AM could be activated with lipopolysaccharide or antigen to produce significant levels of IL-1. Membrane-bound IL-1, thought to be important in the presentation of particulate antigens, was detected on glutaraldehyde-fixed resident AM and was significantly elevated in BCG-activated macrophages. The frequency of cell surface Ia antigen expression was low in resident AM (4%), but could be increased (35%) after in vivo activation with BCG. Recombinant interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), known to enhance expression of Ia antigen and production of IL-1, had no effect on AM-mediated suppression when used either to pretreat AM, when present during the entire period of culture, or when injected into mice before culture initiation. Treatment with IFN-gamma, however, resulted in a slight increase in the expression of Ia antigen. These results indicate that the immunosuppressive activity of AM is neither related to a defect in IL-1 production or expression nor to a deficiency in Ia antigen expression and therefore can not be explained by the inefficient antigen-presenting function of alveolar macrophages.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubas P., Cosso B., Godard P., Michel F. B., Clot J. Decreased suppressor cell activity of alveolar macrophages in bronchial asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Nov;130(5):875–878. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.5.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker S. Effect of interferon-gamma on class-II antigen expression and accessory cell function. Surv Immunol Res. 1985;4(2):135–145. doi: 10.1007/BF02918809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boraschi D., Censini S., Tagliabue A. Interferon-gamma reduces macrophage-suppressive activity by inhibiting prostaglandin E2 release and inducing interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):764–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowing C., Schwartz B. D., Dickler H. B. Macrophage Ia antigens. I. macrophage populations differ in their expression of Ia antigens. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):378–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden E., Turino G. M. Interleukin-1 secretion by human alveolar macrophages stimulated with endotoxin is augmented by recombinant immune (gamma) interferon. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Mar;133(3):455–460. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.3.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier M., Touaty E., Gerber F., Medrano G., Pariente R. Suppression of bronchoalveolar lymphocyte antibody secretion by alveolar macrophage: an in vitro study in the rabbit. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1984 May-Jun;20(3):229–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara H., Kleinhenz M. E., Wallis R. S., Ellner J. J. Increased interleukin-1 production and monocyte suppressor cell activity associated with human tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jan;133(1):73–77. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenberg D. J., Daniele R. P. The alveolar macrophage: its capacity to act as an accessory cell in mitogen-stimulated proliferation of guinea pig lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1978 Mar 1;36(1):115–127. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90255-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression of murine immune interferon cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herscowitz H. B. In defense of the lung: paradoxical role of the pulmonary alveolar macrophage. Ann Allergy. 1985 Nov;55(5):634–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking W. G., Golde D. W. The pulmonary-alveolar macrophage (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 Sep 13;301(11):580–587. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197909133011104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G. Alveolar macrophages. II. Inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation by purified macrophages from rat lung. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):429–436. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltreider H. B. Alveolar macrophages. Enhancers or suppressors of pulmonary immune reactivity? Chest. 1982 Sep;82(3):261–262. doi: 10.1378/chest.82.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Gillis S., Mizel S. B., Shevach E. M., Malek T. R., Dinarello C. A., Lachman L. B., Janeway C. A., Jr Growth of a cloned helper T cell line induced by a monoclonal antibody specific for the antigen receptor: interleukin 1 is required for the expression of receptors for interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Allred C., Cohen S., Yoshida T. Role of interleukin 1 in experimental pulmonary granuloma in mice. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):358–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Elias J. A., Kay S. L., Rossman M. D., Nowell P. C., Daniele R. P. Spontaneous production of interleukin-1 by human alveolar macrophages. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1983 Dec;29(3):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(83)90047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Virgin H. W., 4th, Unanue E. R. Relationship of macrophage Ia and membrane IL 1 expression to antigen presentation. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3652–3654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb M. F., Toews G. B., Lyons C. R., Uhr J. W. Antigen presentation by guinea pig alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):286–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Gubler U., Hellmann C. P., Dukovich M., Giri J. G., Pan Y. C., Collier K., Semionow R., Chua A. O., Mizel S. B. Cloning and expression of murine interleukin-1 cDNA in Escherichia coli. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):458–462. doi: 10.1038/312458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mbawuike I. N., Luhr J. E., Herscowitz H. B. Enhanced recovery of murine alveolar macrophages: morphological and functional characteristics following intravenous injection of heat-killed Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):483–489. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.483-489.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mbawuike I. N., Luhr J. E., Herscowitz H. B. Reversal of murine alveolar macrophage-mediated suppression of plaque-forming cell response by sodium periodate. Cell Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;99(1):300–307. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarron R. M., Goroff D. K., Luhr J. E., Murphy M. A., Herscowitz H. B. Methods for the collection of peritoneal and alveolar macrophages. Methods Enzymol. 1984;108:274–284. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)08092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and T cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:51–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Manser T., Pearson G. D., Daley M. J., Gefter M. L. Effect of IFN-gamma on the immune response in vivo and on gene expression in vitro. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):381–382. doi: 10.1038/307381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton R. C. Effect of interferon on the induction of human monocyte secretion of interleukin-1 activity. Immunology. 1985 Nov;56(3):441–449. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennline K. J., Conrad R. E., Gerber H. R., Herscowitz H. B. Suppressive effect of alveolar macrophages on the in vitro immune response of rabbit lymphocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 May;25(5):495–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellito J., Caldwell J. L., Kaltreider H. B. Immune functions of murine alveolar macrophages: binding of lymphocytes and support of lymphocyte proliferation. Exp Lung Res. 1983 Feb;4(2):93–107. doi: 10.3109/01902148309055007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venet A., Hance A. J., Saltini C., Robinson B. W., Crystal R. G. Enhanced alveolar macrophage-mediated antigen-induced T-lymphocyte proliferation in sarcoidosis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):293–301. doi: 10.1172/JCI111688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. S., Unanue E. R. Antigen-presenting function of alveolar macrophages: uptake and presentation of Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):794–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


