Abstract
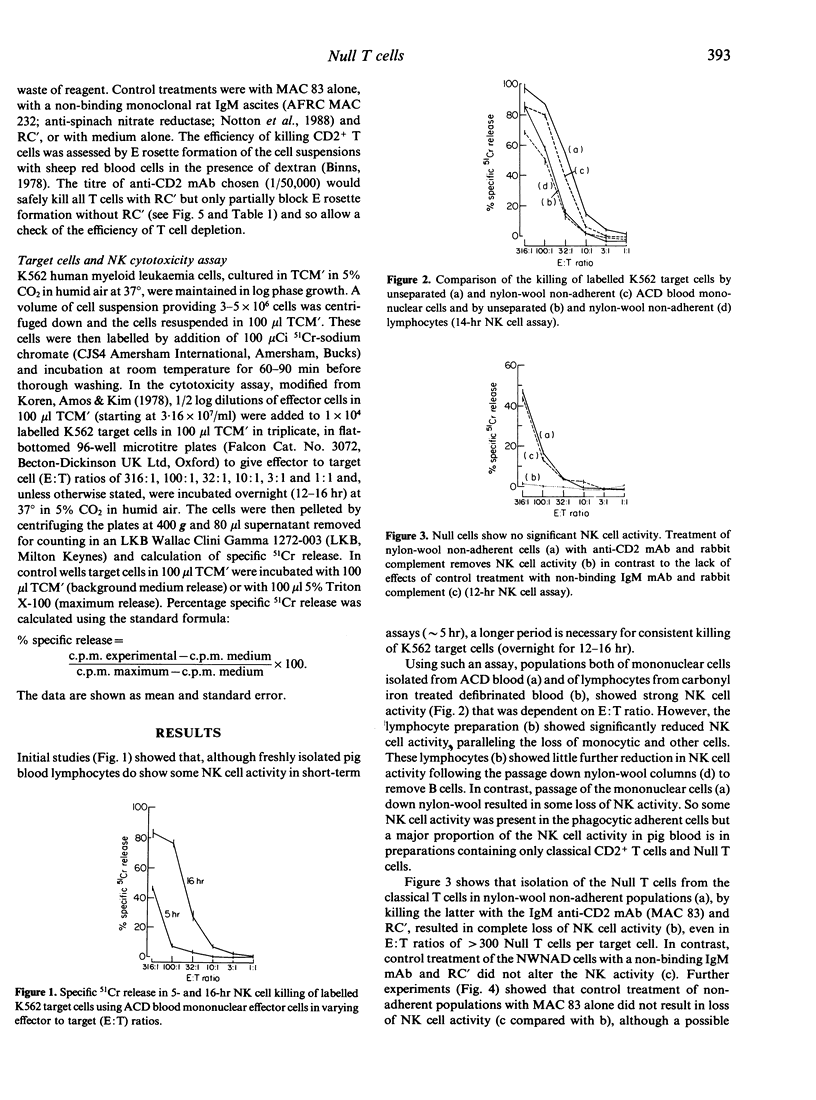
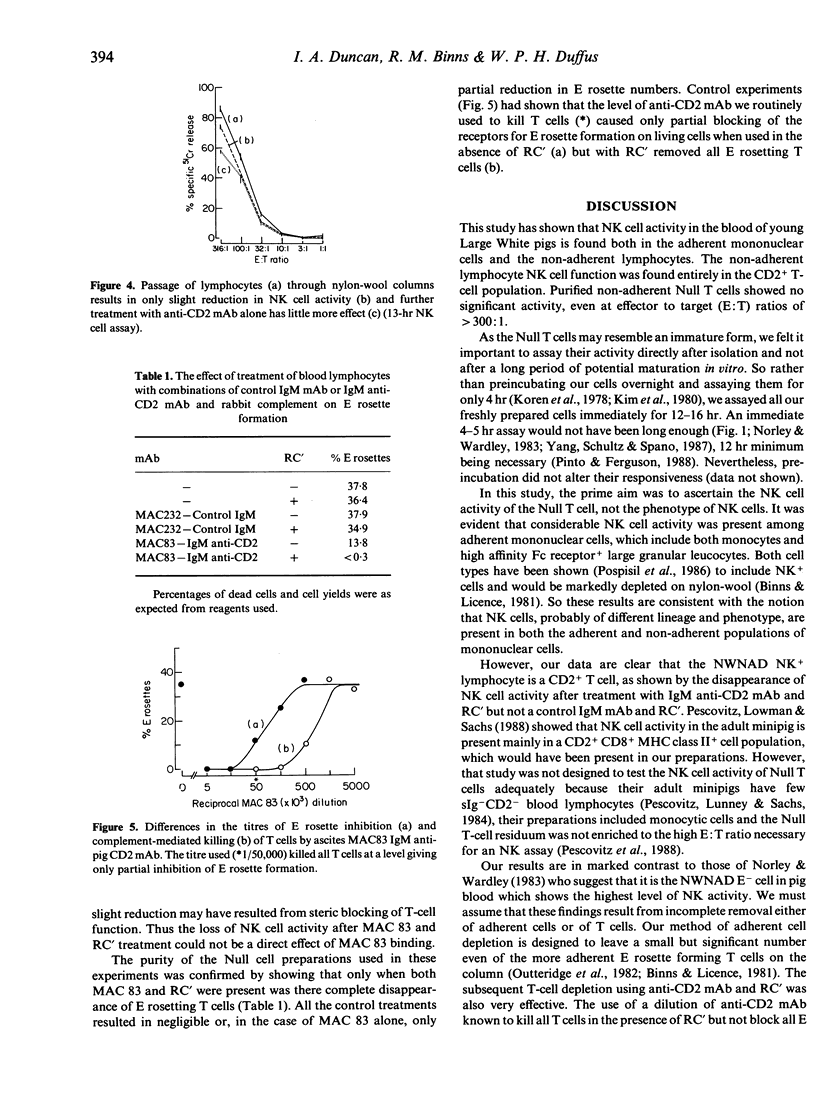
Up to 50% of the blood lymphocytes in young pigs are thymus-derived, lack all subset-specific markers and appear immunologically unresponsive, with no known functional role. In an examination of their possible role in natural killing, NK activity was found in unpurified mononuclear cells and in preparations of unselected and nylon non-adherent lymphocytes (T cells and Null cells). However, NK activity was abolished by removing the E rosette forming T cells using a rat IgM anti-pig CD2 monoclonal antibody and rabbit complement, but not by control treatments with a non-binding rat IgM monoclonal reagent and complement or with any other reagent alone. Thus the resting Null T cell appears not to play a significant role in natural killing.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binns R. M., Blakeley D., Licence S. T. Migration of fluoresceinated pig lymphocytes in vivo: technical aspects and use in studies of autologous and homologous cell survival for up to three weeks. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;66(3):341–349. doi: 10.1159/000232839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M., Licence S. T. A major subpopulation of Fc receptor-bearing lymphocytes revealed by rosette formation in dextran media: studies with pig, sheep and rat lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(2):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M. Organisation of the lymphoreticular system and lymphocyte markers in the pig. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 Jan;3(1-2):95–146. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M., Pabst R., Licence S. T. Subpopulations of T lymphocytes emigrating in venous blood draining pig thymus labelled in vivo with fluorochrome. Immunology. 1988 Feb;63(2):261–267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M., Pallares V., Symons D. B., Sibbons P. Effect of thymectomy on lymphocyte subpopulations in the pig. Demonstration of a thymus-dependent 'null' cell. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;55(1-6):96–101. doi: 10.1159/000231915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M. Sheep erythrocyte rosettes in pigs, sheep, cattle and goats demonstrated in the presence of dextran. J Immunol Methods. 1978;21(3-4):197–210. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binns R. M., Vaiman M., Davies H., Symons D. B. Characterization of pig lymphocyte subpopulations by adherence to nylon wool. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1979;58(2):128–134. doi: 10.1159/000232184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. B., Huh N. D., Koren H. S., Amos D. B. Natural killing (NK) and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) in specific pathogen-free (SPF) miniature swine and germfree piglets. I. Comparison of NK and ADCC. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):755–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Amos D. B., Kim Y. B. Natural killing and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity are independent immune functions in the Minnesota miniature swine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5127–5131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. Sheep leukocyte molecules: a review of their distribution, structure and possible function. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Jul;19(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(88)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norley S. G., Wardley R. C. Investigation of porcine natural-killer cell activity with reference to African swine-fever virus infection. Immunology. 1983 Aug;49(4):593–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Outteridge P. M., Binns R. M., Licence S. T. Subpopulations of pig blood E-rosette-forming lymphocytes and thymus-dependent null cells: separation by nylon wool columns, rosette formation and macrophage-dependent mitogen and antigen responsiveness. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;67(1):18–24. doi: 10.1159/000232982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lowman M. A., Sachs D. H. Expression of T-cell associated antigens by porcine natural killer cells. Immunology. 1988 Oct;65(2):267–271. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with porcine PBL. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):368–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pospísil M., Kubrycht J., Bezouska K., Táborský O., Novák M., Kocourek J. Lactosamine type asialooligosaccharide recognition in NK cytotoxicity. Immunol Lett. 1986 Mar;12(2-3):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(86)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W. C., Schultz R. D., Spano J. S. Isolation and characterization of porcine natural killer (NK) cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Apr;14(4):345–356. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(87)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Clouse K. A., Biddison W. E., Kung P. C. Phenotypes of human natural killer cell populations detected with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2575–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


