Abstract
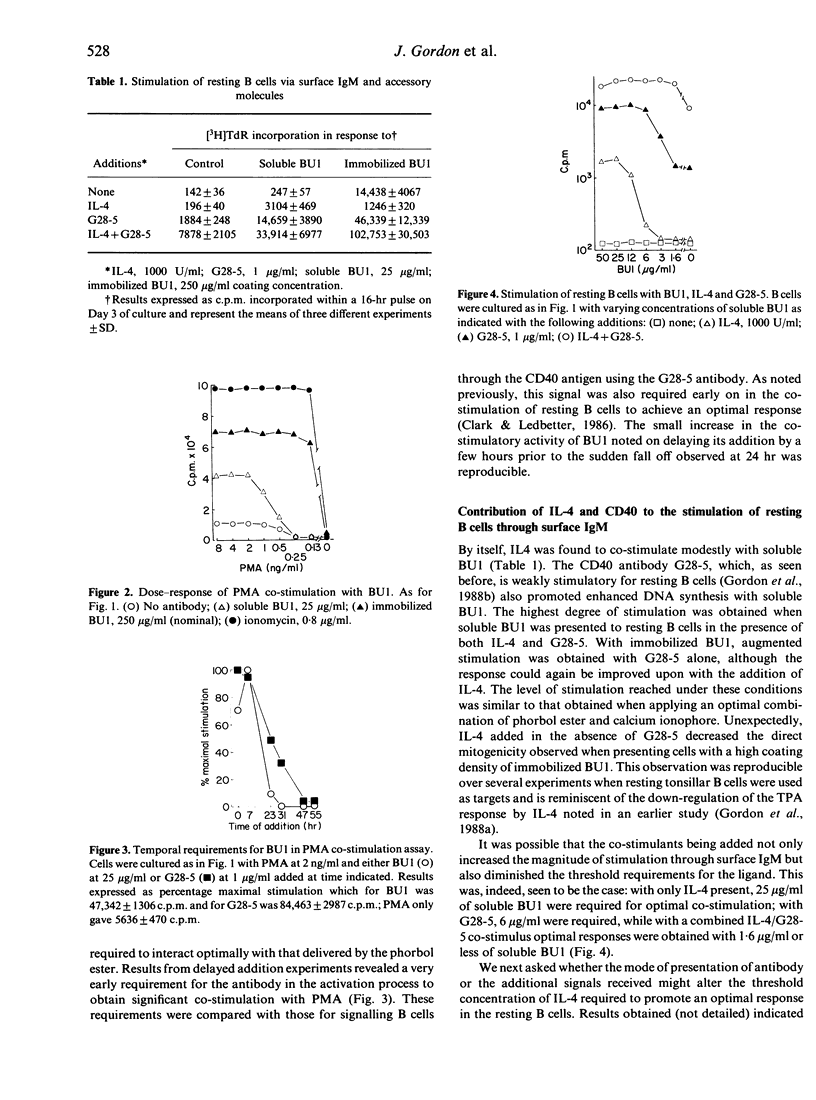
Experiments were designed in order to compare directly the ability of a new and potent monoclonal anti-mu chain antibody to initiate or maintain stimulation in resting and cycling B lymphocytes, respectively. Resting B cells could be stimulated by soluble anti-mu only in the presence of additional signals; these could be supplied by a high dose of phorbol ester or a combination of interleukin-4 (IL-4) and the CD40 antibody, G28-5. Immobilization of anti-mu not only increased the magnitude of the resting B-cell response but also diminished the co-factor requirements. The 'background' stimulation obtained when using a high concentration of immobilized anti-mu was unexpectedly reduced in the presence of IL-4 alone. The duration, but not the magnitude, of the IL-4 signal required for promoting optimal responses varied with the co-stimulation applied. Importantly, the threshold concentrations of soluble anti-mu needed to trigger the resting B cells were reduced upon the addition of each co-stimulant. With actively cycling B cells, both soluble and immobilized anti-mu were now capable of sustaining stimulation which could be prolonged on the addition of IL-4 and/or G28-5. In both resting and cycling populations, a strong correlation was noted between the magnitude of stimulation elicited when IL-4 was present and the release of the soluble CD23 molecule. Moreover, IL-4-promoted, but not other, stimulations could be augmented up to 10-fold by the inclusion of the CD23 antibody MHM6. Both the resting and cycling B-cell populations were found to secrete IgM in direct response to IL-4 and G28-5; this factor-driven production of IgM was differentially modulated by soluble and immobilized anti-mu in the two populations.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas A. K., Klaus G. G. Inhibition of antibody production in plasmacytoma cells by antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Oct;7(10):667–674. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830071003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aston R., Cowden W. B., Ada G. L. Antibody-mediated enhancement of hormone activity. Mol Immunol. 1989 May;26(5):435–446. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonvini E., Ruscetti F. W., Ponzoni M., Hoffman T., Farrar W. L. Interleukin 2 rapidly stimulates synthesis and breakdown of polyphosphoinositides in interleukin 2-dependent, murine T-cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4160–4164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairns J., Flores-Romo L., Millsum M. J., Guy G. R., Gillis S., Ledbetter J. A., Gordon J. Soluble CD23 is released by B lymphocytes cycling in response to interleukin 4 and anti-Bp50 (CDw40). Eur J Immunol. 1988 Mar;18(3):349–353. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow M. K., Jover J. A., Friedman S. M. Direct T helper-B cell interactions induce an early B cell activation antigen. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1760–1772. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Sarfati M., Hofstetter H. Human IgE-binding factors. Immunol Today. 1989 May;10(5):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Romo L., Foster D., Guy G. R., Gordon J. Phorbol ester and calcium ionophore are sufficient to promote cell replication in cultures of quiescent human B lymphocytes. Immunology. 1989 Feb;66(2):228–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Cairns J. A., Millsum M. J., Gillis S., Guy G. R. Interleukin 4 and soluble CD23 as progression factors for human B lymphocytes: analysis of their interactions with agonists of the phosphoinositide "dual pathway" of signalling. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1561–1565. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Flores-Romo L., Cairns J. A., Millsum M. J., Lane P. J., Johnson G. D., MacLennan I. C. CD23: a multi-functional receptor/lymphokine? Immunol Today. 1989 May;10(5):153–157. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Millsum M. J., Guy G. R., Ledbetter J. A. Resting B lymphocytes can be triggered directly through the CDw40 (Bp50) antigen. A comparison with IL-4-mediated signaling. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1425–1430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Rowe M., Walker L., Guy G. Ligation of the CD23,p45 (BLAST-2,EBVCS) antigen triggers the cell-cycle progression of activated B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Sep;16(9):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy G. R., Bunce C. M., Gordon J., Michell R. H., Brown G. A combination of calcium ionophore and 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate (TPA) stimulates the growth of purified resting B cells. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Nov;22(5):591–596. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Lipsky P. E. Inhibitory influence of IL-4 on human B cell responsiveness. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):164–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C., Gray D. Antigen-driven selection of virgin and memory B cells. Immunol Rev. 1986 Jun;91:61–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuguchi J., Beaven M. A., Li J. H., Paul W. E. Phorbol myristate acetate inhibits anti-IgM-mediated signaling in resting B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. C. Stimulation of mouse lymphocytes by insoluble anti-mouse immunoglobulin. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):361–363. doi: 10.1038/258361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Ohara J. B-cell stimulatory factor-1/interleukin 4. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:429–459. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudich S. M., Winchester R., Mongini P. K. Human B cell activation. Evidence for diverse signals provided by various monoclonal anti-IgM antibodies. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1236–1255. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


