Abstract
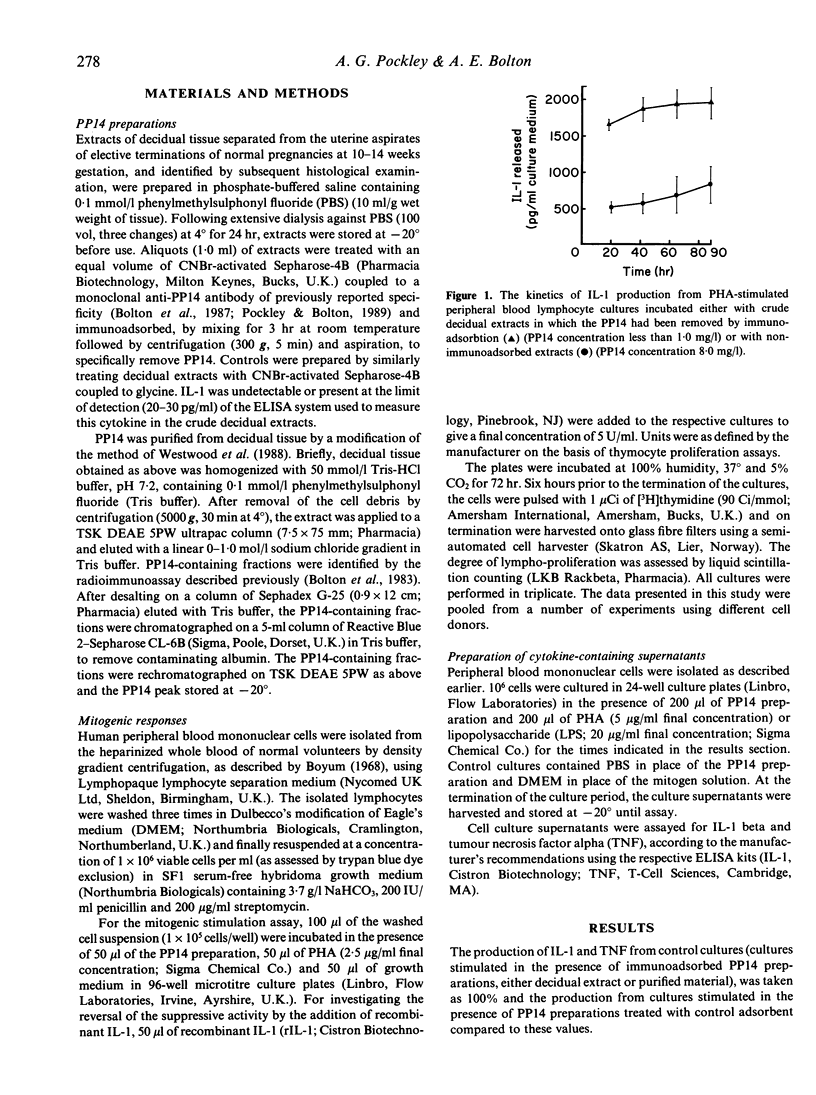
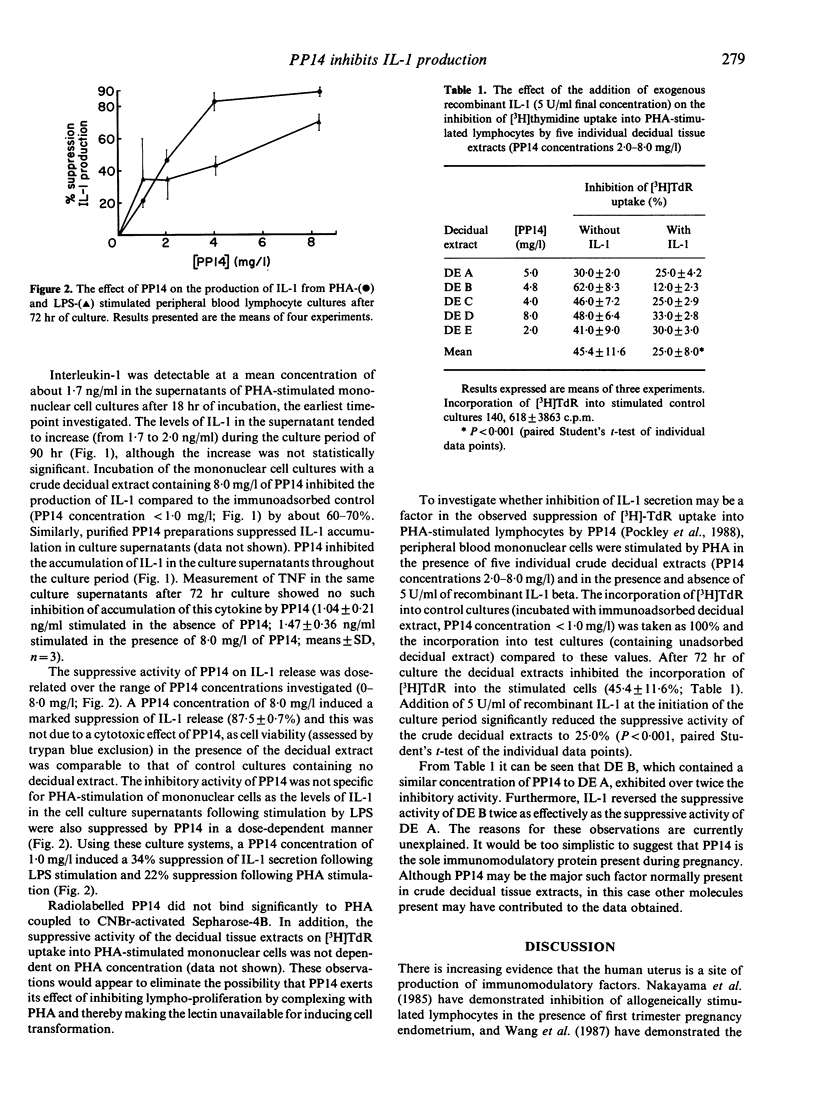
Crude human decidual tissue extracts containing placental protein 14 (PP14) were shown to inhibit the production of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1) from mitogenically stimulated mononuclear cell cultures. The inhibition was dose-dependent over the range of PP14 concentrations investigated (0-8.0 mg/l) and was effective on both phytohaemagglutinin-(PHA) and lipopolysaccharide- (LPS)-induced IL-1 secretion. Using these culture systems, a PP14 concentration of 1.0 mg/l induced a 34% suppression of IL-1 secretion following LPS stimulation and 22% following PHA stimulation. For PHA stimulation the suppression of IL-1 secretion was effective throughout the culture period investigated (0-89 hr). Individual crude decidual extracts inhibited the incorporation of [3H]thymidine into PHA-stimulated lymphocytes, such inhibition being partially reversed by the addition of exogenous recombinant IL-1 to the cultures. These results suggest that the previously reported immunosuppressive activity of PP14 may be mediated by the suppression of IL-1 secretion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohn H., Kraus W., Winckler W. New soluble placental tissue proteins: their isolation, characterization, localization and quantification. Placenta Suppl. 1982;4:67–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Chapman M. G., Stoker R. J., Andrew C. E., Wass D., Bohn H. The radioimmunoassay of human placental protein 14 (PP14). Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Dec 30;135(3):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90287-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Pockley A. G., Clough K. J., Mowles E. A., Stoker R. J., Westwood O. M., Chapman M. G. Identification of placental protein 14 as an immunosuppressive factor in human reproduction. Lancet. 1987 Mar 14;1(8533):593–595. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia Domingo C., Moreno A., Palomino P. The effect of human pregnancy serum on the synthesis and action of interleukin-1. J Reprod Immunol. 1988 Jun;13(1):17–30. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(88)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julkunen M., Rutanen E. M., Koskimies A., Ranta T., Bohn H., Seppälä M. Distribution of placental protein 14 in tissues and body fluids during pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1985 Nov;92(11):1145–1151. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1985.tb03027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Phan S. H. Prostaglandins as endogenous mediators of interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Wiggins R. C., Chensue S. W., Larrick J. Regulation of macrophage tumor necrosis factor production by prostaglandin E2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S., Yoshimura N., Oka T. Characterization and analysis of soluble suppressor factor from early human decidual cells. Transplantation. 1989 Apr;47(4):678–683. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198904000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama E., Asano S., Kodo H., Miwa S. Suppression of mixed lymphocyte reaction by cells of human first trimester pregnancy endometrium. J Reprod Immunol. 1985 Aug;8(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(85)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numerof R. P., Aronson F. R., Mier J. W. IL-2 stimulates the production of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4250–4257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parhar R. S., Yagel S., Lala P. K. PGE2-mediated immunosuppression by first trimester human decidual cells blocks activation of maternal leukocytes in the decidua with potential anti-trophoblast activity. Cell Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;120(1):61–74. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pockley A. G., Bolton A. E. Placental protein 14 (PP14) inhibits the synthesis of interleukin-2 and the release of soluble interleukin-2 receptors from phytohaemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Aug;77(2):252–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pockley A. G., Mowles E. A., Stoker R. J., Westwood O. M., Chapman M. G., Bolton A. E. Suppression of in vitro lymphocyte reactivity to phytohemagglutinin by placental protein 14. J Reprod Immunol. 1988 Jun;13(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(88)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C., Rusk C. M. Low and high affinity cellular receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for the level of Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1126–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. S., Kanzaki H., Yoshida M., Sato S., Tokushige M., Mori T. Suppression of lymphocyte reactivity in vitro by supernatants of explants of human endometrium. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Oct;157(4 Pt 1):956–963. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(87)80095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westwood O. M., Chapman M. G., Totty N., Philp R., Bolton A. E., Lazarus N. R. N-terminal sequence analysis of human placental protein 14, purified in high yield from decidual cytosol. J Reprod Fertil. 1988 Mar;82(2):493–500. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0820493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


