Abstract
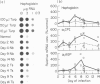
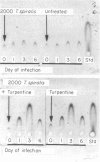
During acute inflammation, the mammalian liver responds with increased production and secretion of a series of plasma glycoproteins, collectively termed the acute-phase proteins, resulting from the release at the site of inflammation of polypeptide cytokines, including IL-1 and IL-6, which interact with receptors on hepatocytes and alter gene expression. This attribute of the systemic acute-phase response was studied throughout the course of infection with two nematode parasites in rats. Significant increases in serum haptoglobin, alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and alpha 1-cysteine protease inhibitor were detected coincident with episodes of skin, lung and intestinal pathology during Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, but were not seen during Trichinella spiralis, infection of the rat despite similar intestinal pathology. These changes were seen at both the protein and mRNA levels in the liver. Infection with T. spiralis was not anti-inflammatory, as macrophages from various sites could be induced in vitro to release inflammatory cytokines, and in vivo induction of inflammation by turpentine injection was similar in control and infected animals. However, macrophage populations recovered from animals infected with T. spiralis were not activated. Moreover, intestinal infection alone with intestinal stages of N. brasiliensis also failed to elicit the systemic acute-phase protein response, requiring an explanation involving skin and lung for the acute-phase response during gut inflammation in a primary infection with N. brasiliensis. Taken together, these data suggest that during the intestinal phase of nematode infection, with pathological changes to the gut, the systemic acute-phase response is not elicited through compromise or lack of stimulation of inflammatory cells in the intestine. The systemic parameters of the acute-phase response may not be a component of gastrointestinal pathology.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ash C., Crompton D. W., Lunn P. G. Impact of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (Nematoda) on the serum albumin and amino acid concentrations of rats fed adequate or protein-deficient diets. Parasitology. 1985 Feb;90(Pt 1):157–168. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000049106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. G., McGregor D. D. Trichinella spiralis: role of different life cycle phases in induction, maintenance, and expression of rapid expulsion in rats. Exp Parasitol. 1979 Aug;48(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(79)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernuau D., Rogier E., Feldmann G. Decreased albumin and increased fibrinogen secretion by single hepatocytes from rats with acute inflammatory reaction. Hepatology. 1983 Jan-Feb;3(1):29–33. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro G. A., Malone C., Smith S. Systemic anti-inflammatory effect associated with enteric trichinellosis in the rat. J Parasitol. 1980 Jun;66(3):407–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. J., Salem S. I., Hafez A. S., Galal O. M., Massoud A. Plasma albumin, parasitic infection and pubertal development in Egyptian boys. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(1):17–20. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egwang T. G., Befus A. D., Gauldie J. Activation of alveolar macrophages following infection with the parasitic nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Immunology. 1985 Mar;54(3):581–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egwang T. G., Gauldie J., Befus D. Broncho-alveolar leucocyte responses during primary and secondary Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection in the rat. Parasite Immunol. 1984 May;6(3):191–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1984.tb00792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner C. H. Habitat and reproductive behavior of Trichinella spiralis. J Parasitol. 1976 Dec;62(6):865–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Lamontagne L., Stadnyk A. Acute phase response in infectious disease. Surv Synth Pathol Res. 1985;4(2):126–151. doi: 10.1159/000156970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glibetic M. D., Baumann H. Influence of chronic inflammation on the level of mRNA for acute-phase reactants in the mouse liver. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1616–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. C. Nippostrongylus brasiliensis: observations on the comparative immunogenicity of adult worms from primary and immune-adapted infections. Parasitology. 1972 Dec;65(3):547–550. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000044152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., Gauldie J., Regoeczi E., Sauder D. N., Sweeney G. D. The acute-phase response of cultured rat hepatocytes. System characterization and the effect of human cytokines. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):505–514. doi: 10.1042/bj2240505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., Gauldie J., Sweeney G. D., Regoeczi E., Sauder D. N. A simple bioassay for monocyte-derived hepatocyte stimulating factor: increased synthesis of alpha 2-macroglobulin and reduced synthesis of albumin by cultured rat hepatocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Feb 11;76(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90309-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., Kurdowska A., Magielska-Zero D., Rokita H., Sipe J. D., Dayer J. M., Demczuk S., Gauldie J. Limited effects of recombinant human and murine interleukin 1 and tumour necrosis factor on production of acute phase proteins by cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem Int. 1987 Mar;14(3):553–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamontagne L. R., Gauldie J., Befus A. D., McAdam K. P., Baltz M. L., Pepys M. B. The acute phase response in parasite infection. Nippostrongylus brasiliensis in the mouse. Immunology. 1984 Aug;52(4):733–741. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamontagne L. R., Stadnyk A. W., Gauldie J. Synthesis of alpha 1-protease inhibitor by resident and activated mouse alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):321–325. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamontagne L., Gauldie J., Stadnyk A., Richards C., Jenkins E. In vivo initiation of unstimulated in vitro interleukin-1 release by alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):326–330. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Best Y. Immunobiology of trichinosis. J Natl Med Assoc. 1983 Jun;75(6):565–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Best Y. Trichinella spiralis: changes in leucocytes during infection. J Natl Med Assoc. 1983 Dec;75(12):1205–1214. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Reed D. L., Roberts R. C., Hebert R. R., Hillman M. C., Kutney R. M. Three high molecular weight protease inhibitors of rat plasma. Isolation, characterization, and acute phase changes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):438–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milanino R., Cassini A., Conforti A., Franco L., Marrella M., Moretti U., Velo G. P. Copper and zinc status during acute inflammation: studies on blood, liver and kidneys metal levels in normal and inflamed rats. Agents Actions. 1986 Nov;19(3-4):215–223. doi: 10.1007/BF01966209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northemann W., Andus T., Gross V., Nagashima M., Schreiber G., Heinrich P. C. Messenger RNA activities of four acute phase proteins during inflammation. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 19;161(2):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGILVIE B. M. ROLE OF ADULT WORMS IN IMMUNITY OF RATS TO NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS. Parasitology. 1965 May;55:325–335. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000068797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovington K. S., Bacarese-Hamilton A. J., Bloom S. R. Nippostrongylus brasiliensis: changes in plasma levels of gastrointestinal hormones in the infected rat. Exp Parasitol. 1985 Dec;60(3):276–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(85)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovington K. S. Dose-dependent relationships between Nippostrongylus brasiliensis populations and rat food intake. Parasitology. 1985 Aug;91(Pt 1):157–167. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000056596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovington K. S. Nippostrongylus brasiliensis: physiological and metabolic responses of rats to primary infection. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Feb;63(1):10–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashid S. A., O'Quigley J., Axon A. T., Cooper E. H. Plasma protein profiles and prognosis in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 1982 Mar;45(3):390–394. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokita H., Magielska-Zero D., Dubin A., Chandler A. M., Koj A. Plasma proteinase inhibitors in Morris hepatoma-bearing rats: changes in the blood level and synthesis in tissue slices. Int J Biochem. 1985;17(11):1267–1270. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(85)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. L., Levy D. A. Nippostrongylus brasiliensis: peripheral leukocyte responses and correlation of basophils with blood histamine concentration during infection in rats. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Dec;50(3):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saverymuttu S. H., Hodgson H. J., Chadwick V. S., Pepys M. B. Differing acute phase responses in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Gut. 1986 Jul;27(7):809–813. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.7.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber G., Aldred A. R., Thomas T., Birch H. E., Dickson P. W., Tu G. F., Heinrich P. C., Northemann W., Howlett G. J., de Jong F. A. Levels of messenger ribonucleic acids for plasma proteins in rat liver during acute experimental inflammation. Inflammation. 1986 Mar;10(1):59–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00916041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Wei H., Manogue K. R., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Kuo G. C., Beutler B., Cotran R. S., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1211–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Remington J. S. Role for activated macrophages in resistance against Trichinella spiralis. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):398–404. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.398-404.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Miller H. R., Huntley J. F., Newlands G. F., Palliser A. C., Wakelin D. Mucosal mast cells are functionally active during spontaneous expulsion of intestinal nematode infections in rat. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):450–452. doi: 10.1038/312450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]