Abstract
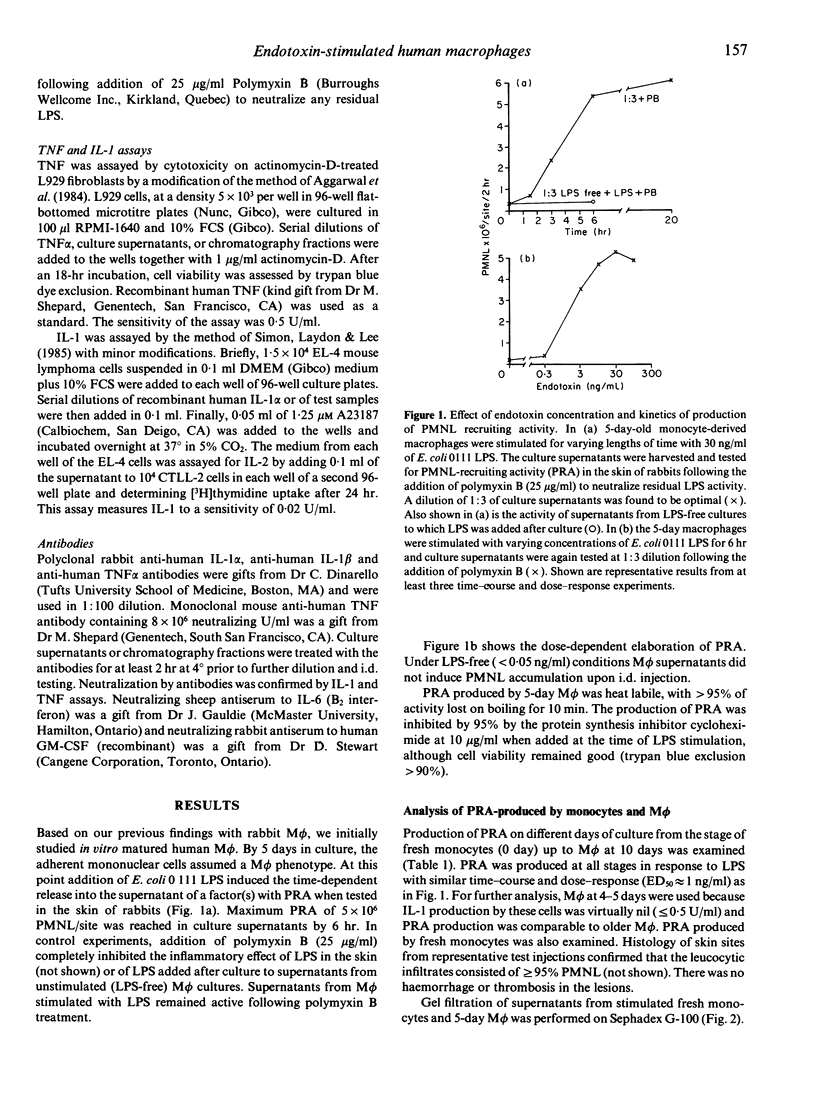
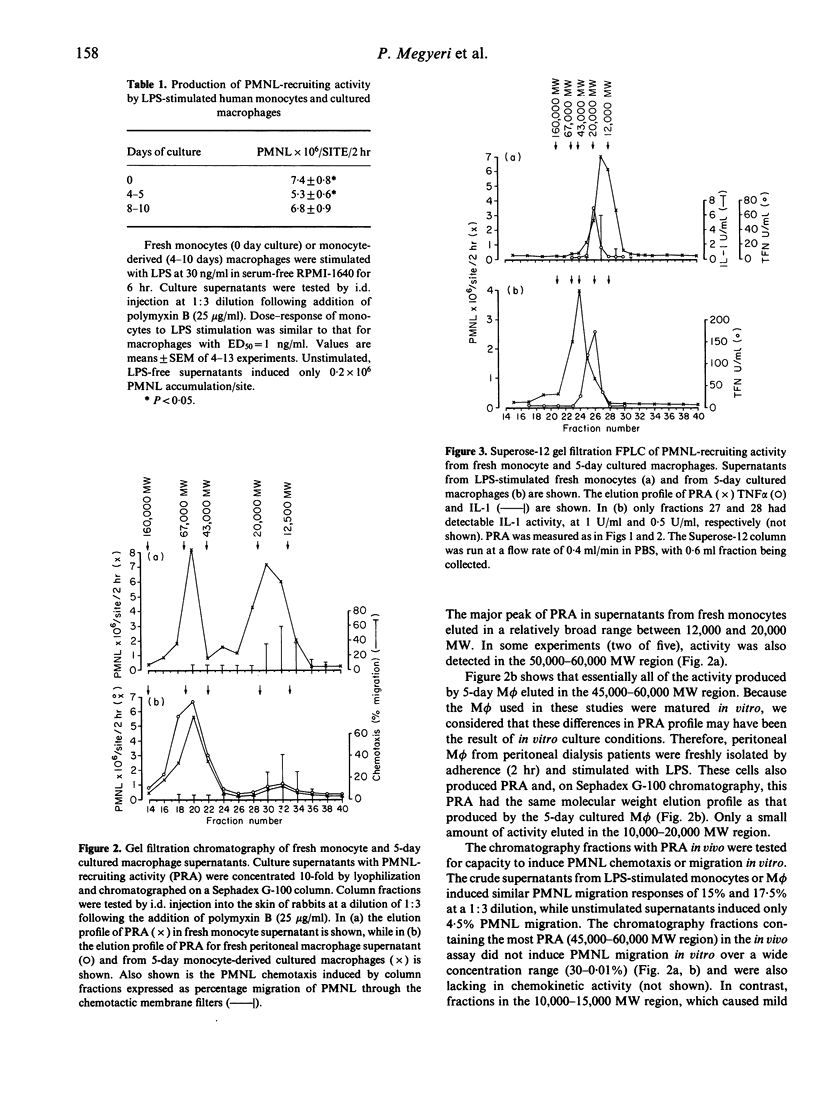
Previously we reported that rabbit macrophages (M phi) in the presence of nanogram quantities of endotoxin (LPS) release factors that induce polymorphonuclear leucocyte (PMNL) infiltration into the skin of rabbits following i.d. injection. The predominant factor was a de novo synthesized protein of 45,000 MW on gel filtration that was distinguishable from IL-1 but not from TNF alpha. Here we examined human monocytes, in vitro monocyte-derived M phi and peritoneal M phi for the production of an analogous protein. Upon stimulation with LPS, they all rapidly (6 hr) produced a factor(s) that caused PMNL accumulation in the skin of rabbits when injected i.d. This activity, referred to as PMNL-recruiting activity (PRA), was heat labile and its production was blocked by cycloheximide. By Sephadex-G100 chromatography the major PRA of cultured M phi or peritoneal M phi had a molecular weight (MW) of 45,000-60,000. The active fractions were free of IL-1 (less than 0.2 U/ml) and Superose-12 FPLC chromatography separated the peak of PRA, which eluted at 45,000 MW, from TNF alpha, eluting at 20,000 MW. The peak PRA was not neutralized by antisera to IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, TNF alpha, IL-6 or GM-CSF, indicating that it was distinct from these cytokines. The major PRA did not induce the migration of PMNL in vitro in a filter chemotaxis assay. In contrast to the M phi, the major PRA produced by LPS-stimulated monocytes eluted at 15,000-20,000 MW, contained IL-1 activity and was neutralized by antisera to IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta. Monocytes from a few donors also produced the 45,000-60,000 MW PRA simultaneously. We conclude that human peritoneal M phi and in vitro monocyte-derived M phi exposed to LPS secrete a protein of 45,000-60,000 MW, which is a potent inducer of PMNL infiltration but is distinct from IL-1, TNF alpha, IL-6, GM-CSF and PMNL chemotactic factors.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker S., Johnson C., Halme J., Haskill S. Interleukin-1 production and antigen presentation by normal human peritoneal macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;98(2):467–476. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S. American Association of Pathologists president's address. New roles for the endothelium in inflammation and immunity. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):407–413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Harnish D., Lansdorp P., Baumann H. Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7251–7255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granstein R. D., Margolis R., Mizel S. B., Sauder D. N. In vivo inflammatory activity of epidermal cell-derived thymocyte activating factor and recombinant interleukin 1 in the mouse. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):1020–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI112354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Fales H. M., Crystal R. G. Human alveolar macrophage-derived chemotactic factor for neutrophils. Stimuli and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):473–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI109878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Bhimji S., Bortolussi R. Effect of immune serum or polymyxin B on Escherichia coli-induced inflammation and vascular injury. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):548–557. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.548-557.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Bhimji S. Role for endotoxin in the leukocyte infiltration accompanying Escherichia coli inflammation. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):558–566. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.558-566.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Megyeri P., Issekutz T. B. Role for macrophage products in endotoxin-induced polymorphonuclear leukocyte accumulation during inflammation. Lab Invest. 1987 Jan;56(1):49–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Movat H. Z. The in vivo quantitation and kinetics of rabbit neutrophil leukocyte accumulation in the skin in response to chemotactic agents and Escherichia coli. Lab Invest. 1980 Mar;42(3):310–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopaniak M. M., Issekutz A. C., Movat H. Z. Kinetics of acute inflammation induced by E coli in rabbits. Quantitation of blood flow, enhanced vascular permeability, hemorrhage, and leukocyte accumulation. Am J Pathol. 1980 Feb;98(2):485–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming W. J., Bersani L., Mantovani A. Tumor necrosis factor is chemotactic for monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1469–1474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Cybulsky M. I. Neutrophil emigration and microvascular injury. Role of chemotaxins, endotoxin, interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Pathol Immunopathol Res. 1987;6(3):153–176. doi: 10.1159/000157043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mrowietz U., Schröder J. M., Christophers E. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor alpha lacks chemotactic activity for human peripheral blood neutrophils and monocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1223–1228. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northoff H., Andus T., Tran-Thi T. A., Bauer J., Decker K., Kubanek B., Heinrich P. C. The inflammation mediators interleukin 1 and hepatocyte-stimulating factor are differently regulated in human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 May;17(5):707–711. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peveri P., Walz A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1547–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers T. J., Wiltrout T. A., Bull C. A., Denn A. C., 3rd, Pilaro A. M., Lokesh B. Effect of cytokines on polymorphonuclear neutrophil infiltration in the mouse. Prostaglandin- and leukotriene-independent induction of infiltration by IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1670–1677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Mrowietz U., Morita E., Christophers E. Purification and partial biochemical characterization of a human monocyte-derived, neutrophil-activating peptide that lacks interleukin 1 activity. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3474–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon P. L., Laydon J. T., Lee J. C. A modified assay for interleukin-1 (IL-1). J Immunol Methods. 1985 Nov 28;84(1-2):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90417-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valone F. H., Franklin M., Sun F. F., Goetzl E. J. Alveolar macrophage lipoxygenase products of arachidonic acid: isolation and recognition as the predominant constituents of the neutrophil chemotactic activity elaborated by alveolar macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 1;54(2):390–401. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wankowicz Z., Megyeri P., Issekutz A. Synergy between tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 in the induction of polymorphonuclear leukocyte migration during inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Apr;43(4):349–356. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpe S. D., Davatelis G., Sherry B., Beutler B., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Moldawer L. L., Nathan C. F., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Macrophages secrete a novel heparin-binding protein with inflammatory and neutrophil chemokinetic properties. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):570–581. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J., Leonard E. J. Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human blood mononuclear leukocytes: partial characterization and separation from interleukin 1 (IL 1). J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


