Abstract
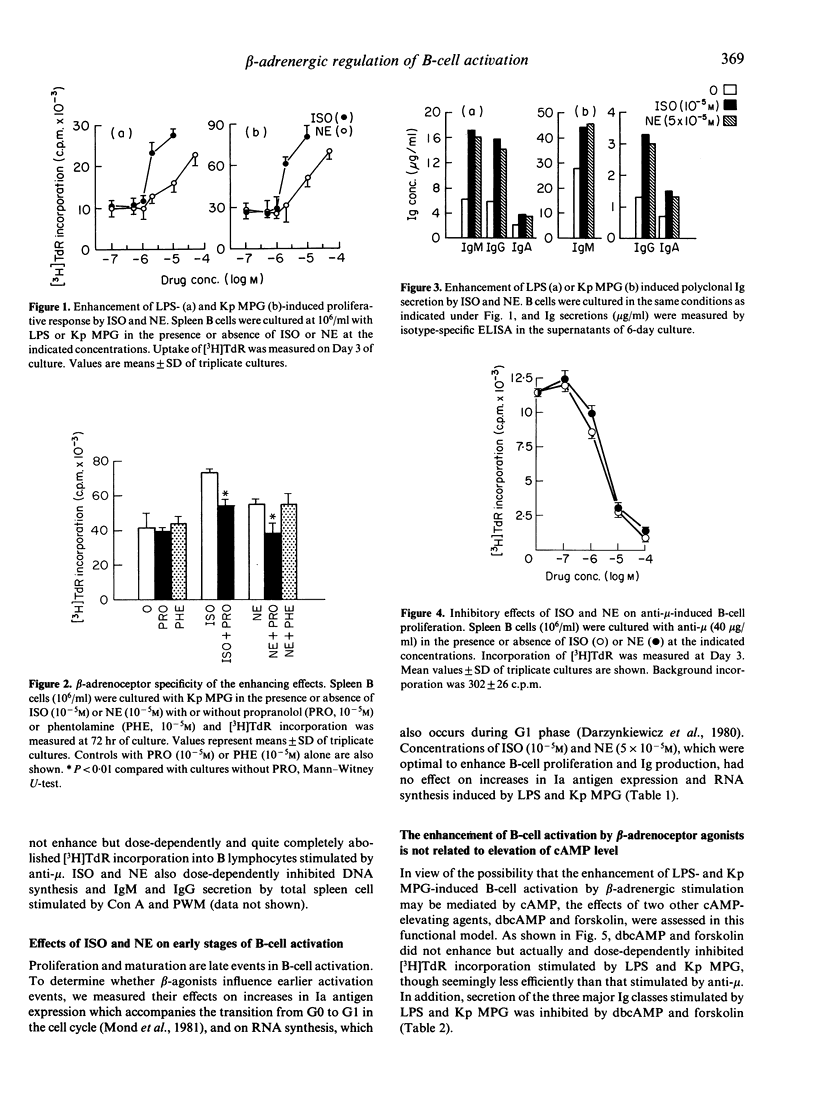
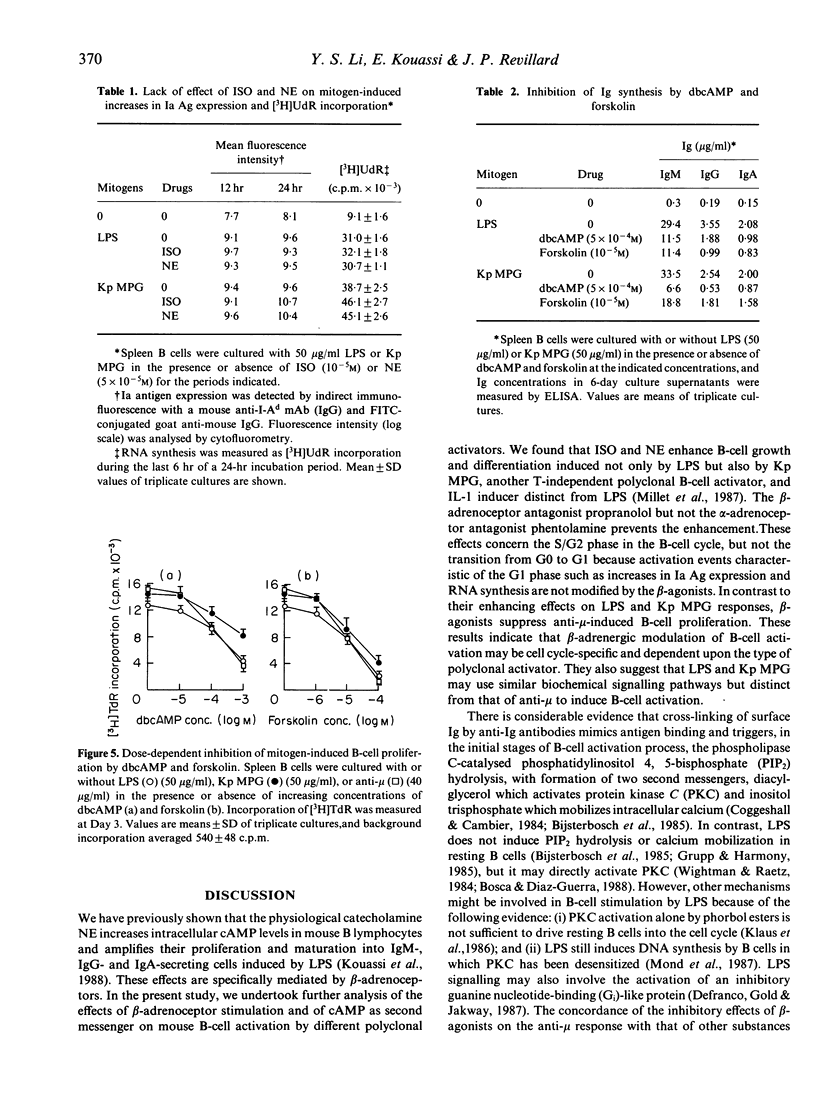
We investigated the effects of the beta-adrenoceptor agonist isoproterenol (ISO) and the alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor agonist norepinephrine (NE) on murine B-cell activation. Cells were stimulated either by anti-mouse mu-chain antibodies (anti-mu), or by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), or a membrane proteoglycan of Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kp MPG), a T-independent polyclonal activator distinct from LPS, which induces B-cell proliferation and Ig synthesis. ISO and NE enhanced LPS- and Kp MPG-induced B-cell proliferation and maturation into IgM-, IgG- and IgA-secreting cells. The enhancement was prevented by prior addition of the beta-adrenoceptor antagonist propranolol but not by the alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist phentolamine. Earlier events in the LPS- and Kp MPG-stimulated B-cell activation, such as increases in Ia antigen expression and RNA synthesis, were not modified by the catecholamines. Unlike ISO and NE, the membrane-permeant cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP) analogue dibutyryl cAMP (dbcAMP), and the potent adenylate cyclase activator forskolin did not enhance but even inhibited DNA synthesis and Ig secretion stimulated by LPS and Kp MPG. In addition, ISO and NE did not enhance but strongly inhibited anti-mu-induced B-cell proliferation, and these effects were mimicked by dbcAMP and forskolin. Collectively, the data demonstrate that beta-agonists differently modulate B-cell activation depending upon the polyclonal activator, and provide additional evidence for distinct biochemical mechanisms of B-cell activation by anti-mu and LPS. Moreover, our results indicate that beta-adrenergic stimulation up-regulates B-cell responses to LPS and Kp MPG by a novel and cAMP-independent pathway.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akahoshi T., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. Induction of high-affinity interleukin 1 receptor on human peripheral blood lymphocytes by glucocorticoid hormones. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):924–936. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Meade C. J., Turner G. A., Klaus G. G. B lymphocyte receptors and polyphosphoinositide degradation. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boscá L., Díaz-Guerra M. J. Activation of protein kinase C from B lymphocytes by lipid A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):149–154. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80692-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. G., Hadden J. W. Neurotransmitters, hormones, and cyclic nucleotides in lymphocyte regulation. Fed Proc. 1985 Jan;44(1 Pt 1):112–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggeshall K. M., Cambier J. C. B cell activation. VIII. Membrane immunoglobulins transduce signals via activation of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3382–3386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., De Blasi A. Glucocorticoids increase beta-adrenoceptors on human intact lymphocytes in vitro. Life Sci. 1984 Dec 3;35(23):2359–2364. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90528-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz Z., Sharpless T., Staiano-Coico L., Melamed M. R. Subcompartments of the G1 phase of cell cycle detected by flow cytometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6696–6699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Gold M. R., Jakway J. P. B-lymphocyte signal transduction in response to anti-immunoglobulin and bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Immunol Rev. 1987 Feb;95:161–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Quan Z. S., Wall K. A., Pierres A., Quintáns J., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Fitch F. W. Characterization of the murine T cell surface molecule, designated L3T4, identified by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: similarity of L3T4 to the human Leu-3/T4 molecule. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2445–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. D., Hunninghake G. W., McArdle W. L. Beta-adrenergic-receptor-mediated suppression of interleukin 2 receptors in human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3355–3359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felten D. L., Felten S. Y., Bellinger D. L., Carlson S. L., Ackerman K. D., Madden K. S., Olschowki J. A., Livnat S. Noradrenergic sympathetic neural interactions with the immune system: structure and function. Immunol Rev. 1987 Dec;100:225–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman E. M., Vayuvegula B., Gupta S., van den Noort S. Norepinephrine inhibits gamma-interferon-induced major histocompatibility class II (Ia) antigen expression on cultured astrocytes via beta-2-adrenergic signal transduction mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1292–1296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupp S. A., Harmony J. A. Increased phosphatidylinositol metabolism is an important but not an obligatory early event in B lymphocyte activation. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4087–4094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden J. W., Hadden E. M., Middleton E., Jr Lymphocyte blast transformation. I. Demonstration of adrenergic receptors in human peripheral lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1970 Dec;1(6):583–595. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., O'Garra A., Bijsterbosch M. K., Holman M. Activation and proliferation signals in mouse B cells. VIII. Induction of DNA synthesis in B cells by a combination of calcium ionophores and phorbol myristate acetate. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jan;16(1):92–97. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., Vondy K., Holman M. Selective effects of cholera toxin on the activation of mouse B cells by different polyclonal activators. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1787–1792. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff W. C., Fann A. V., Dunegan M. A., Lachman L. B. Catecholamine-induced suppression of interleukin-1 production. Lymphokine Res. 1986 Fall;5(4):239–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouassi E., Li Y. S., Boukhris W., Millet I., Revillard J. P. Opposite effects of the catecholamines dopamine and norepinephrine on murine polyclonal B-cell activation. Immunopharmacology. 1988 Nov-Dec;16(3):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(88)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A., Jacobson B., Miller R. A. Cyclic AMP concentrations modulate both calcium flux and hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol phosphates in mouse T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 1;140(3):936–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millet I., Lafont S., de Fraissinette A., Jeannin M., Revillard J. P., Normier G., Dussourd d'Hinterland L. Polyclonal activation of murine B cells by a membrane proteoglycan of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Oct;70(1):201–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Feuerstein N., Finkelman F. D., Huang F., Huang K. P., Dennis G. B-lymphocyte activation mediated by anti-immunoglobulin antibody in the absence of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8588–8592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Seghal E., Kung J., Finkelman F. D. Increased expression of I-region-associated antigen (Ia) on B cells after cross-linking of surface immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):881–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H., Gottlieb P. D., Bevan M. J. Fractionation of lymphocyte populations with monoclonal antibodies specific for LYT-2.2 and LYT-3.1. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1136–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders V. M., Munson A. E. Beta adrenoceptor mediation of the enhancing effect of norepinephrine on the murine primary antibody response in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jul;230(1):183–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wightman P. D., Raetz C. R. The activation of protein kinase C by biologically active lipid moieties of lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10048–10052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


