Abstract
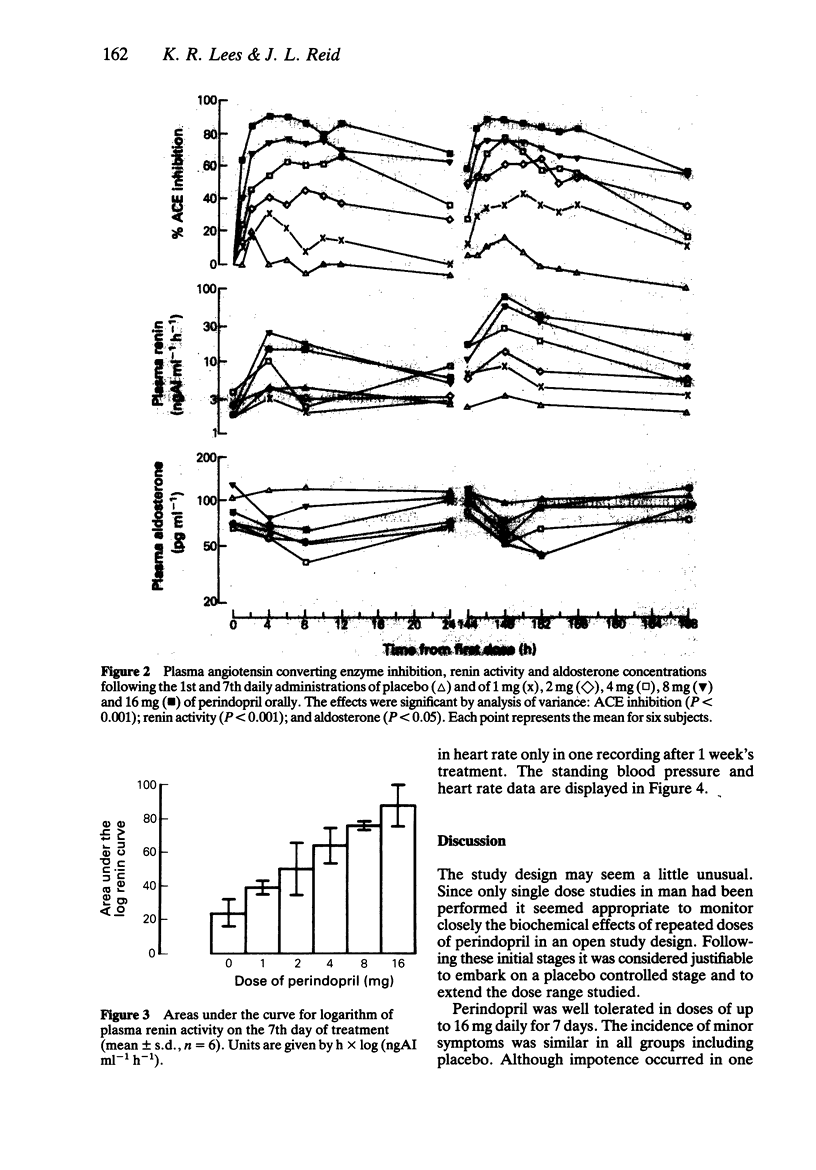
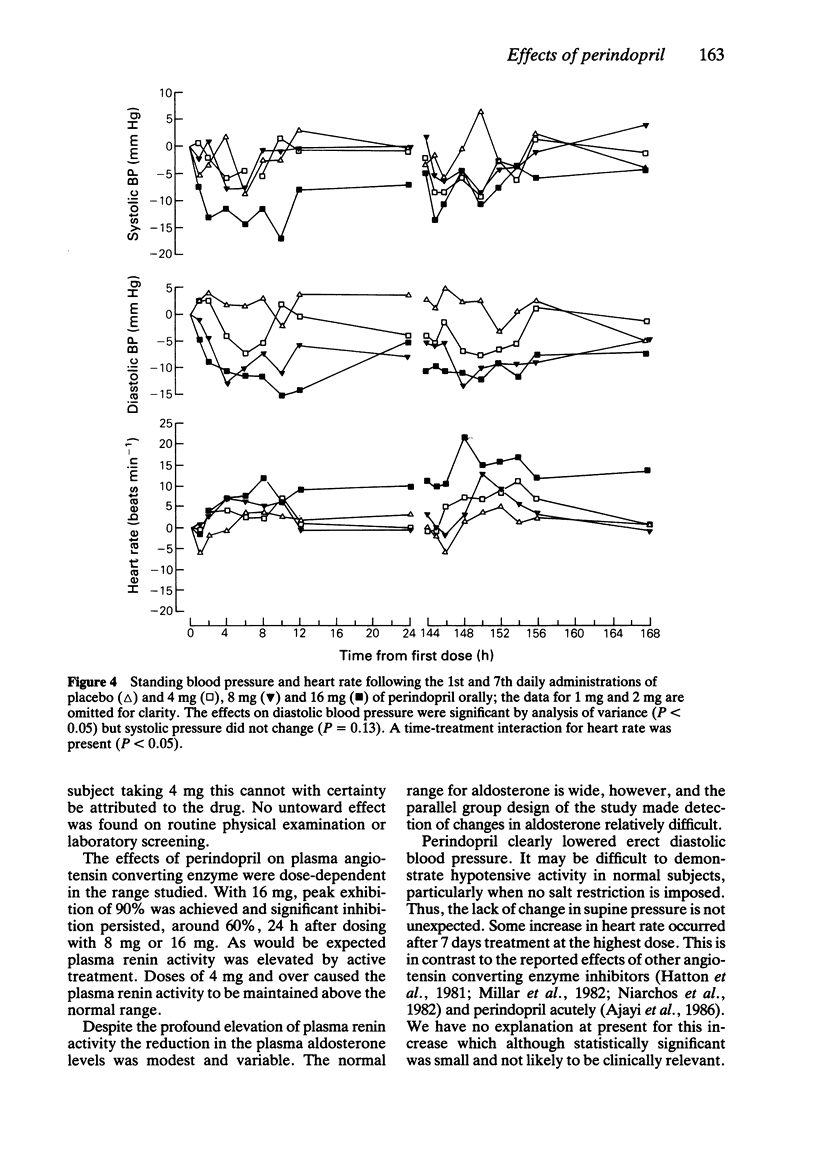
The tolerance to and dynamic effects of 1 week's oral treatment with the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, perindopril, were assessed in a placebo controlled, parallel group study in 36 normotensive males. The daily dose of perindopril was 1, 2, 4, 8 or 16 mg. The drug was well tolerated and produced no change in routine haematology or serum biochemistry tests. Dose related inhibition of plasma angiotensin converting enzyme was observed. Perindopril 16 mg produced 90% inhibition 4 h after dosing and 60% after 24 h. A dose related rise in plasma renin activity followed doses of 4 mg and over. The renin remained above the normal range for 24 h. Perindopril caused a modest lowering of plasma aldosterone levels but had no effect on plasma adrenaline or noradrenaline levels. Standing diastolic blood pressure was lowered, particularly with 16 mg daily of perindopril but only a slight rise in heart rate occurred. Perindopril appears to be a well tolerated inhibitor of plasma angiotensin converting enzyme, with predictable effects on the renin angiotensin system and blood pressure. An appropriate dose range for further study would appear to be 4 to 16 mg daily.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajayi A. A., Lees K. R., Reid J. L. Effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, perindopril, on autonomic reflexes. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;30(2):177–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00614298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiknas S. G. A liquid chromatography-assisted assay for angiotensin-converting enzyme (peptidyl dipeptidase) in serum. Clin Chem. 1979 Jul;25(7):1259–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman D. W., Cheung H. S. Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Jul;20(7):1637–1648. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Prada M., Zürcher Simultaneous radioenzymatic determination of plasma and tissue adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine within the femtomole range. Life Sci. 1976 Oct 15;19(8):1161–1174. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90251-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton R., Clough D., Faulkner K., Conway J. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor resets baroreceptor reflexes in conscious dogs. Hypertension. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):676–681. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.6.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laubie M., Schiavi P., Vincent M., Schmitt H. Inhibition of angiotensin I-converting enzyme with S 9490: biochemical effects, interspecies differences, and role of sodium diet in hemodynamic effects. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984 Nov-Dec;6(6):1076–1082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. K., Clements J. A. Simplified radioimmunoassay for serum aldosterone utilizing increased antibody specificity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Apr;38(4):622–627. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-4-622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. A., Derkx F. H., McLean K., Reid J. L. Pharmacodynamics of converting enzyme inhibition: the cardiovascular, endocrine and autonomic effects of MK421 (enalapril) and MK521. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;14(3):347–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01990.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niarchos A. P., Pickering T. G., Morganti A., Laragh J. H. Plasma catecholamines and cardiovascular responses during converting enzyme inhibition in normotensive and hypertensive man. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1982;4(4-5):761–789. doi: 10.3109/10641968209061612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richer C., Giroux B., Plouin P. F., Maarek B., Giudicelli J. F. Captopril: pharmacokinetics, antihypertensive and biological effects in hypertensive patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;17(3):243–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


