Abstract
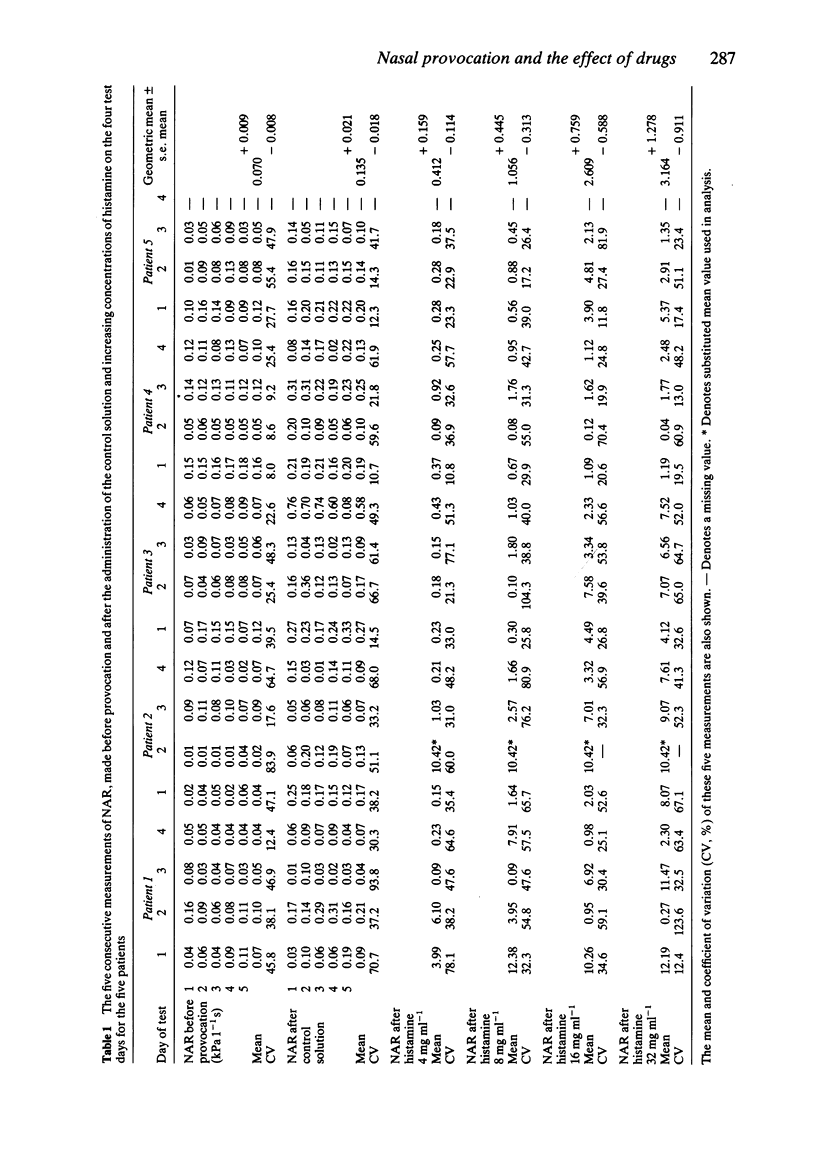
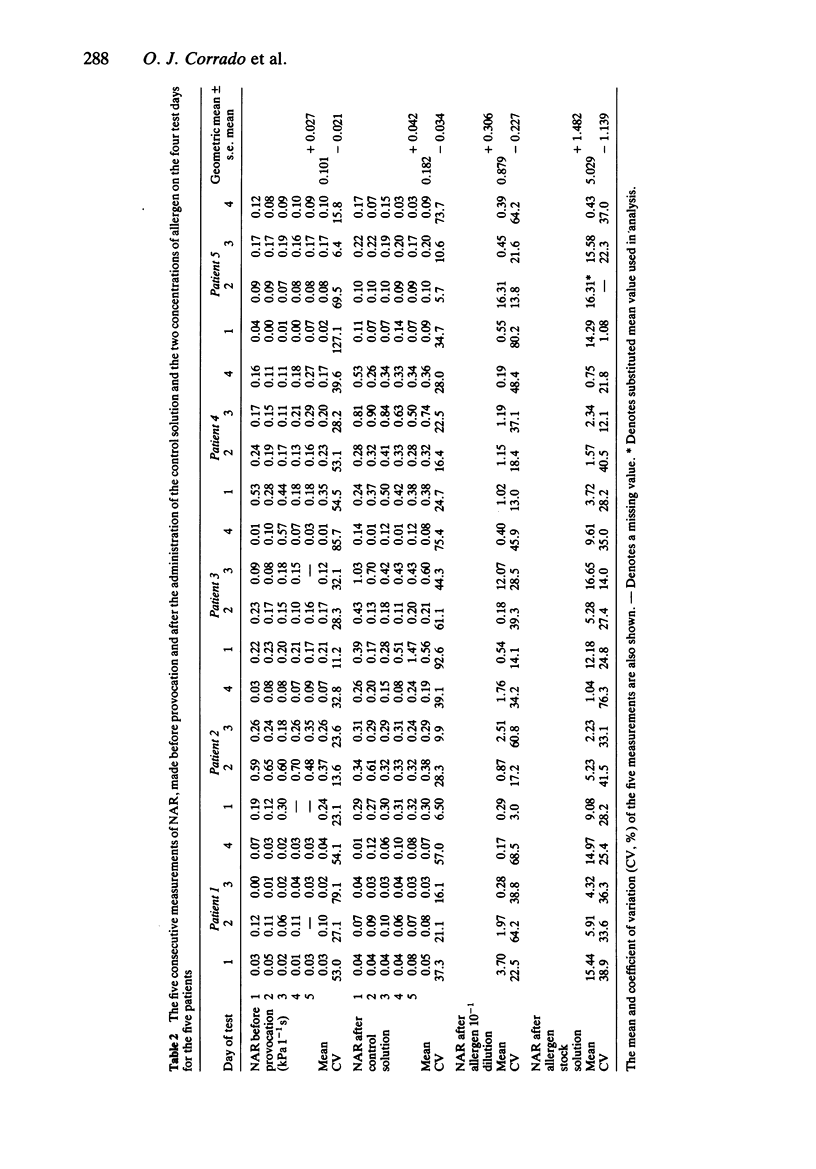
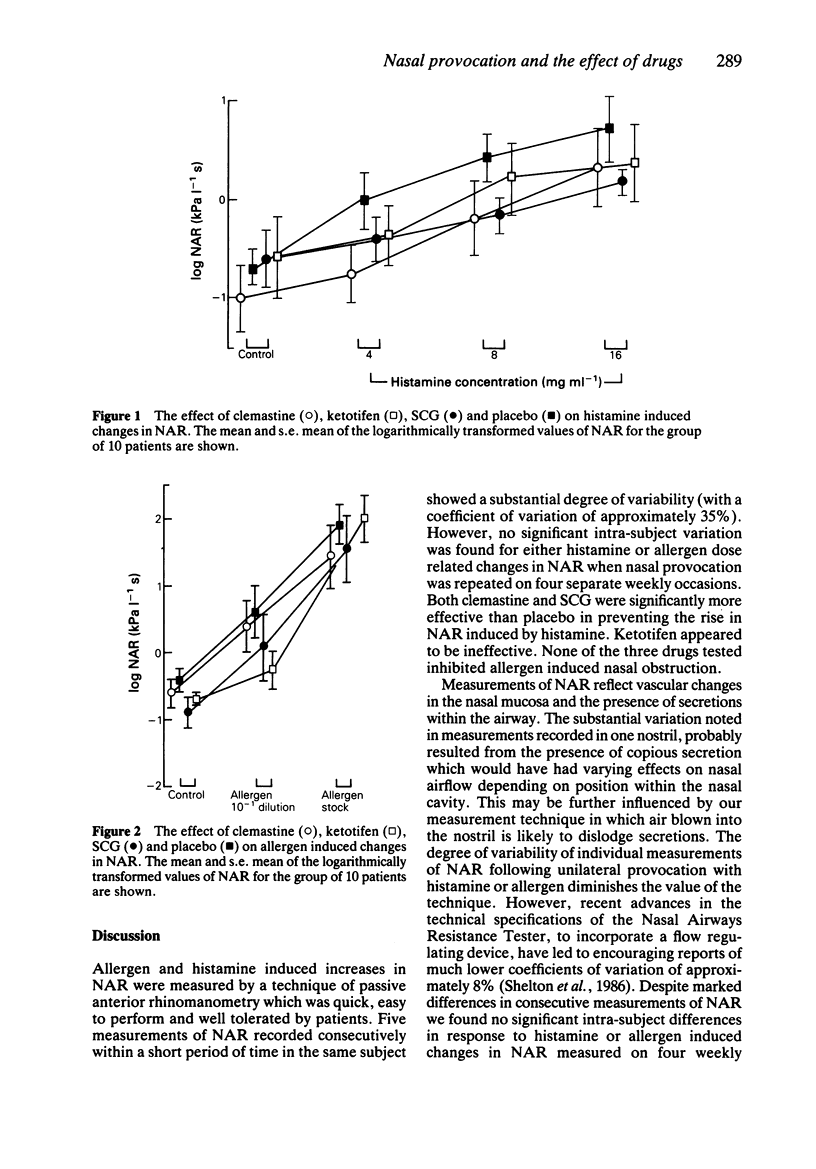
1. Changes in nasal airways resistance (NAR) following the topical application of histamine and allergen solutions were measured by passive anterior rhinomanometry. 2. The repeatability of five consecutive measurements of resting NAR prior to provocation with histamine or allergen (expressed as the coefficient of variation) was 32.8% and following instillation of saline control solution 37.2%. 3. The repeatability of five consecutive measurements of NAR during the nasal obstruction produced by histamine and allergen was similar to that recorded prior to provocation; the coefficients of variation (median values) being 39.6% and 33.1% respectively. The degree of variability was not related to the dose of agonist or the degree of nasal obstruction. 4. The reproducibility of histamine or allergen induced changes in NAR on four separate weekly occasions showed no significant intra-subject differences. 5. The effects of sodium cromoglycate (SCG), clemastine and ketotifen administered to the nasal mucosa 30 min before provocation with histamine and allergen were compared in a random order, double-blind, placebo controlled study. 6. Clemastine and SCG, but not ketotifen, significantly inhibited the nasal response to increasing concentrations of histamine. None of the drugs administered in the concentrations used in this study significantly inhibited the nasal response to allergen.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blair H., Herbert R. L. Treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis with 2 percent sodium cromoglycate (BP) solution. Clin Allergy. 1973 Sep;3(3):283–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1973.tb01335.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton M. G., Empey D. W., John G. C., McDonnell K. A., Hughes D. T. Histamine challenge and anterior nasal rhinometry: their use in the assessment of pseudoephedrine and triprolidine as nasal decongestants in subjects with hayfever. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Jul;6(1):51–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement P. A. Committee report on standardization of rhinomanometry. Rhinology. 1984 Sep;22(3):151–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Killian D. N., Mellon J. J., Hargreave F. E. Protective effect of drugs on histamine-induced asthma. Thorax. 1977 Aug;32(4):429–437. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell J. T. A novel method to assess antihistamine and decongestant efficacy. Ann Allergy. 1979 May;42(5):278–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. S. Disodium cromoglycate. Mode of action and its possible relevance to the clinical use of the drug. Br J Dis Chest. 1971 Oct;65(4):189–204. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(71)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graamans K. Rhinometry. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1981 Aug;6(4):291–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1981.tb01550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes R. L., Ingram R. H., Jr, McFadden E. R., Jr An assessment of the pulmonary response to exercise in asthma and an analysis of the factors influencing it. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Oct;114(4):739–752. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.4.739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howarth P. H., Holgate S. T. Comparative trial of two non-sedative H1 antihistamines, terfenadine and astemizole, for hay fever. Thorax. 1984 Sep;39(9):668–672. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.9.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illum P., Meistrup-Larsen U., Moesner J., Olesen K., Olsen S. Z. Disodium cromoglycate (Lomudal) in the treatment of hay fever. Acta Allergol. 1973 Dec;28(5):416–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1973.tb01455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue S., Nishima M. [Effect of Intal (disodium cromoglycate) on bronchial asthma in children]. Arerugi. 1969 Aug;18(8):692–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. M., Richards I. M. The effects of sodium cromoglycate on histamine aerosol-induced reflex bronchoconstriction in the anaesthetized dog. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;61(2):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb08413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenssen A. O. Measurement of resistance to air flow in the nose in a trial with sodium cromoglycate (BP)solution in allergen-induced nasal stenosis. Clin Allergy. 1973 Sep;3(3):277–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1973.tb01334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juniper E. F., Frith P. A., Dunnett C., Cockcroft D. W., Hargreave F. E. Reproducibility and comparison of responses to inhaled histamine and methacholine. Thorax. 1978 Dec;33(6):705–710. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.6.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang B., Townley R. G., Lee C. K., Miller Kolotkin B. Bronchial reactivity to histamine before and after sodium cromoglycate in bronchial asthma. Br Med J. 1976 Apr 10;1(6014):867–870. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6014.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern E. B. Committee report on standardization of rhinomanometry. Rhinology. 1981 Dec;19(4):231–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. W., Govindaraj M., Patel K. R. Effect of alpha-receptor blocking drugs and disodium cromoglyate on histamine hypersensitivity in bronchial asthma. Br Med J. 1970 Apr 18;2(5702):139–141. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5702.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard J., Secher C., Borum P., Mygind N. Inhibition of histamine-induced nasal symptoms by the H1 antihistamine chlorpheniramine maleate: demonstration of topical effect. Br J Dis Chest. 1983 Apr;77(2):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(83)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemire I., Cartier A., Malo J. L., Pineau L., Ghezzo H., Martin R. R. Effect of sodium cromoglycate on histamine inhalation tests. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Feb;73(2):234–239. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(84)80013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin U., Römer D. The pharmacological properties of a new, orally active antianaphylactic compound: ketotifen, a benzocycloheptathiophene. Arzneimittelforschung. 1978;28(5):770–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogrady S. G., Bevan C. Inhaled antihistamines--bronchodilatation and effects on histamine- and methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction. Thorax. 1978 Dec;33(6):700–704. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.6.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda M., Ohtsuka H., Sakaguchi K., Watase T. Nasal histamine sensitivity in allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy. 1983 Jul;51(1 Pt 1):51–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F. Immunochemical and biologic properties of rat IgE. II. Capacity to mediate the immunologic releas of histamine an slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A). J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1087–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER C. D., BILBO R. E., REED C. E. METHACHOLINE AEROSOL AS TEST FOR BRONCHIAL ASTHMA. Arch Intern Med. 1965 Apr;115:452–458. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1965.03860160078013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegelow K. O. Bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine in asthmatic patients, before and after administration of atropine, phentolamine or disodium cromoglycate. Acta Allergol. 1974 Oct;29(5):365–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1974.tb01472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelikan Z., Snoek W. J., Booij-Noord H., Orie N. G., de Vries K. Protective effect of disodium cromoglycate on the allergen provocation of the nasal mucosa. Ann Allergy. 1970 Nov;28(11):548–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. J., Meyrick Thomas R. H., Moodley I., Davies R. J. A comparison of the in vivo effects of ketotifen, clemastine, chlorpheniramine and sodium cromoglycate on histamine and allergen induced weals in human skin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;15(3):277–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01500.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. J., Ollier S., Gould C., Davies R. J. Effect of antihistamines and antiallergic drugs on responses to allergen and histamine provocation tests in asthma. Thorax. 1984 May;39(5):345–351. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.5.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secher C., Kirkegaard J., Borum P., Maansson A., Osterhammel P., Mygind N. Significance of H1 and H2 receptors in the human nose: rationale for topical use of combined antihistamine preparations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Sep;70(3):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. J., Fitzharris P., Cromwell O., Wardlaw A. J., Kay A. B. Allergen-induced release of sulphidopeptide leukotrienes (SRS-A) and LTB4 in allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 1985 Jan;40(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1985.tb04147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes T. C., Morley J. Prospects for an oral Intal. Br J Dis Chest. 1981 Jan;75(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(81)80002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Shivalkar P. R. Disodium cromoglycate: laboratory studies and clinical trial in allergic rhinitis. Clin Allergy. 1971 Jun;1(2):189–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1971.tb03018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd G., Hopkins P., Maclay W. P. Double-blind trials of clemastine ('Tavegil') in allergic rhinitis. Curr Med Res Opin. 1975;3(3):126–131. doi: 10.1185/03007997509113659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wihl J. A. Methods for assessing nasal reactivity. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1983;128(Pt 1):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woenne R., Kattan M., Levison H. Sodium cromoglycate-induced changes in the dose-response curve of inhaled methacholine and histamine in asthmatic children. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jun;119(6):927–932. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.6.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong L., Hendeles L., Weinberger M. Pharmacologic prophylaxis of allergic rhinitis: relative efficacy of hydroxyzine and chlorpheniramine. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1981 Mar;67(3):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(81)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


