Abstract
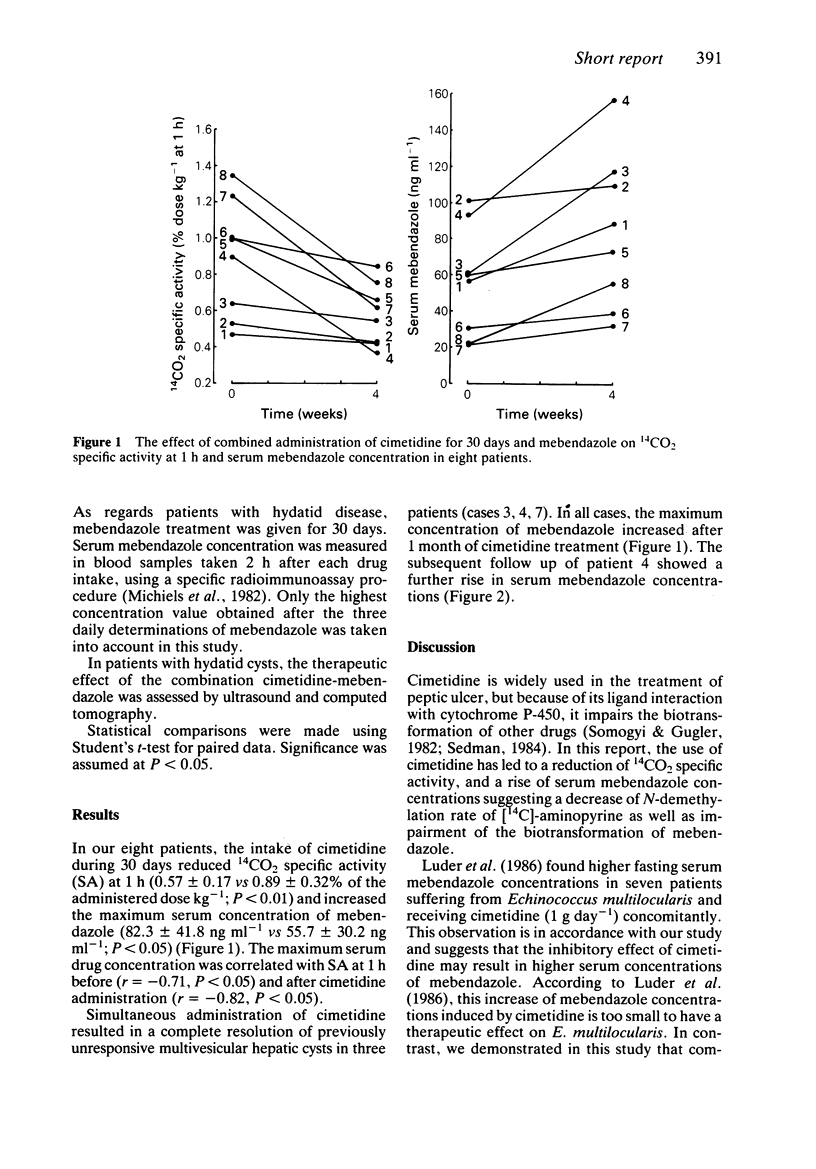
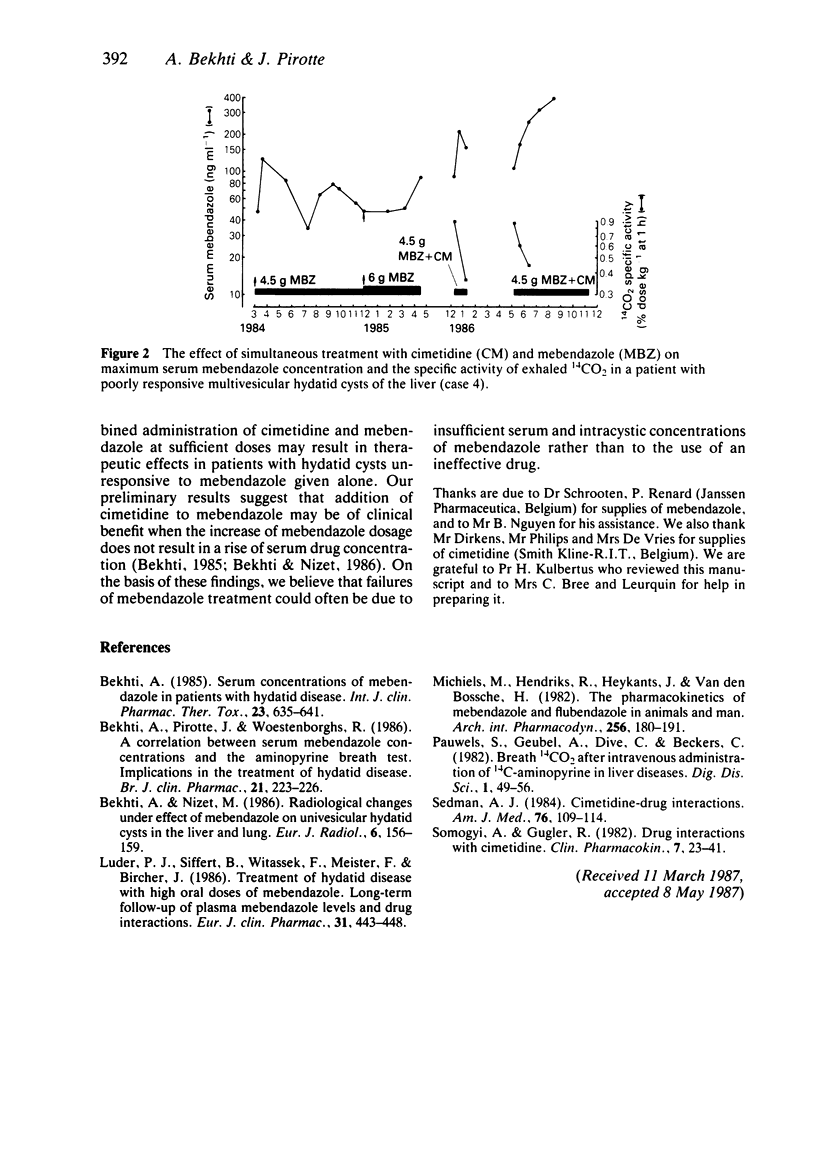
In eight patients (five with peptic ulcer disease and three with hydatid cysts), the [14C]-aminopyrine breath test (ABT) and maximum serum concentration of mebendazole following a dose of 1.5 g of mebendazole three times daily were determined before and after treatment with cimetidine (400 mg three times daily for 30 days). Serum mebendazole concentrations were measured in blood samples taken 2 h after each drug intake. Cimetidine lowered the 14CO2 specific activity (SA) at 1 h (P less than 0.01) and increased the maximum serum concentration of mebendazole (P less than 0.01). A significant correlation was found between SA at 1 h and the highest concentration of mebendazole before (r = -0.71, P less than 0.05) and after (r = -0.82, P less than 0.05) cimetidine ingestion. Combined administration of cimetidine and mebendazole resulted in the complete resolution of previously unresponsive hydatid cysts.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bekhti A., Nizet M. Radiological changes under effect of mebendazole on univesicular hydatid cysts in the liver and lung. Eur J Radiol. 1986 May;6(2):156–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekhti A., Pirotte J., Woestenborghs R. A correlation between serum mebendazole concentrations and the aminopyrine breath test. Implications in the treatment of hydatid disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;21(2):223–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb05179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekhti A. Serum concentrations of mebendazole in patients with hydatid disease. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol. 1985 Dec;23(12):633–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luder P. J., Siffert B., Witassek F., Meister F., Bircher J. Treatment of hydatid disease with high oral doses of mebendazole. Long-term follow-up of plasma mebendazole levels and drug interactions. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;31(4):443–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00613522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels M., Hendriks R., Heykants J., van den Bossche H. The pharmacokinetics of mebendazole and flubendazole in animals and man. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1982 Apr;256(2):180–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels S., Geubel A. P., Dive C., Beckers C. Breath 14CO2 after intravenous administration of [14C]aminopyrine in liver diseases. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Jan;27(1):49–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01308121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedman A. J. Cimetidine-drug interactions. Am J Med. 1984 Jan;76(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90758-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi A., Gugler R. Drug interactions with cimetidine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1982 Jan-Feb;7(1):23–41. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198207010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


