Abstract
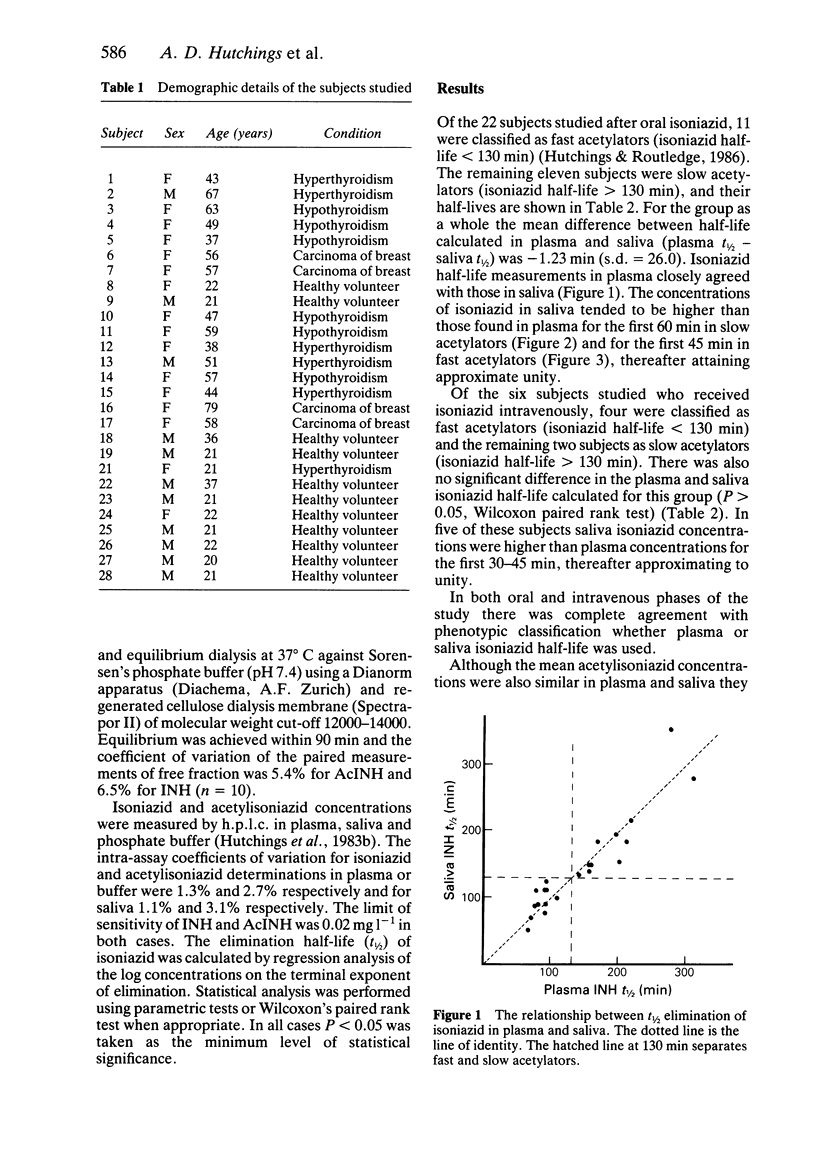
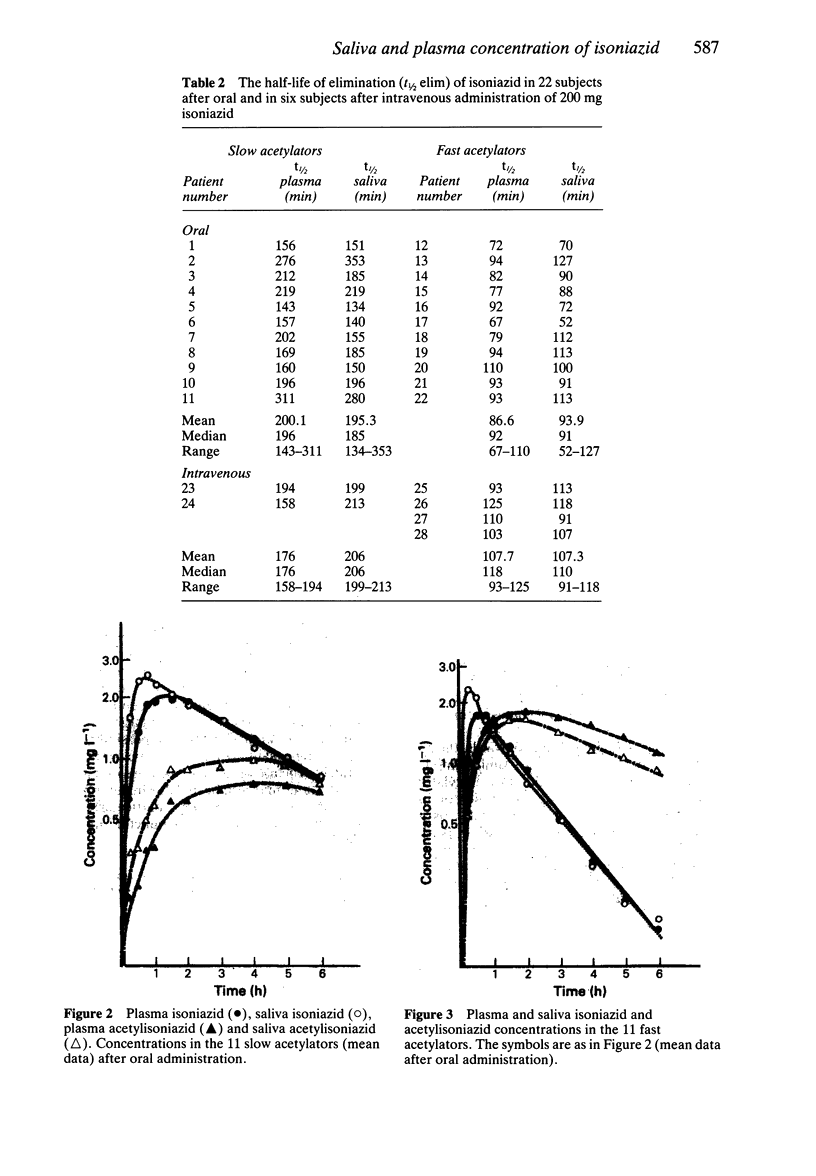
1. The pharmacokinetics of isoniazid and acetylisoniazid in plasma and saliva were compared following administration of oral and intravenous doses (200 mg) to healthy volunteers and patients. 2. In the 22 subjects studied after oral administration and the six subjects studied after intravenous administration there was complete phenotypic agreement for both slow (t1/2 greater than 130 min) and fast (t1/2 less than 130 min) acetylators using either saliva or plasma. 3. Acetylator phenotyping based on the t1/2 of INH determined using saliva collected at 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 h after a 200 mg oral dose appears to be as reliable as that based on plasma. 4. Salivary isoniazid concentrations may provide a non-invasive alternative to plasma concentrations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boxenbaum H. G., Berkersky I., Mattaliano V., Kaplan S. A. Plasma and salivary concentrations of isoniazid in man: preliminary findings in two slow acetylator subjects. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1975 Dec;3(6):443–456. doi: 10.1007/BF01059476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings A., Monie R. D., Spragg B., Routledge P. A. A method to prevent the loss of isoniazid and acetylisoniazid in human plasma. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Feb;15(2):263–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings A., Monie R. D., Spragg B., Routledge P. A. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of isoniazid and acetylisoniazid in biological fluids. J Chromatogr. 1983 Oct 14;277:385–390. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84863-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings A., Routledge P. A. A simple method for determining acetylator phenotype using isoniazid. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Sep;22(3):343–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin S. B., Wan S. H., Karam J. H. Pharmacokinetics of tolbutamide: prediction by concentration in saliva. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Dec;16(6):1052–1058. doi: 10.1002/cpt19741661052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W. W., Hein D. W. Clinical pharmacokinetics of isoniazid. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1979 Nov-Dec;4(6):401–422. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197904060-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


