Abstract
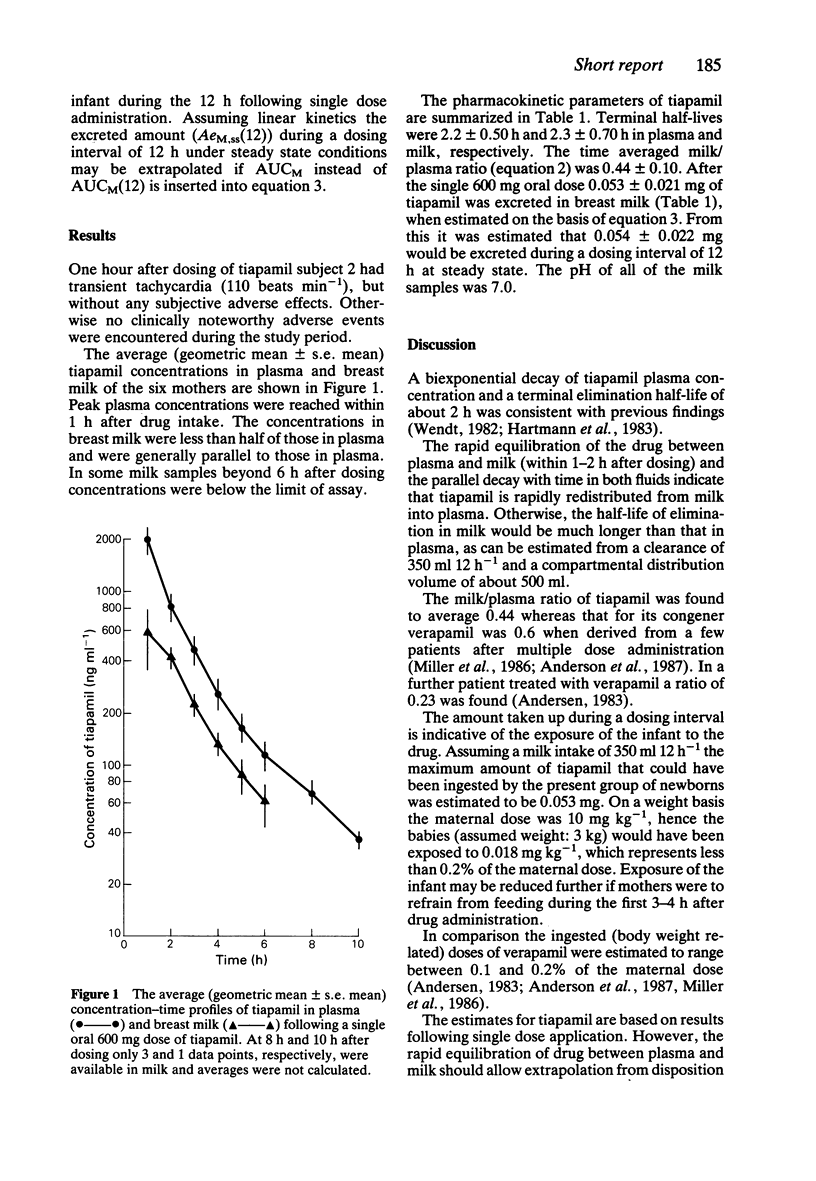
The excretion of tiapamil in breast milk was studied in six lactating mothers (3-7 days post partum) following a single oral 600 mg dose of the drug. The milk/plasma ratio of tiapamil derived from the areas under the plasma and milk concentration-time curves was 0.44 +/- 0.10 mean +/- s.d.). Assuming an intake of 350 ml of milk during a dosing interval of 12 h, the newborn would be exposed at the maximum to 0.053 mg tiapamil. This small amount does not represent a risk for the baby.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen H. J. Excretion of verapamil in human milk. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;25(2):279–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00543804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Bondesson U., Mattiasson I., Johansson B. W. Verapamil and norverapamil in plasma and breast milk during breast feeding. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;31(5):625–627. doi: 10.1007/BF00606644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balansard P., Elkik F., Levenson J. A., Ciampi M., Sans P. Effect of a new calcium antagonist, tiapamil, in hypertension of the elderly. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;18(6):823–829. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigenmann R., Blaber L., Nakamura K., Thorens S., Haeusler G. Tiapamil, a new calcium antagonist. 1. Demonstration of calcium antagonistic activity and related studies. Arzneimittelforschung. 1981;31(9):1393–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigenmann R., Gerold M., Hefti F., Jovanovic D., Haeusler G. Tiapamil, a new calcium antagonist. 2. Further pharmacological characterization and toxicology. Arzneimittelforschung. 1981;31(9):1401–1410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. W. The distribution of some commonly used drugs in human breast milk. Drug Metab Rev. 1983;14(4):653–684. doi: 10.3109/03602538308991403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleishaker J. C., Desai N., McNamara P. J. Factors affecting the milk-to-plasma drug concentration ratio in lactating women: physical interactions with protein and fat. J Pharm Sci. 1987 Mar;76(3):189–193. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600760302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heizmann P., Wendt G., Von Alten R., Zinapold K., Buser C. Determination of tiapamil and of its two main metabolites in plasma and in urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1984 Sep 14;310(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(84)80073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinderling P. H., Eckert M., Gasic S., Eichler H. G., Pötzi R., Heizmann P. Comparative pharmacokinetics and cardiovascular effects of tiapamil in healthy volunteers and patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;31(4):397–404. doi: 10.1007/BF00613513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. R., Withers R., Bhamra R., Holt D. W. Verapamil and breast-feeding. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;30(1):125–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00614209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramuz H. A new Ca++ antagonist, Ro 11-1781, and its metabolites. Synthesis and physicochemical properties. Arzneimittelforschung. 1978;28(11):2048–2051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhomberg F., Bachmann K., Bächtold H., Müller P. Erste Erfahrungen mit dem Calcium-Antagonisten Tiapamil in der Behandlung der arteriellen Hypertonie. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1983 Dec 10;113(49):1845–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salorinne Y., Himberg J. J., Eskelinen E. Long-term tiapamil treatment of patients with angina pectoris. Clin Cardiol. 1983 Apr;6(4):171–175. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960060404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer S. A., Hull D. Fat content of expressed breast milk: a case for quality control. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Jan 10;282(6258):99–100. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6258.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syversen G. B., Ratkje S. K. Drug distribution within human milk phases. J Pharm Sci. 1985 Oct;74(10):1071–1074. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600741010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt G. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of tiapamil. Cardiology. 1982;69 (Suppl):68–78. doi: 10.1159/000173539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R. G., Paul A. A. Infant growth and human milk requirements. A fresh approach. Lancet. 1981 Jul 25;2(8239):161–163. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90352-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., Brown R. D., Hinson J. L., Dailey J. W. Pharmacokinetic pitfalls in the estimation of the breast milk/plasma ratio for drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:667–689. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T. Determinants and consequences of drug excretion in breast milk. Drug Metab Rev. 1983;14(4):619–652. doi: 10.3109/03602538308991402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


