Abstract
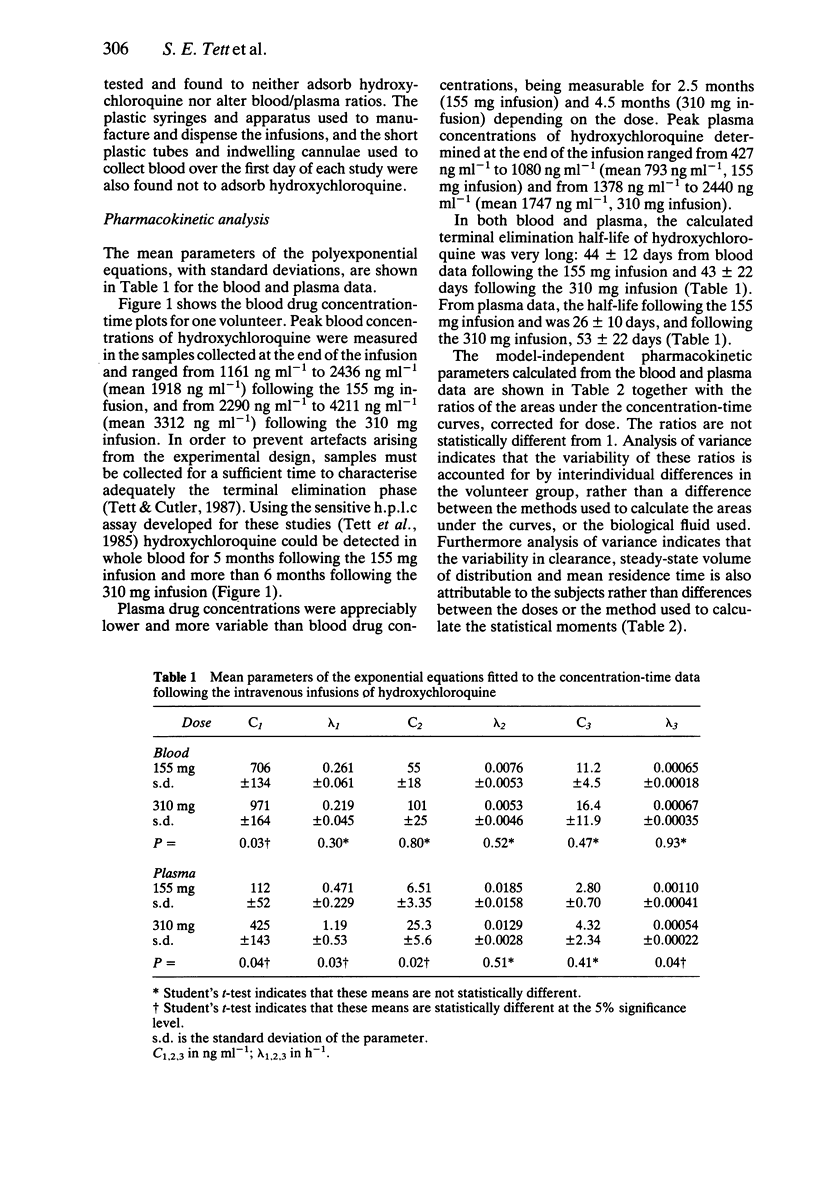
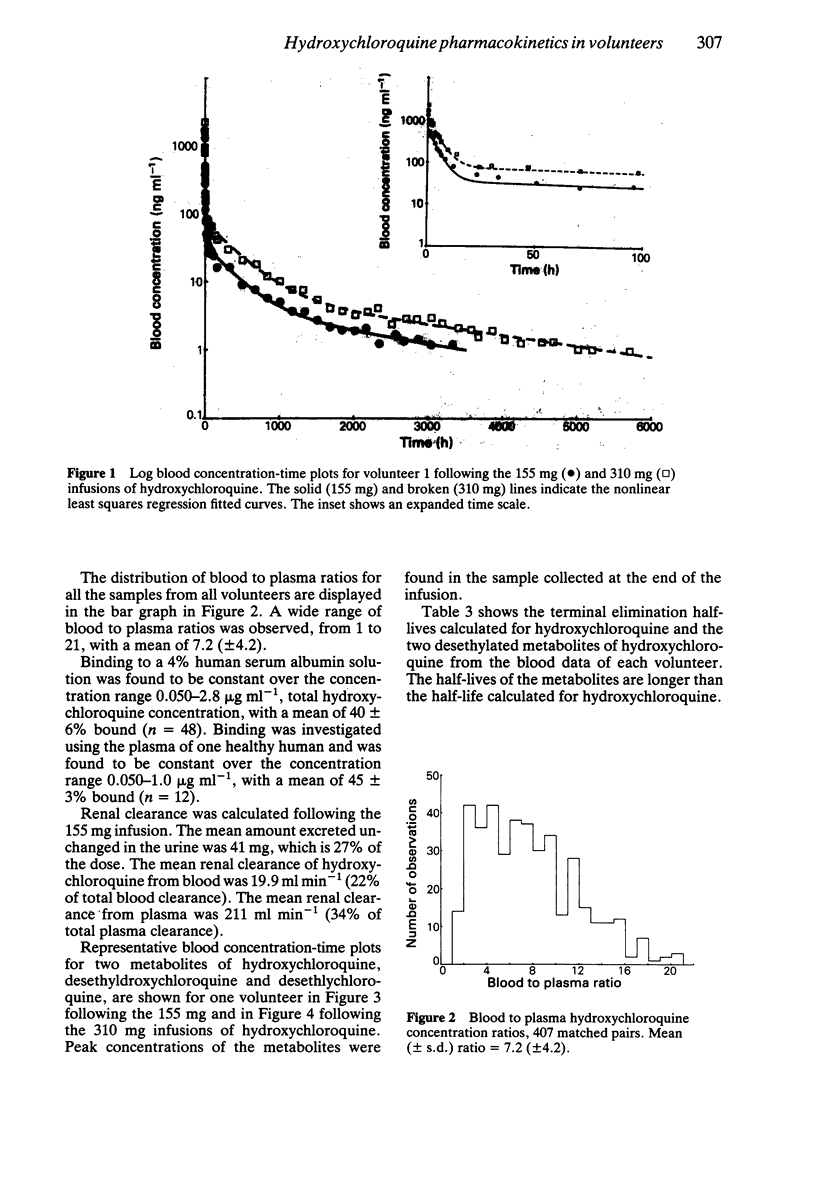
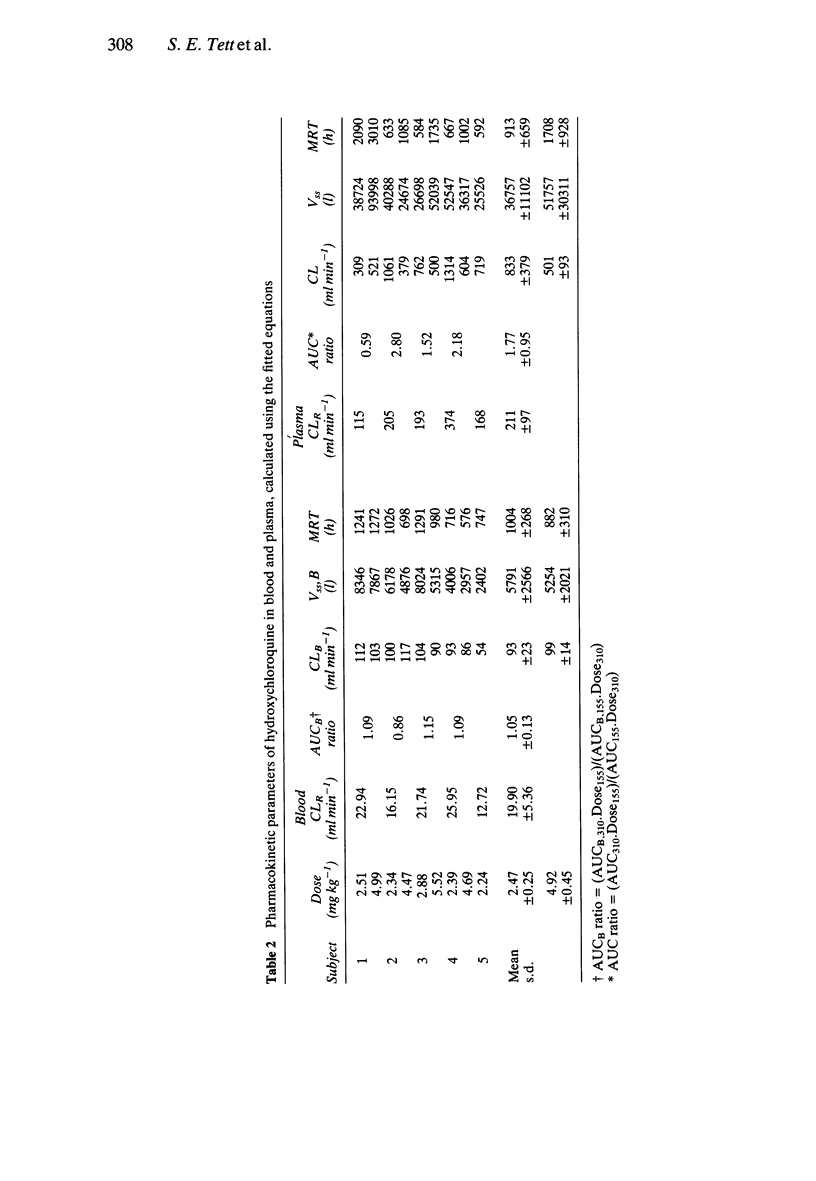
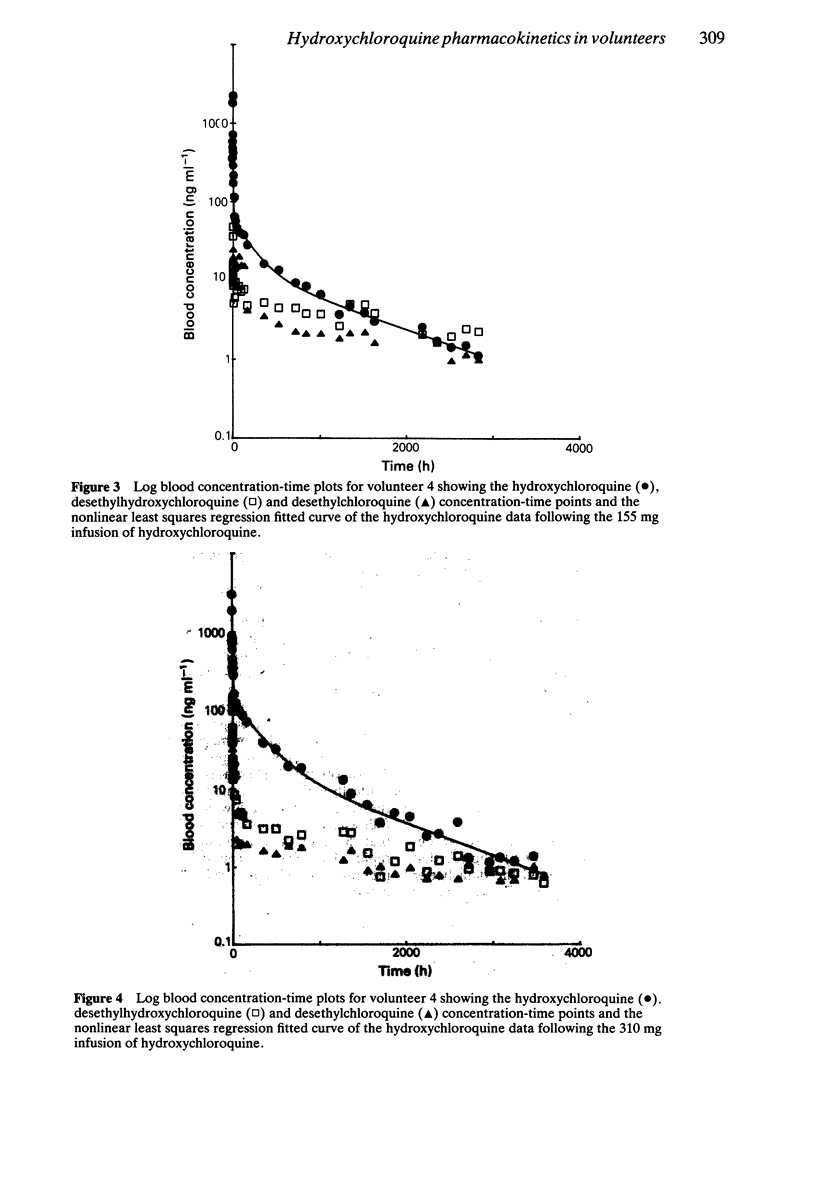
1. The pharmacokinetics of hydroxychloroquine were studied in five healthy volunteers following an intravenous infusion of 155 mg (2.47 +/- 0.25 mg kg-1) racemic hydroxychloroquine. Four of these volunteers also received a further 310 mg (4.92 +/- 0.45 mg kg-1) infusion of hydroxychloroquine and evidence of nonlinearities in the pharmacokinetics of hydroxychloroquine were sought. 2. No nonlinear elimination or distribution processes appeared to be operating at the doses of hydroxychloroquine used in this study, supporting the hypothesis that in the therapeutic dosing range the pharmacokinetics of hydroxychloroquine are linear. 3. Half-life and mean residence time were long (around 40 days) and large volumes of distribution were calculated (5,522 l from blood, 44,257 l from plasma). Sequestration into the tissues is an important feature of the disposition of hydroxychloroquine. The persistence of hydroxychloroquine in the body is due primarily to this extensive tissue distribution, rather than to low clearance (667 ml min-1 based on plasma data, 96 ml min-1 based on blood data). 4. Plasma data were more variable than blood data. Blood to plasma concentration ratios were not constant (mean +/- s.d.: 7.2 +/- 4.2). The data indicate that it is preferable to measure whole blood concentrations of hydroxychloroquine, rather than plasma concentrations, in pharmacokinetic studies. 5. The pharmacokinetics of hydroxychloroquine are similar to those of chloroquine.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderounmu A. F., Salako L. A., Lindström B., Walker O., Ekman L. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of chloroquine after single intravenous and intramuscular administration in healthy Africans. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;22(5):559–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02935.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adjepon-Yamoah K. K., Ofori-Adjei D., Woolhouse N. M., Lindström B. Whole-blood single-dose kinetics of chloroquine and desethylchloroquine in Africans. Ther Drug Monit. 1986;8(2):195–199. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198606000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergqvist Y., Domeij-Nyberg B. Distribution of chloroquine and its metabolite desethyl-chloroquine in human blood cells and its implication for the quantitative determination of these compounds in serum and plasma. J Chromatogr. 1983 Jan 14;272(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)86110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotham R. H., Shand D. Spuriously low plasma propranolol concentrations resulting from blood collection methods. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Nov;18(5 Pt 1):535–538. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975185part1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisk-Holmberg M., Bergkvist Y., Domeij-Nyberg B., Hellström L., Jansson F. Chloroquine serum concentration and side effects: evidence for dose-dependent kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Mar;25(3):345–350. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979253345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisk-Holmberg M., Bergqvist Y., Termond E., Domeij-Nyberg B. The single dose kinetics of chloroquine and its major metabolite desethylchloroquine in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;26(4):521–530. doi: 10.1007/BF00542151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisk-Holmberg M., Bergqvist Y., Termond E. Further support for changes in chloroquine disposition and metabolism between a low and a high dose. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1985;28(6):721–722. doi: 10.1007/BF00607924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary T. G., Akood M. A., Jensen J. B. Characteristics of chloroquine binding to glass and plastic. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jan;32(1):19–23. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson L. L., Rombo L., Alván G., Björkman A., Lind M., Walker O. On the question of dose-dependent chloroquine elimination of a single oral dose. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Sep;34(3):383–385. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson L. L., Walker O., Alván G., Beermann B., Estevez F., Gleisner L., Lindström B., Sjöqvist F. Disposition of chloroquine in man after single intravenous and oral doses. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Apr;15(4):471–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01532.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rombo L., Ericsson O., Alván G., Lindström B., Gustafsson L. L., Sjöqvist F. Chloroquine and desethylchloroquine in plasma, serum, and whole blood: problems in assay and handling of samples. Ther Drug Monit. 1985;7(2):211–215. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198506000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tett S. E., Cutler D. J. Apparent dose-dependence of chloroquine pharmacokinetics due to limited assay sensitivity and short sampling times. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;31(6):729–731. doi: 10.1007/BF00541305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tett S. E., Cutler D. J., Brown K. F. High-performance liquid chromatographic assay for hydroxychloroquine and metabolites in blood and plasma, using a stationary phase of poly(styrene divinylbenzene) and a mobile phase at pH 11, with fluorimetric detection. J Chromatogr. 1985 Nov 8;344:241–248. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)82024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tett S. E., Cutler D. J., Brown K. F. Removal of an endogenous fluorescent compound from urine to allow quantitation of low concentrations of hydroxychloroquine and metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1986 Nov 28;383(1):236–238. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)83468-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdier F., Le Bras J., Clavier F. Blood samples and chloroquine assay. Lancet. 1983 May 28;1(8335):1227–1227. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92513-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker O., Salako L. A., Alván G., Ericsson O., Sjöqvist F. The disposition of chloroquine in healthy Nigerians after single intravenous and oral doses. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;23(3):295–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03048.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka K., Nakagawa T., Uno T. Application of Akaike's information criterion (AIC) in the evaluation of linear pharmacokinetic equations. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Apr;6(2):165–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01117450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


