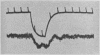
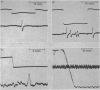
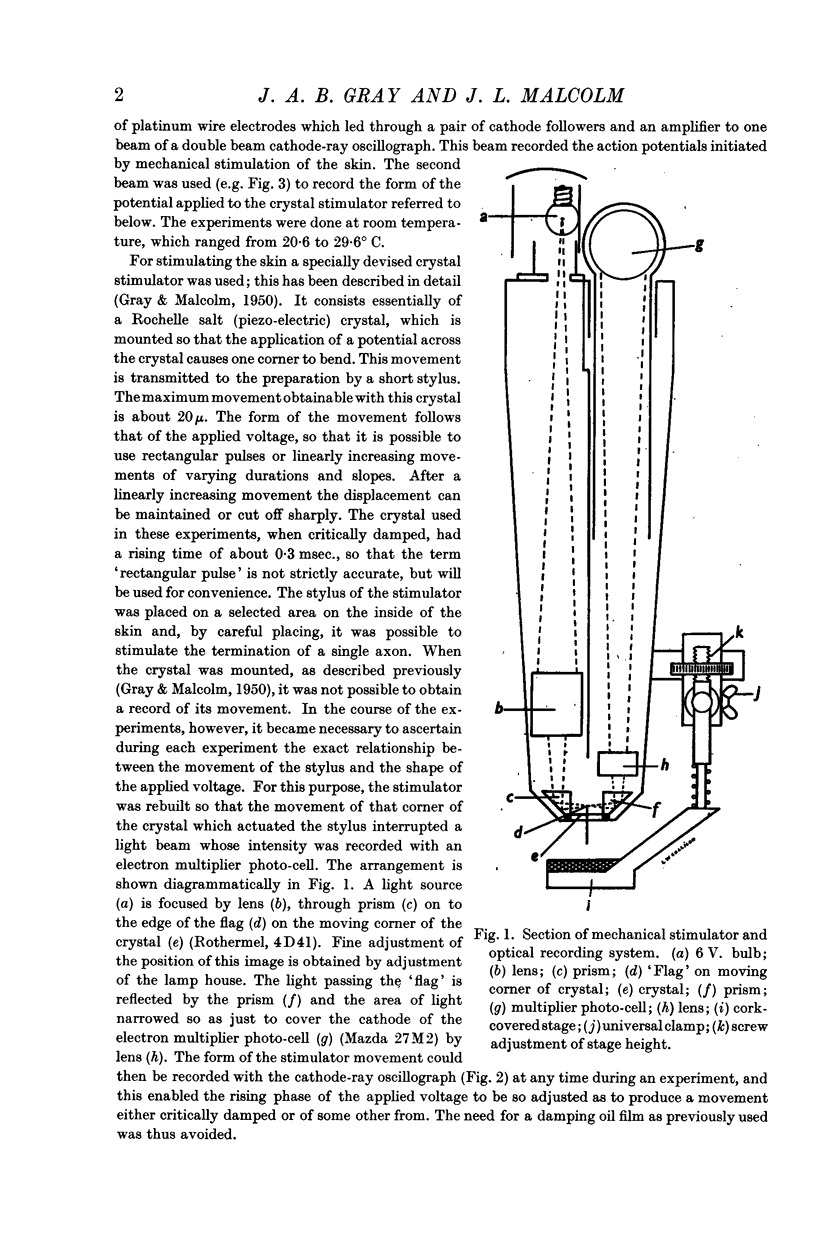
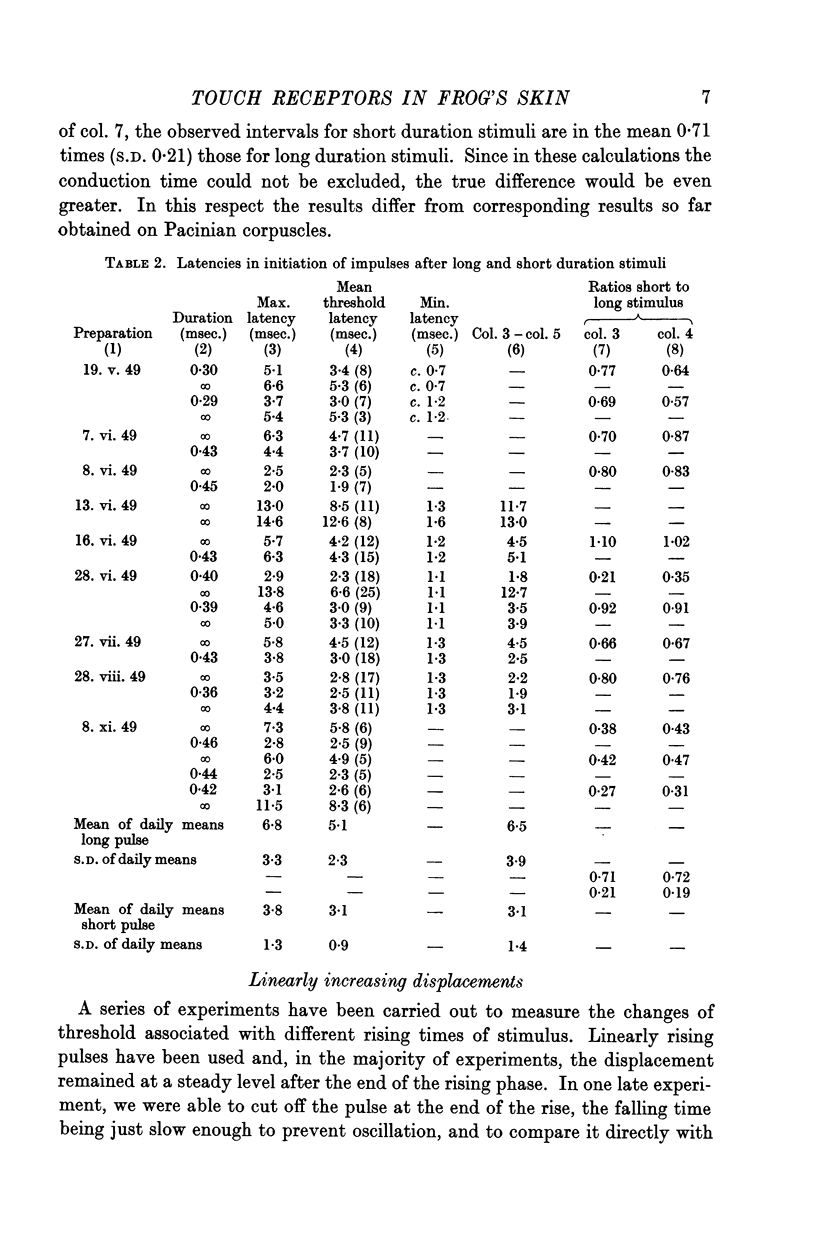
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian E. D., Cattell M., Hoagland H. Sensory discharges in single cutaneous nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1931 Aug 14;72(4):377–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1931.sp002781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian E. D. The impulses produced by sensory nerve-endings: Part 4. Impulses from Pain Receptors. J Physiol. 1926 Oct 30;62(1):33–51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1926.sp002334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
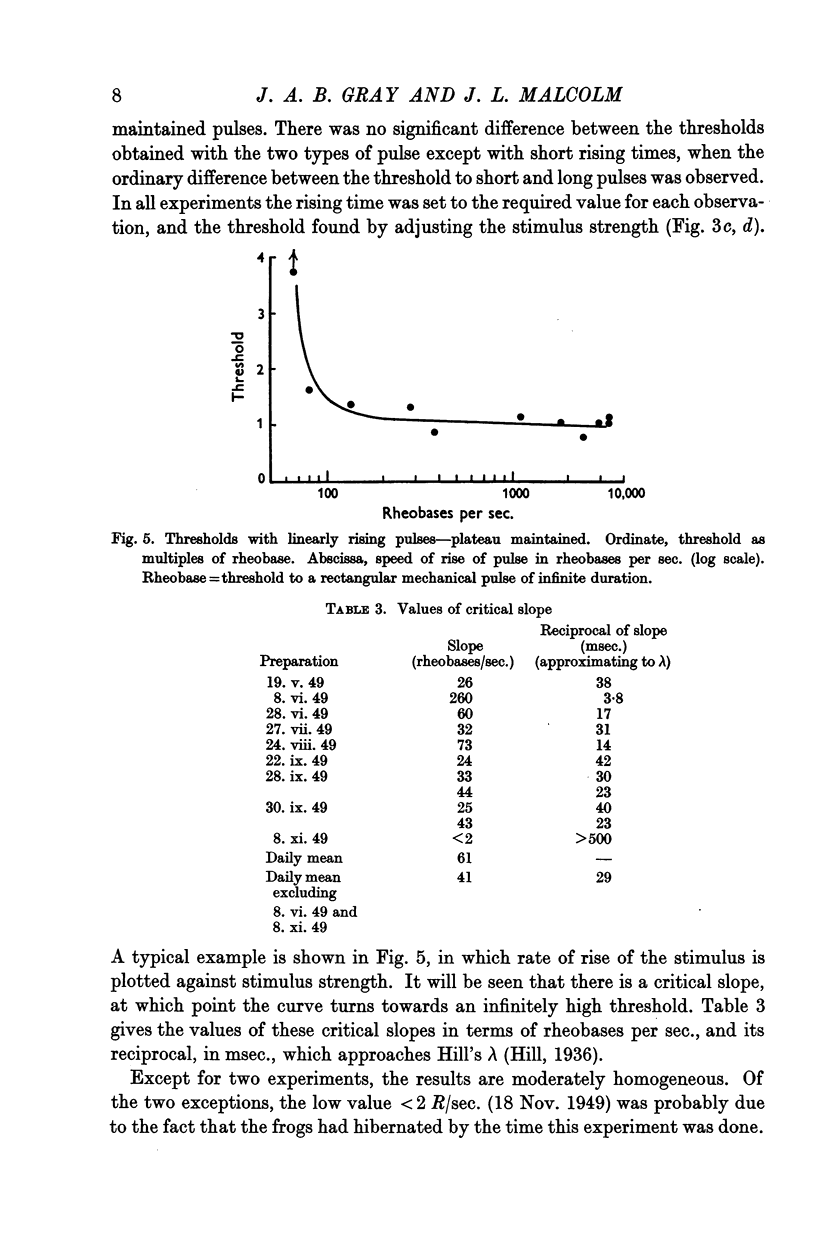
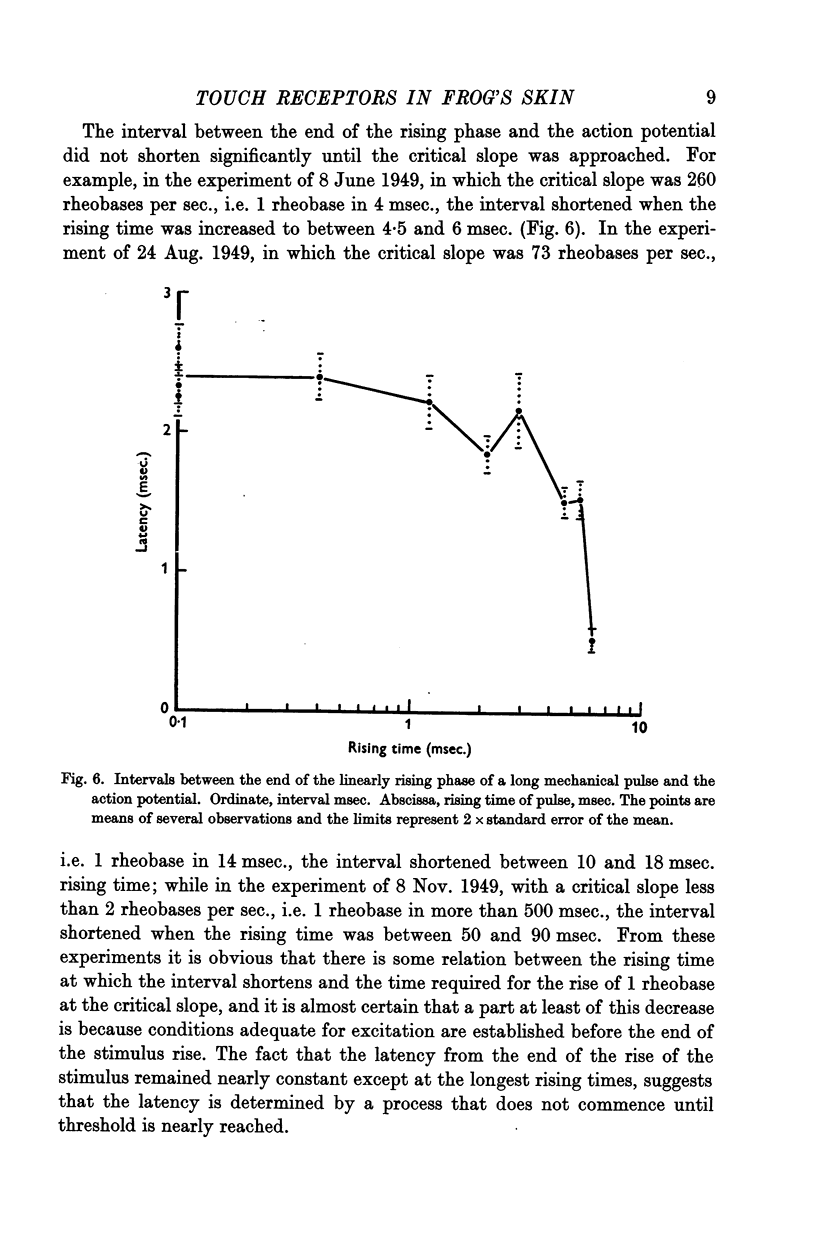
- GRAY J. A. B., MALCOLM J. L. The initiation of nerve impulses by mesenteric Pacinian corpuscles. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1950;137(886):96–114. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1950.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY J. A. B., MATTHEWS P. B. C. A comparison of the adaptation of the Pacinian corpuscle with the accommodation of its own axon. J Physiol. 1951 Aug;114(4):454–464. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L. The membrane resistance of a non-medullated nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1947 Jul 31;106(3):305–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1947.sp004214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B. Depolarization of sensory terminals and the initiation of impulses in the muscle spindle. J Physiol. 1950 Oct 16;111(3-4):261–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1950.sp004479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas K. On the rate of variation of the exciting current as a factor in electric excitation. J Physiol. 1907 Dec 31;36(4-5):253–274. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1907.sp001231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RASHBASS C., RUSHTON W. A. H. The relation of structure to the spread of excitation in the frog's sciatic trunk. J Physiol. 1949 Dec 15;110(1-2):110–135. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan D. The Afferent Nerve Supply of the Mesentery and its Significance in the Causation of Abdominal Pain. J Anat. 1933 Jan;67(Pt 2):233–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]