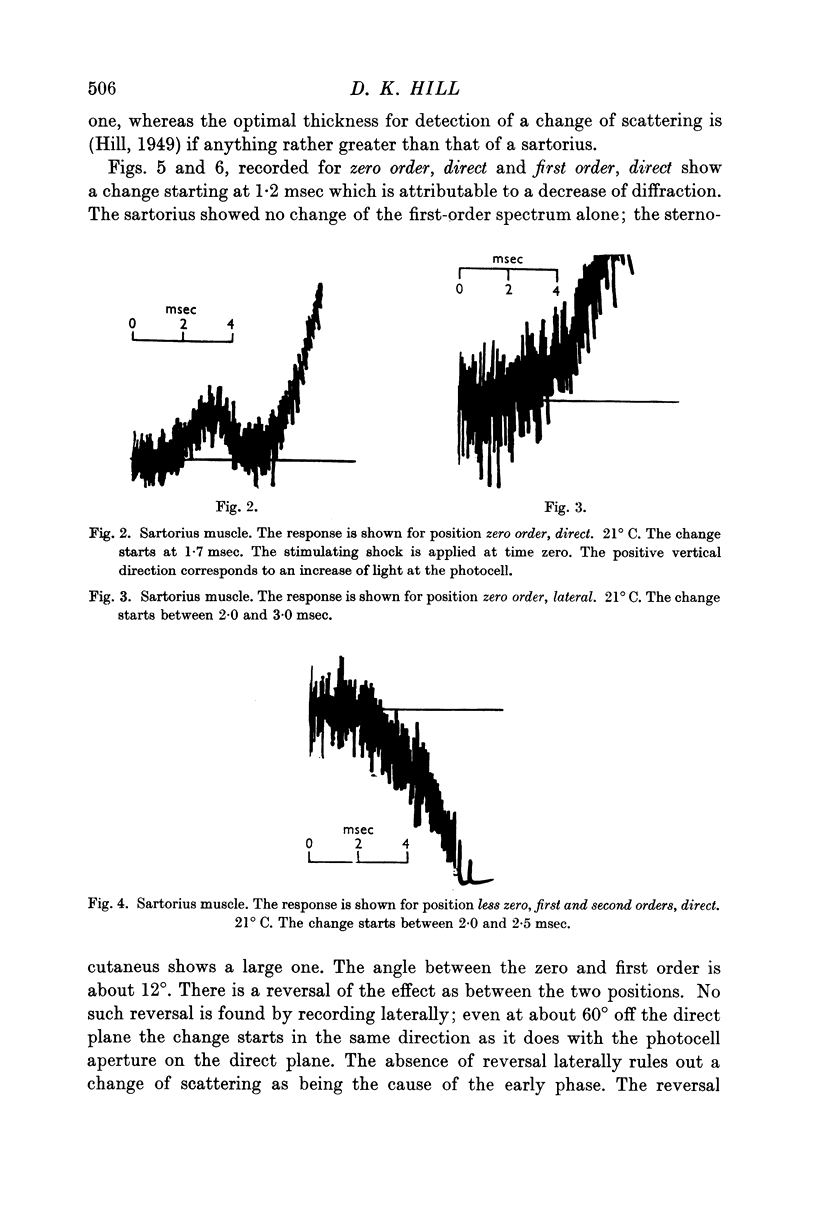
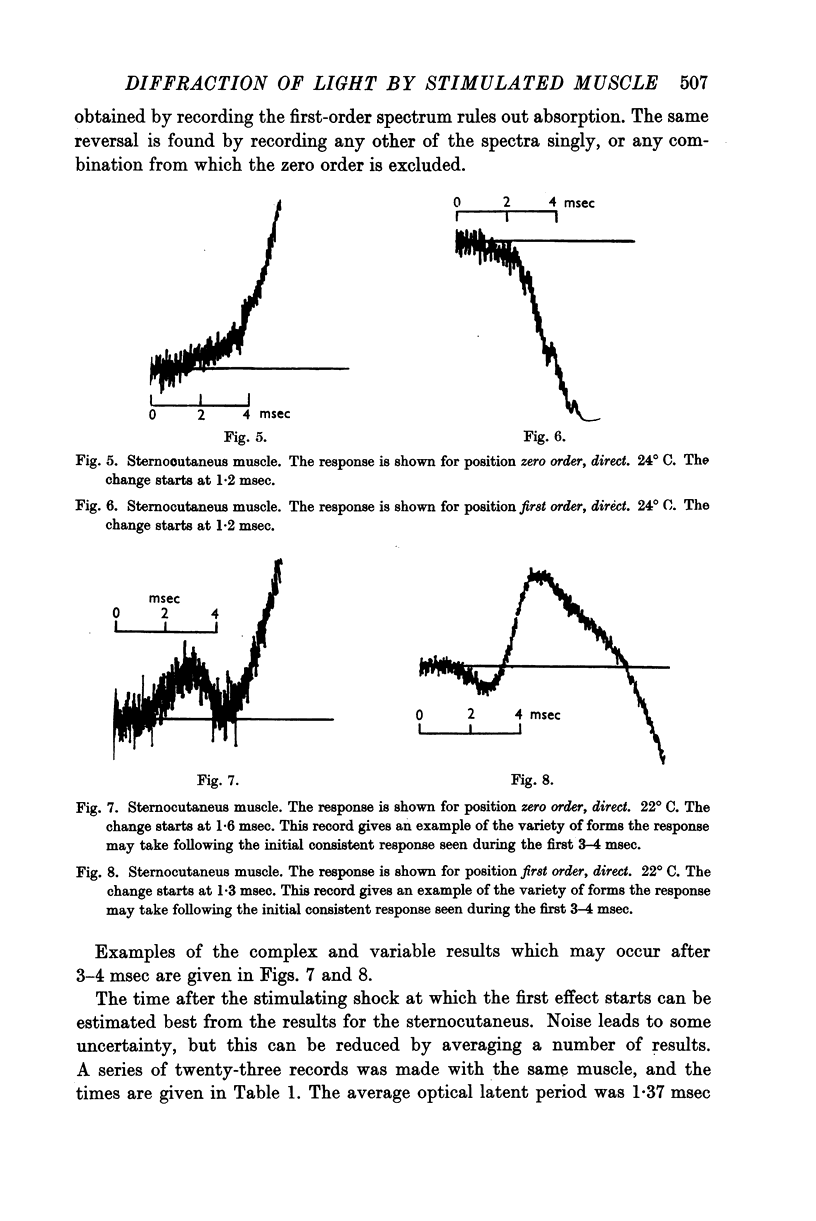
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHLEY C. A., PORTER K. R., PHILPOTT D. E., HASS G. M. Observations by electron microscopy on contraction of skeletal myofibrils induced with adenosinetriphosphate. J Exp Med. 1951 Jul 1;94(1):9–20. doi: 10.1084/jem.94.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON J. Changes in the cross-striation of myofibrils during contraction induced by adenosine triphosphate. Nature. 1952 Mar 29;169(4300):530–533. doi: 10.1038/169530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL D. K. The optical properties of resting striated muscle; the effect of rapid stretch on the scattering and diffraction of light. J Physiol. 1953 Mar;119(4):489–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORVATH B. Contraction and cross-striation of muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1952 Mar;8(3):257–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(52)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. K. Changes in transparency of muscle during a twitch. J Physiol. 1949 May 15;108(3):292–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDOW A. The latent period of muscular contraction. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1950 Jun;31(6):367–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


