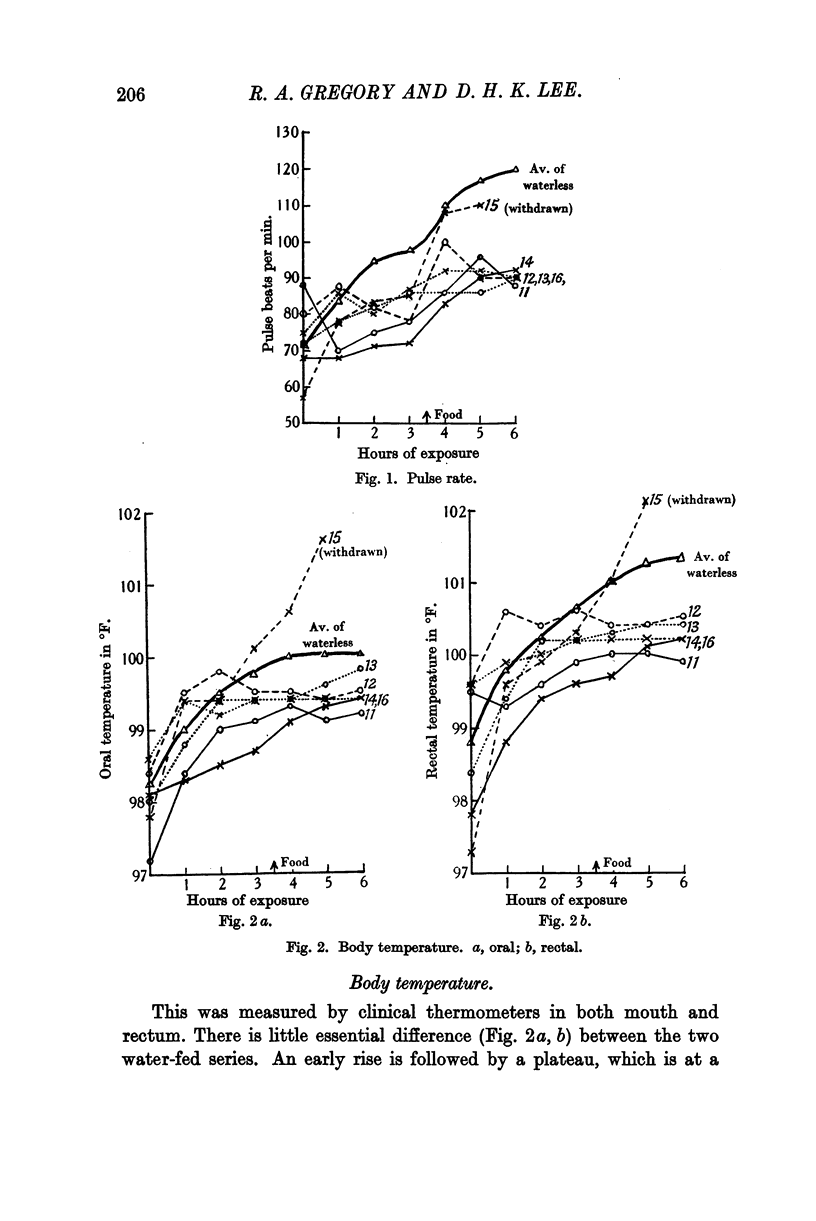
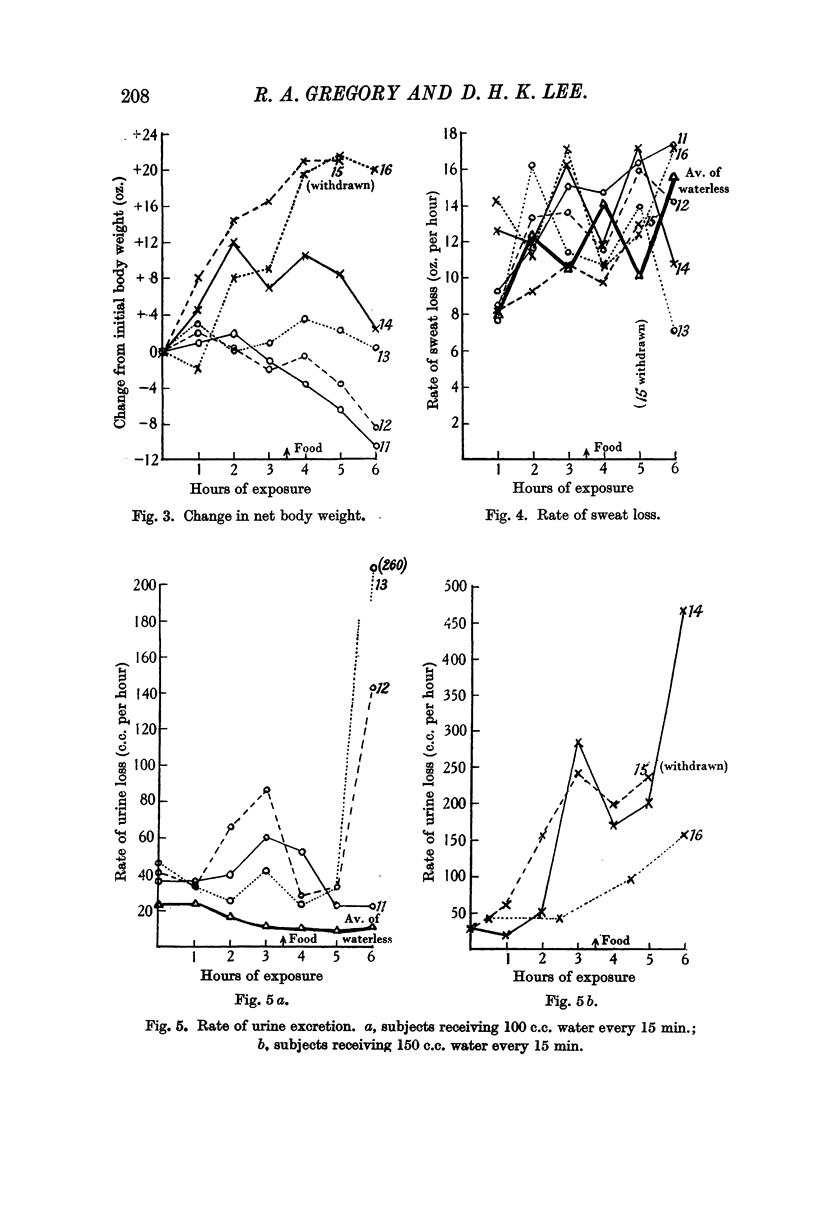
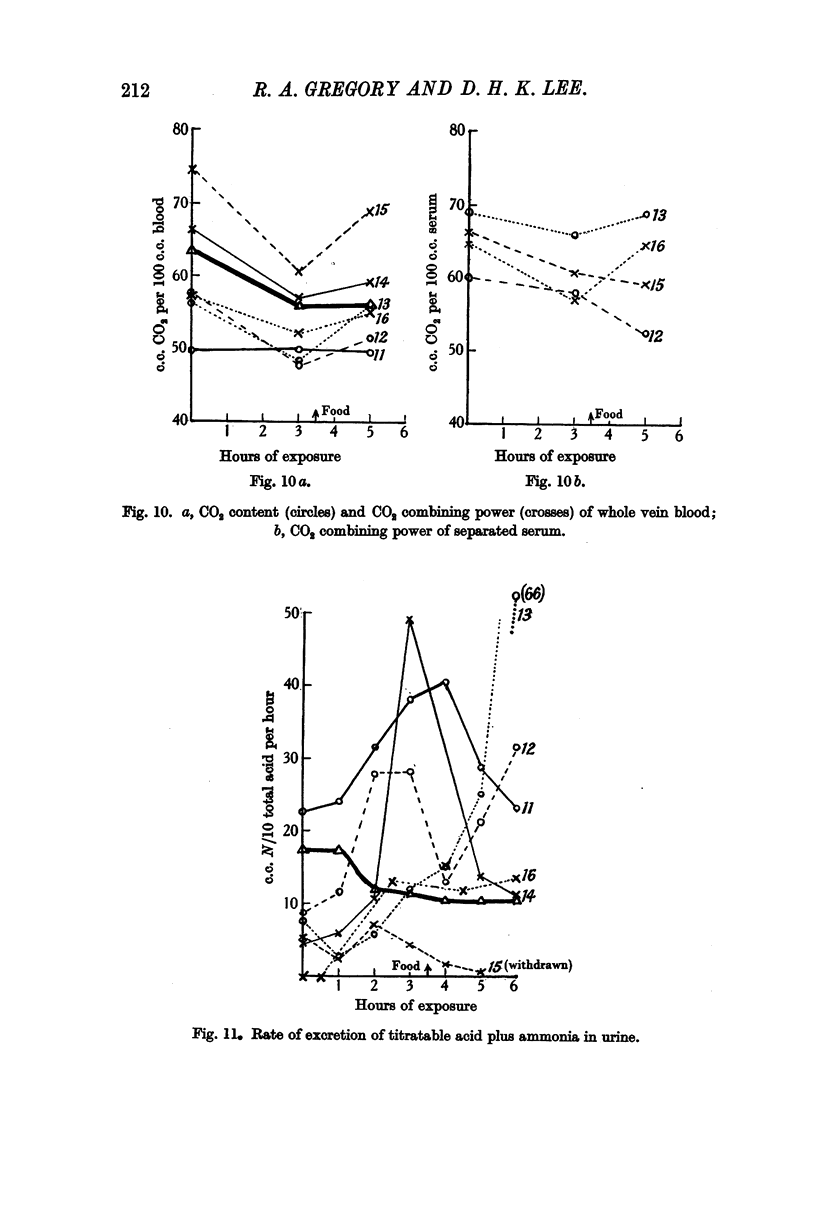
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Darrow D. C., Yannet H. THE CHANGES IN THE DISTRIBUTION OF BODY WATER ACCOMPANYING INCREASE AND DECREASE IN EXTRACELLULAR ELECTROLYTE. J Clin Invest. 1935 Mar;14(2):266–275. doi: 10.1172/JCI100674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. H., Mulder A. G. Some immediate effects of reduced cooling powers upon the water balance and related effects in the human subject. J Physiol. 1935 Jul 24;84(4):410–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1935.sp003290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. H., Mulder A. G. Some immediate physiological effects of reduced cooling powers on human subjects. J Physiol. 1935 Jun 18;84(3):279–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1935.sp003277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehberg P. B. A Method of Microtitration. Biochem J. 1925;19(2):270–277. doi: 10.1042/bj0190270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbott J. H., Michelsen J. HEAT CRAMPS. A CLINICAL AND CHEMICAL STUDY. J Clin Invest. 1933 May;12(3):533–549. doi: 10.1172/JCI100516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Zwalenburg C. Dehydration in Heat Exhaustion and in Fatigue. Cal West Med. 1933 May;38(5):354–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


