Abstract
1. The rate of desensitization of the post-synaptic membrane to prolonged action of acetylcholine was investigated during (a) potassium depolarization of the frog muscle fibre, (b) artificial changes of the membrane potential and (c) in the presence of some multivalent cations and of caffeine.
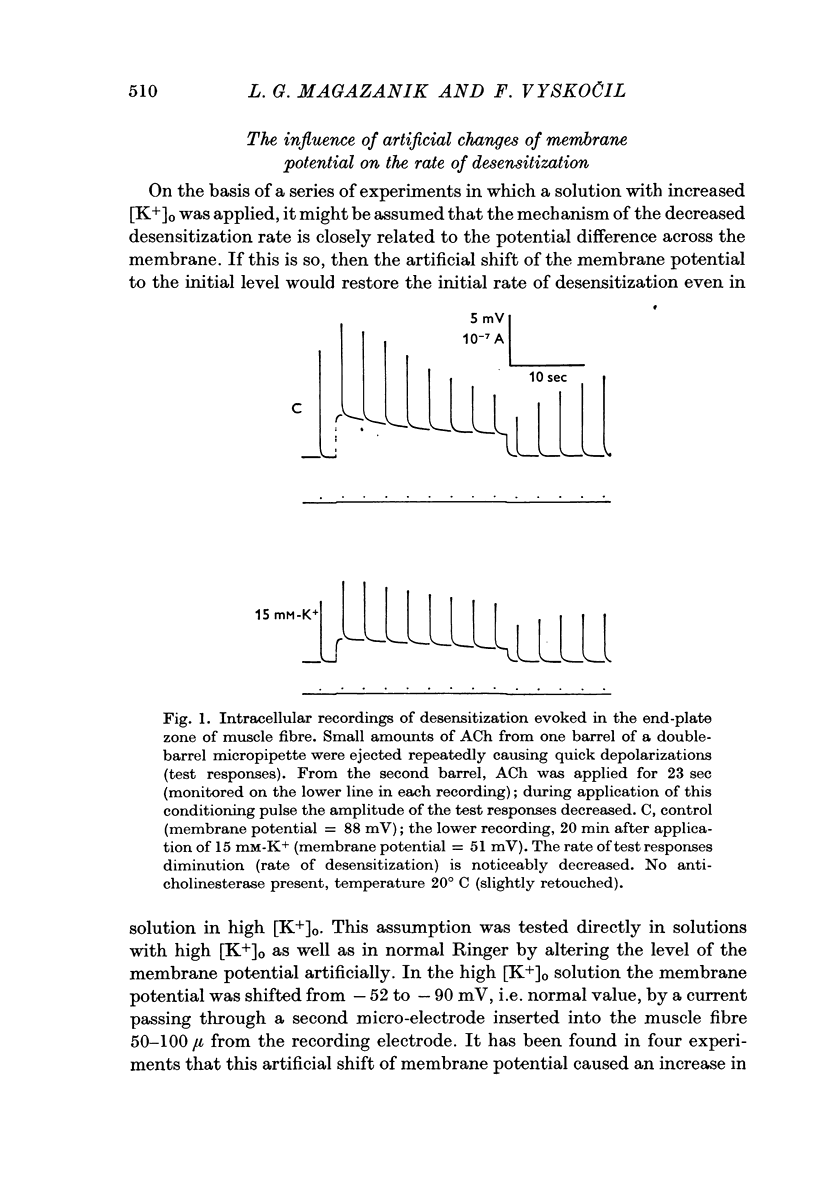
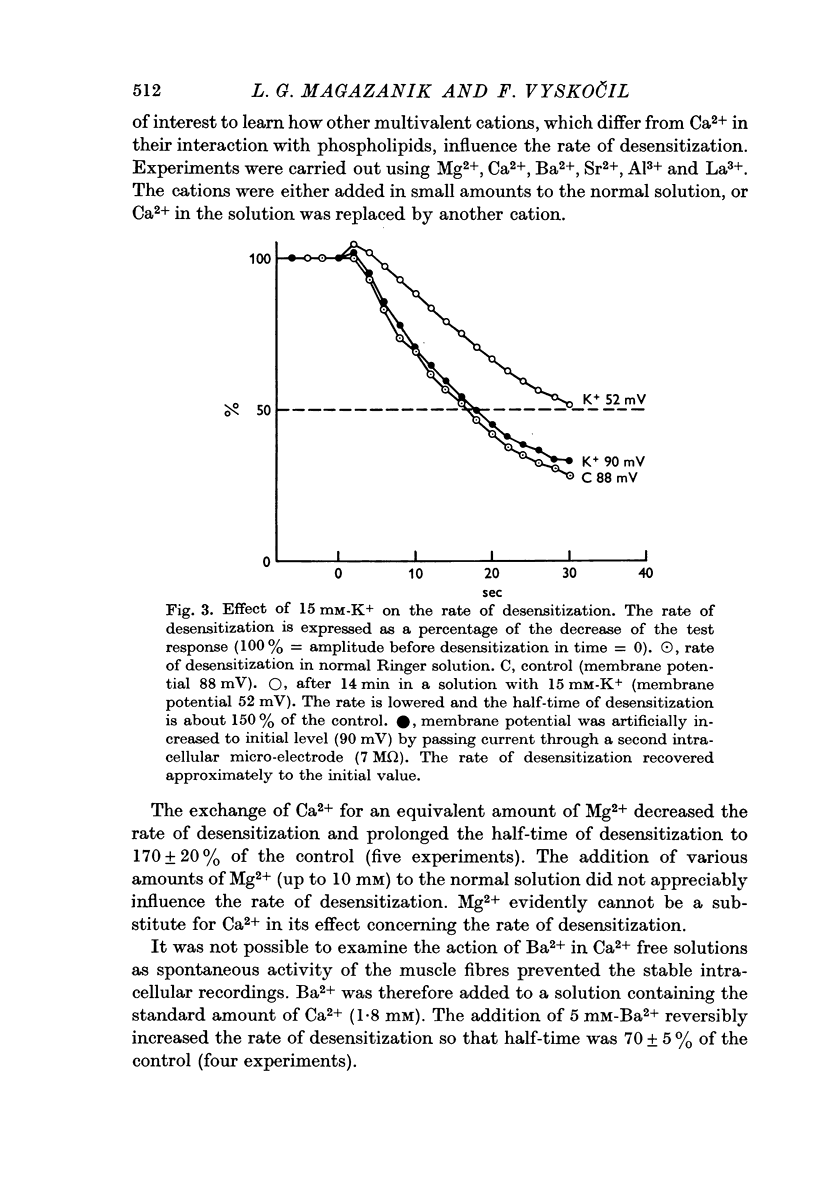
2. Depolarization of the muscle fibre by 15 mM-K+ led to a slowing down in the development of desensitization by 80%. This effect on desensitization produced by membrane potential changes could account for the previously described effect of increased K+ concentration.
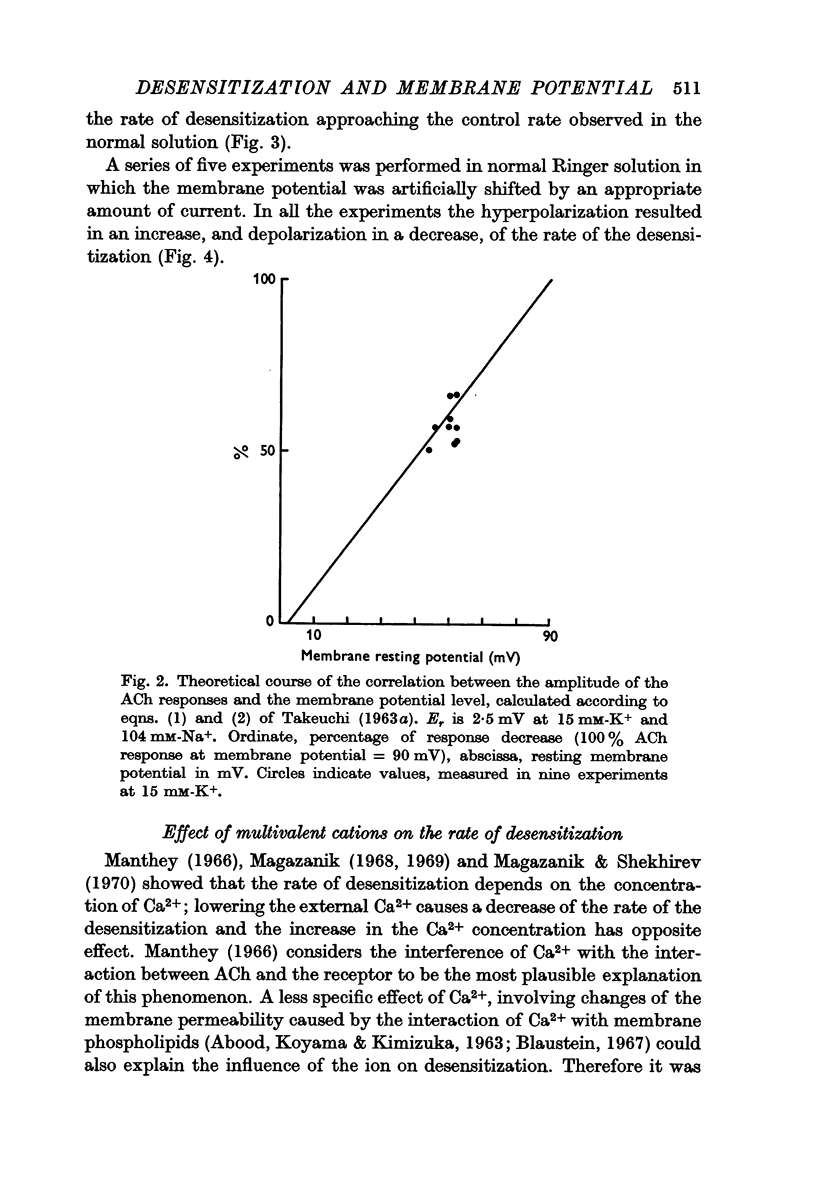
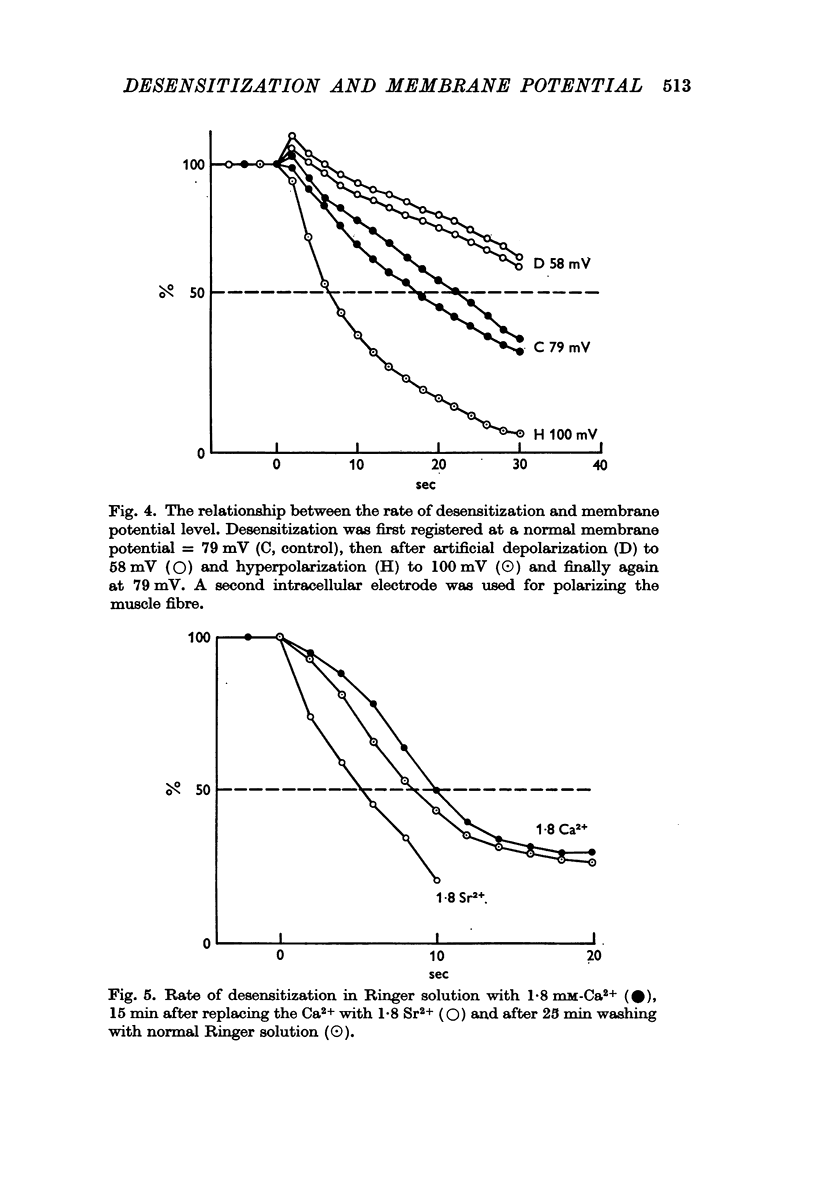
3. Electrotonically produced depolarization of the muscle fibre membrane resulted in a decrease, hyperpolarization in an increase of the rate of desensitization.
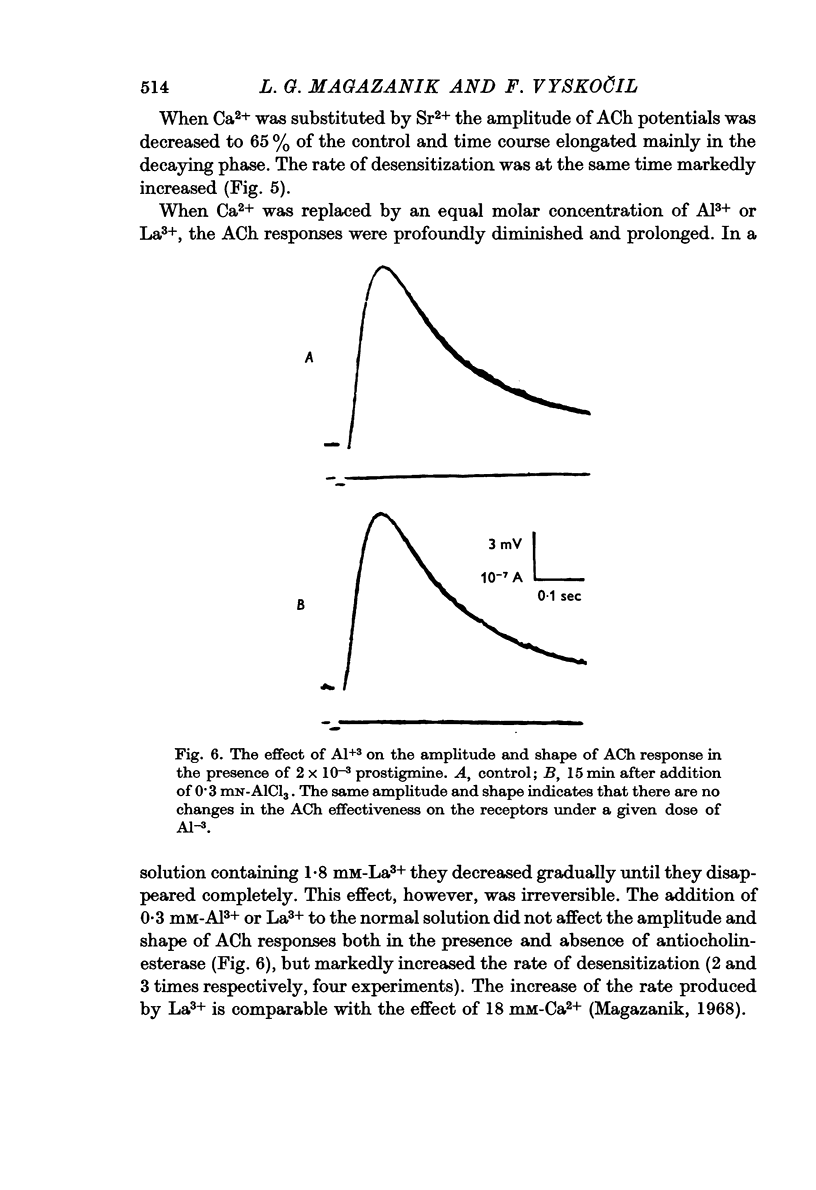
4. Several multivalent cations can be, according to their ability to increase rate of desensitization, arranged in the following series: [Formula: see text]
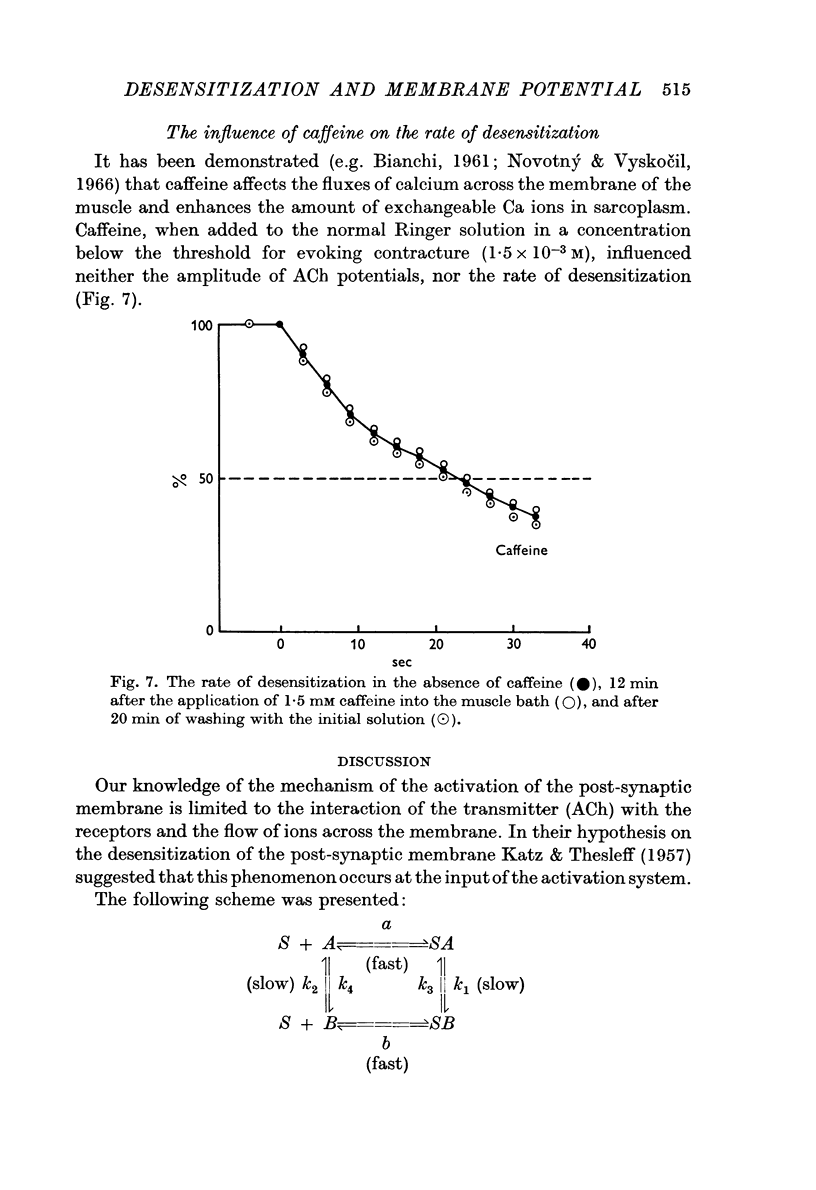
5. Caffeine in a concentration of 1·5 mM does not affect the rate of desensitization.
6. A hypothesis is presented suggesting that desensitization is not only restricted to the receptor level but that it also occurs, at least partly, at the terminal stages of the activation system.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABOOD L. G., KOYAMA I., KIMIZUKA H. A possible mechanism of action of calcium and some psychotomimetic agents on membranes. Nature. 1963 Jan 26;197:367–368. doi: 10.1038/197367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Goldman D. E. The action of certain polyvalent cations on the voltage-clamped lobster axon. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Mar;51(3):279–291. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Phospholipids as ion exchangers: implications for a possible role in biological membrane excitability and anesthesia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 9;135(4):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodorov B. I., Peganov E. M. Vliianie ionov kal'tsiia, magniia, bariia, nikelia i lantana na giperpoliarizatsionnye otvety odinochnogo perekhvata Ranv'e. Biofizika. 1969 May-Jun;14(3):474–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magazanik L. G., Vyskocil F. Different action of atropine and some analogues on the end-plate potentials and induced acetylcholine potentials. Experientia. 1969 Jun 15;25(6):618–619. doi: 10.1007/BF01896548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthey A. A. The effect of calcium on the desensitization of membrane receptors at the neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):963–976. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nastuk W. L. Activation and inactivation of muscle postjunctional receptors. Fed Proc. 1967 Nov-Dec;26(6):1639–1646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotný I., Vyskocil F. Possible role of Ca ions in the resting metabolism of frog sartorius muscle during potassium depolarization. J Cell Physiol. 1966 Feb;67(1):159–168. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040670118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI N. Effects of calcium on the conductance change of the end-plate membrane during the action of transmitter. J Physiol. 1963 Jun;167:141–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI N. Some properties of conductance changes at the end-plate membrane during the action of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1963 Jun;167:128–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


