Abstract
1. Miniature end-plate potentials (min.e.p.p.s) were recorded intracellularly from frog neuromuscular junctions.
2. The `phasic' release of transmitter which is directly related to nerve impulses was suppressed by withdrawal of Ca from the external medium plus addition of Mg.
3. Under these conditions, min.e.p.p.s continued to be discharged even when EGTA was added, although in this case min.e.p.p. frequency appeared to decrease to about half the rate in normal Ringer.
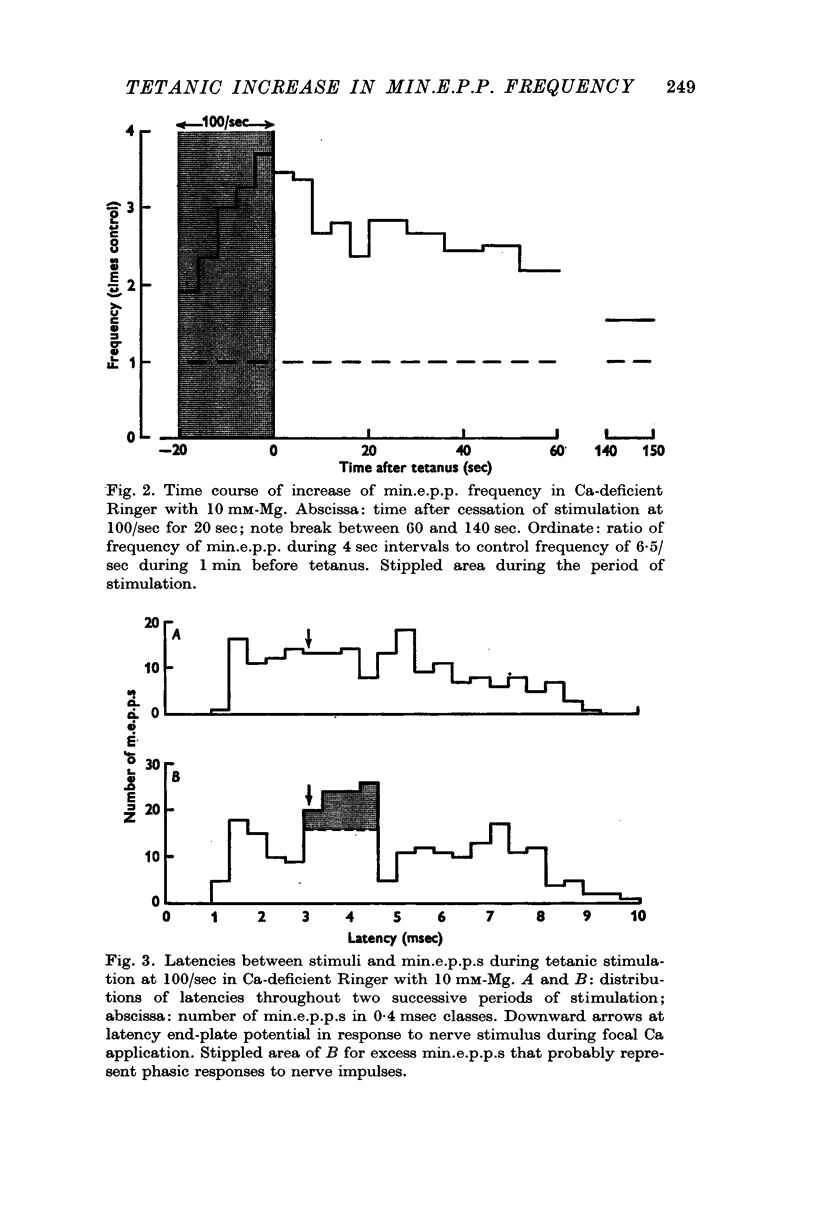
4. Tetanic stimulation of the nerve approximately doubled the rate of min.e.p.p.s even in Ca-free solutions with EGTA added.
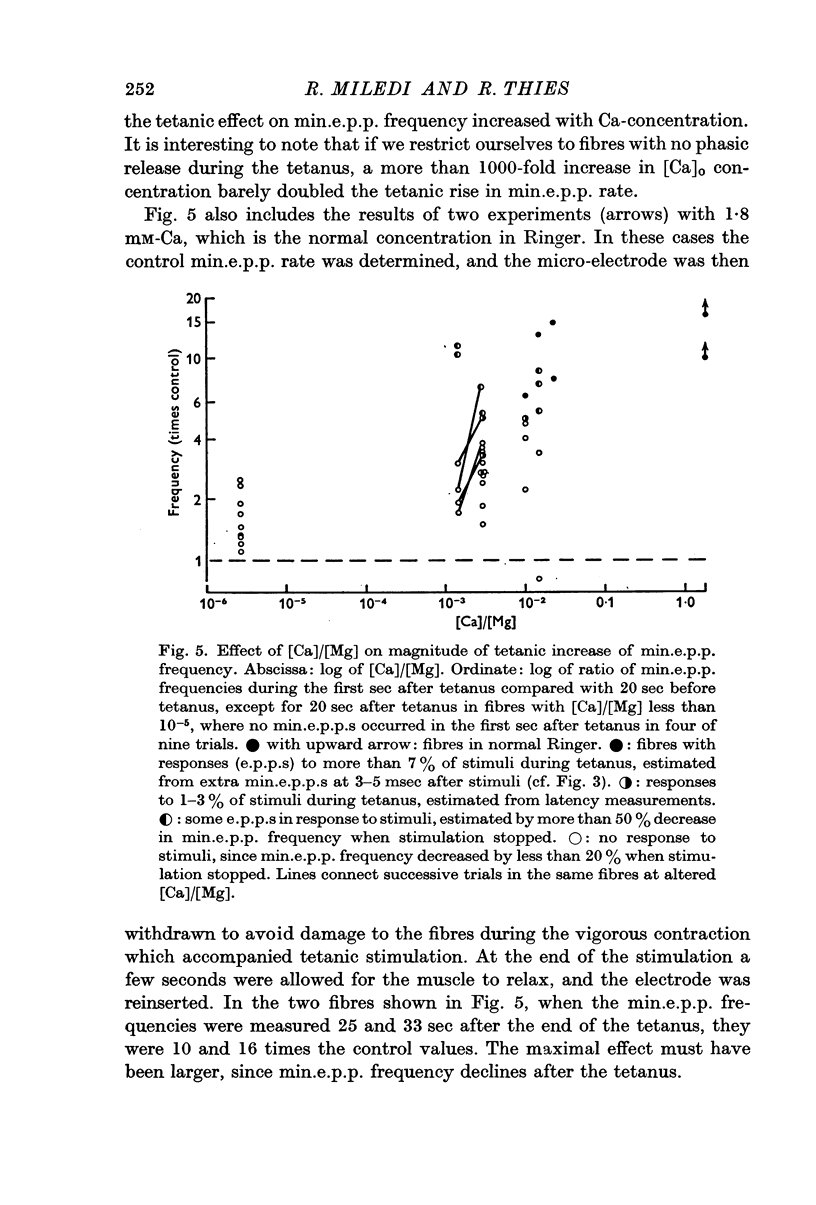
5. The tetanic increase in frequency was greater without EGTA and greater still with some Ca added. Therefore, it is concluded that the tetanic rise in min.e.p.p. frequency can occur even in the absence of the immediate `phasic' release of transmitter normally induced by nerve impulses; and that the magnitude of the increase is related to Ca concentration.
A possible relation between `phasic' and `residual' effects of nerve impulses is described.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROOKS V. B. An intracellular study of the action of repetitive nerve volleys and of botulinum toxin on miniature end-plate potentials. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):264–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M., Schmidt R. F., Zimmermann M. Facilitation at the frog neuromuscular junction during and after repetitive stimulation. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;287(1):41–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00362453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS B. A. Some effects of Ca-free choline-Ringer solution on frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:75–86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Statistical factors involved in neuromuscular facilitation and depression. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):574–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. The effect of magnesium on the activity of motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):553–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge F. A., Jr, Rahamimoff R. Co-operative action a calcium ions in transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):419–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmqvist D., Feldman D. S. Calcium dependence of spontaneous acetylcholine release at mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):487–497. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. The effect of calcium on the myelinated nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):245–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Quastel D. M. Competition between sodium and calcium ions in transmitter release at mammalian neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):95–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I. REPETITIVE STIMULATION AT THE MAMMALIAN NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION, AND THE MOBILIZATION OF TRANSMITTER. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:641–662. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Jones S. F., Landau E. M. On the mechanism by which calcium and magnesium affect the spontaneous release of transmitter from mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(2):355–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. PROPAGATION OF ELECTRIC ACTIVITY IN MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:453–482. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE EFFECT OF CALCIUM ON ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE FROM MOTOR NERVE TERMINALS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:496–503. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., MILEDI R. THE MEASUREMENT OF SYNAPTIC DELAY, AND THE TIME COURSE OF ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Feb 16;161:483–495. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The role of calcium in neuromuscular facilitation. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):481–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. The quantal components of the mammalian end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):571–587. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. Spontaneous synaptic potentials and quantal release of transmitter in the stellate ganglion of the squid. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):379–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Thies R. E. Post-tetanic increase in frequency of miniature end-plate potentials in calcium-free solutions. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):54P–55P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTZEHL H., CALDWELL P. C., RUEEGG J. C. THE DEPENDENCE OF CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION OF MUSCLE FIBRES FROM THE CRAB MAIA SQUINADO ON THE INTERNAL CONCENTRATION OF FREE CALCIUM IONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 25;79:581–591. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M., BIANCHI C. P. The distribution and kinetics of release of radiocalcium in tendon and skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1959 May 20;42(5):1123–1137. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.5.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


