Abstract
1. Changes in membrane and action potentials of cat spinal motoneurones during acute asphyxiation and re-oxygenation were recorded with an intracellular technique.
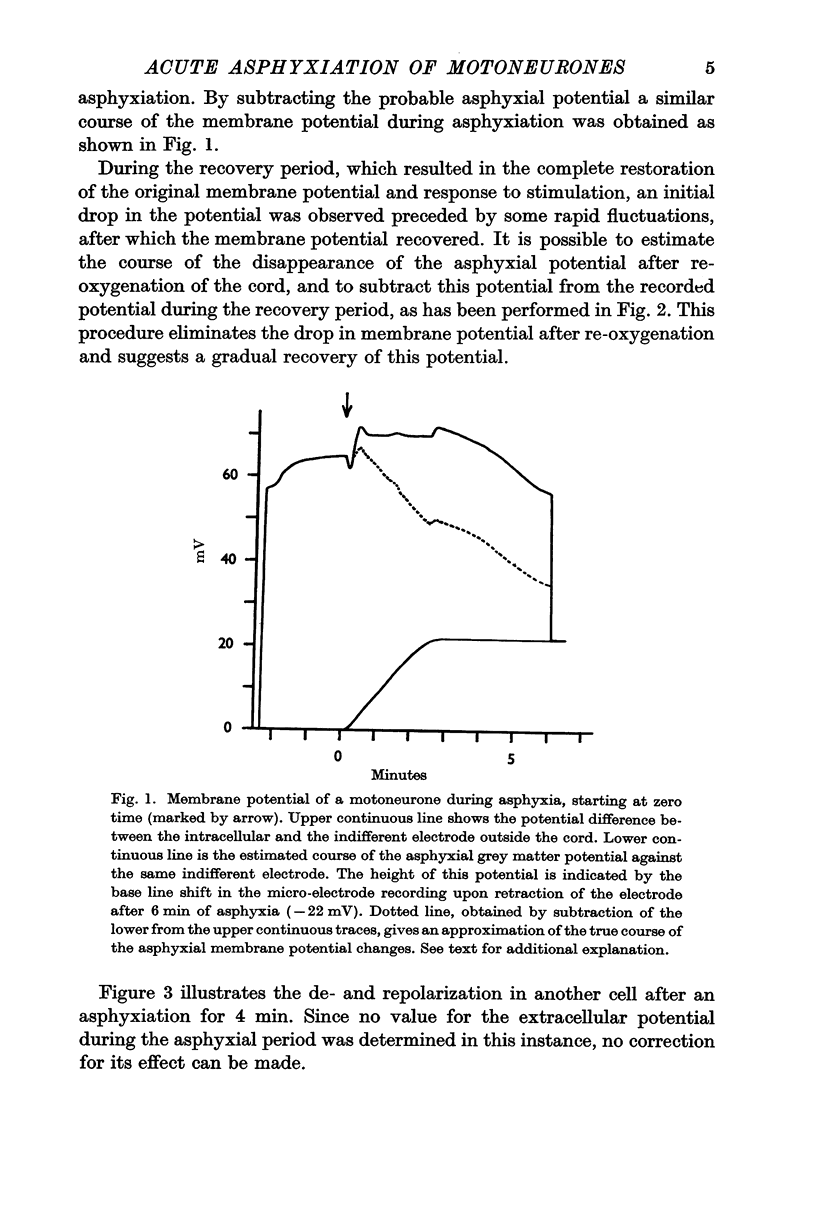
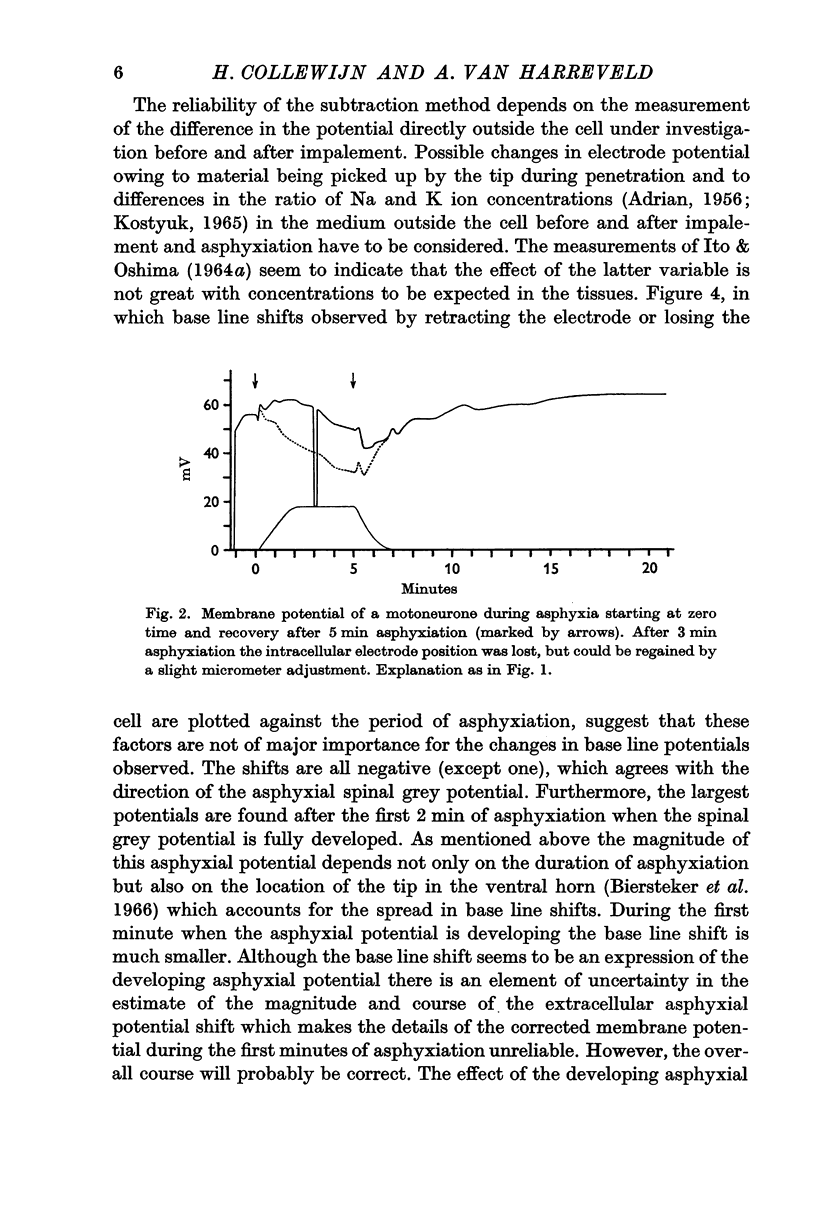
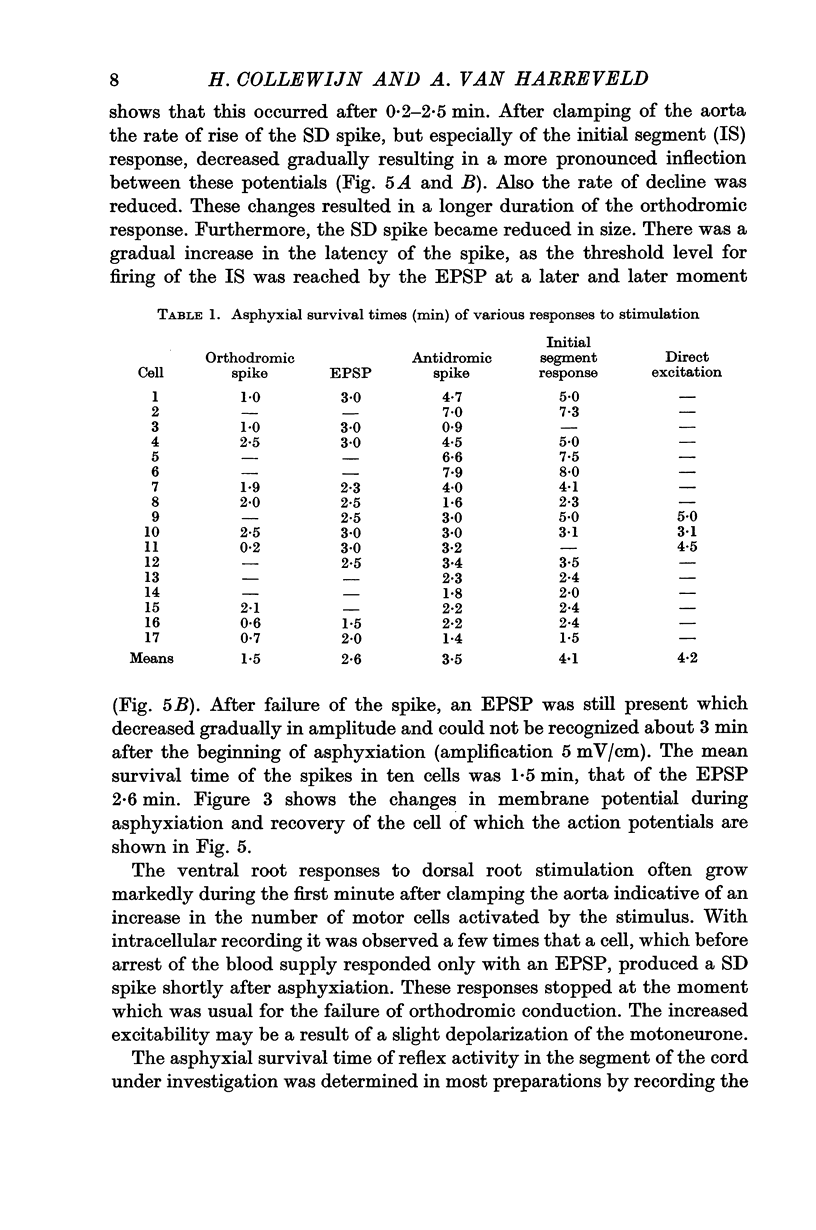
2. The asphyxial potential of the grey matter, which develops in the first 2-2·5 min of asphyxiation, can be expected to interfere with the membrane potential record. After correcting for this effect a gradual depolarization of the soma at a rate of 3-4 mV/min was found, commencing within a fraction of a minute after the start of asphyxiation.
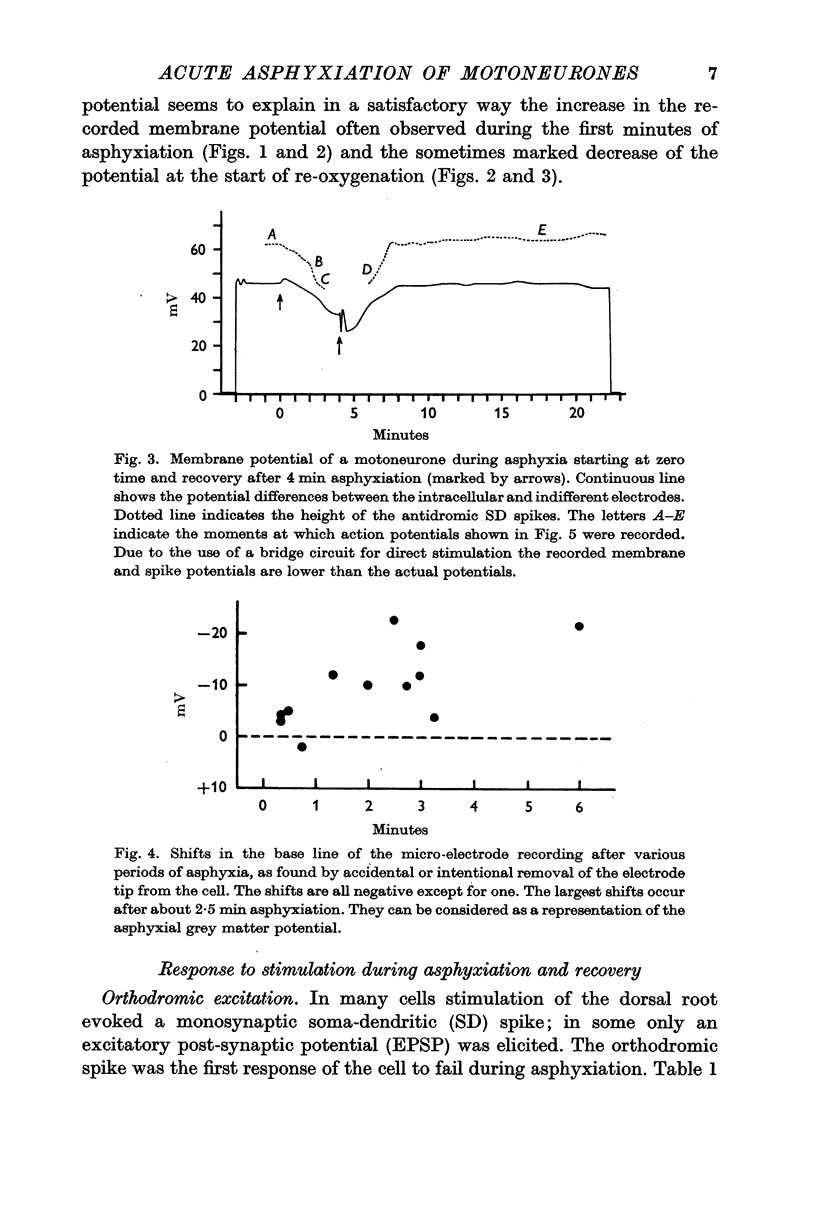
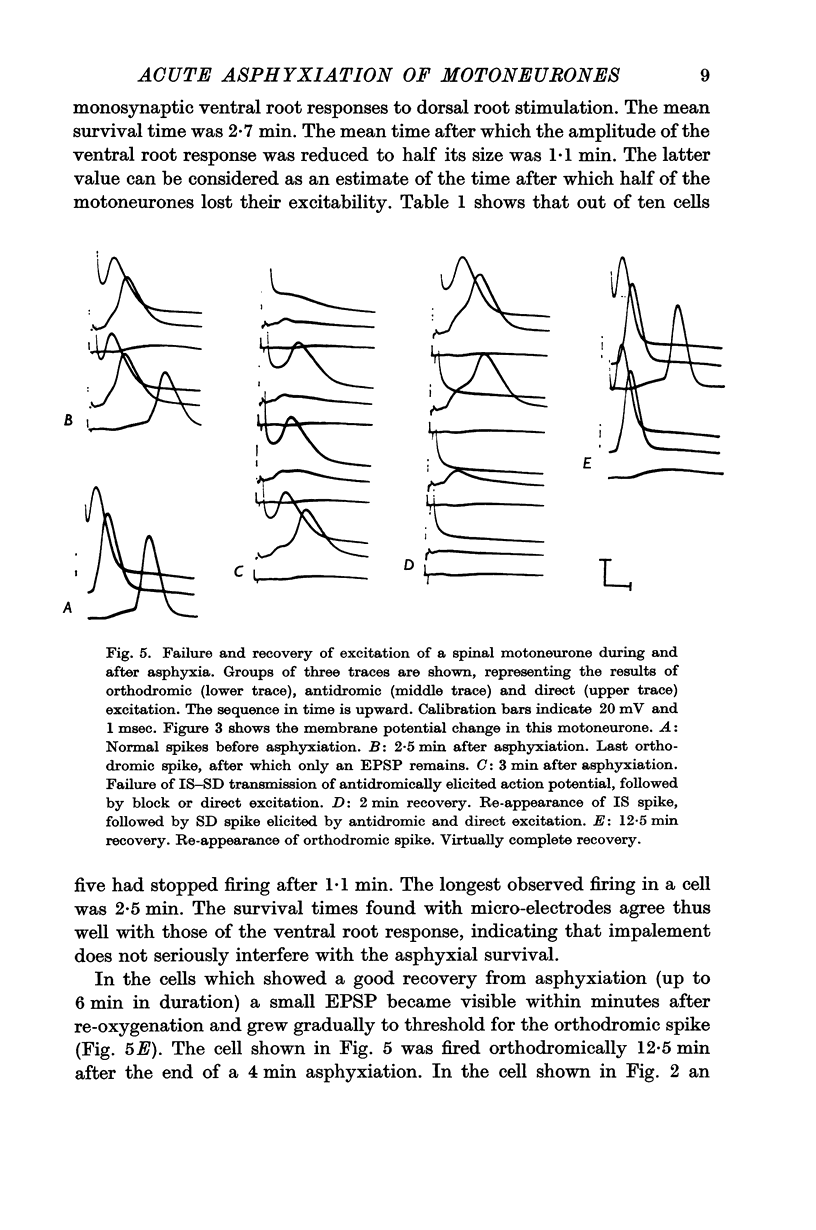
3. The orthodromic responses of the motoneurones were the most vulnerable to O2 lack. They failed earlier than the responses to antidromic and to direct excitation of the cell through the micro-electrode. After failure of the orthodromic spike an excitatory post-synaptic potential remained for a short time. Failure of antidromic excitation began by the dropping out of the some dendritic potential, followed by the arrest of the initial segment response.
4. It was concluded that the early arrest of orthodromic excitation is caused by presynaptic failure.
5. All changes in membrane and action potentials were completely reversible by re-oxygenation after periods of asphyxia lasting from 4 to 6 min. The orthodromic response recovered markedly slower than the antidromic and direct ones.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADRIAN R. H. The effect of internal and external potassium concentration on the membrane potential of frog muscle. J Physiol. 1956 Sep 27;133(3):631–658. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARAKI T., OTANI T. Response of single motoneurons to direct stimulation in toad's spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1955 Sep;18(5):472–485. doi: 10.1152/jn.1955.18.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biersteker P. A., Collewijn H., Van Harreveld A. Asphyxial potentials of spinal grey matter, and of ventral and dorsal roots. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):15–29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collewijn H., Van Harreveld A. Intracellular recording from spinal motoneurones in cats with post-asphyxial rigidity. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(1):30–41. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., KOSTYUK P. G., SCHMIDT R. F. Central pathways responsible for depolarization of primary afferent fibres. J Physiol. 1962 May;161:237–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITO M., OSHIMA T. FURTHER STUDY ON THE ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF SODIUM ACROSS THE MOTONEURONAL MEMBRANE. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Nov 17;161:132–141. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITO M., OSHIMA T. THE ELECTROGENIC ACTION OF CATIONS ON CAT SPINAL MOTONEURONS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Nov 17;161:92–108. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOLMODIN G. M., SKOGLUND C. R. Influence of asphyxia on membrane potential level and action potentials of spinal motoand interneurons. Acta Physiol Scand. 1959 Jan 30;45(1):1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1959.tb01673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSTYUK P. G. INTRINSIC POTENTIALS OF GLASS MICROELECTRODES. Fed Proc Transl Suppl. 1965 Mar-Apr;24:329–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. C. Influence of asphyxia upon the responses of spinal motoneurons. J Gen Physiol. 1953 May;36(5):673–702. doi: 10.1085/jgp.36.5.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON P. G., FRANK K. Intracellularly recorded responses of nerve cells to oxygen deprivation. Am J Physiol. 1963 Jul;205:208–212. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.1.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HARREVELD A. Asphyxial changes in the cerebellar cortex. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1961 Apr;57:101–110. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030570207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HARREVELD A. Water and electrolyte distribution in central nervous tissue. Fed Proc. 1962 May-Jun;21:659–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANHARREVELD A., BIERSTEKER P. A. ACUTE ASPHYXIATION OF THE SPINAL CORD AND OF OTHER SECTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jan;206:8–14. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


