Abstract
1. In intracellular studies of cat lumbar motoneurones constant synaptic stimuli such as stretch, contraction or a high-frequency stimulation of a cut afferent nerve have been superimposed on firing in response to injected currents.
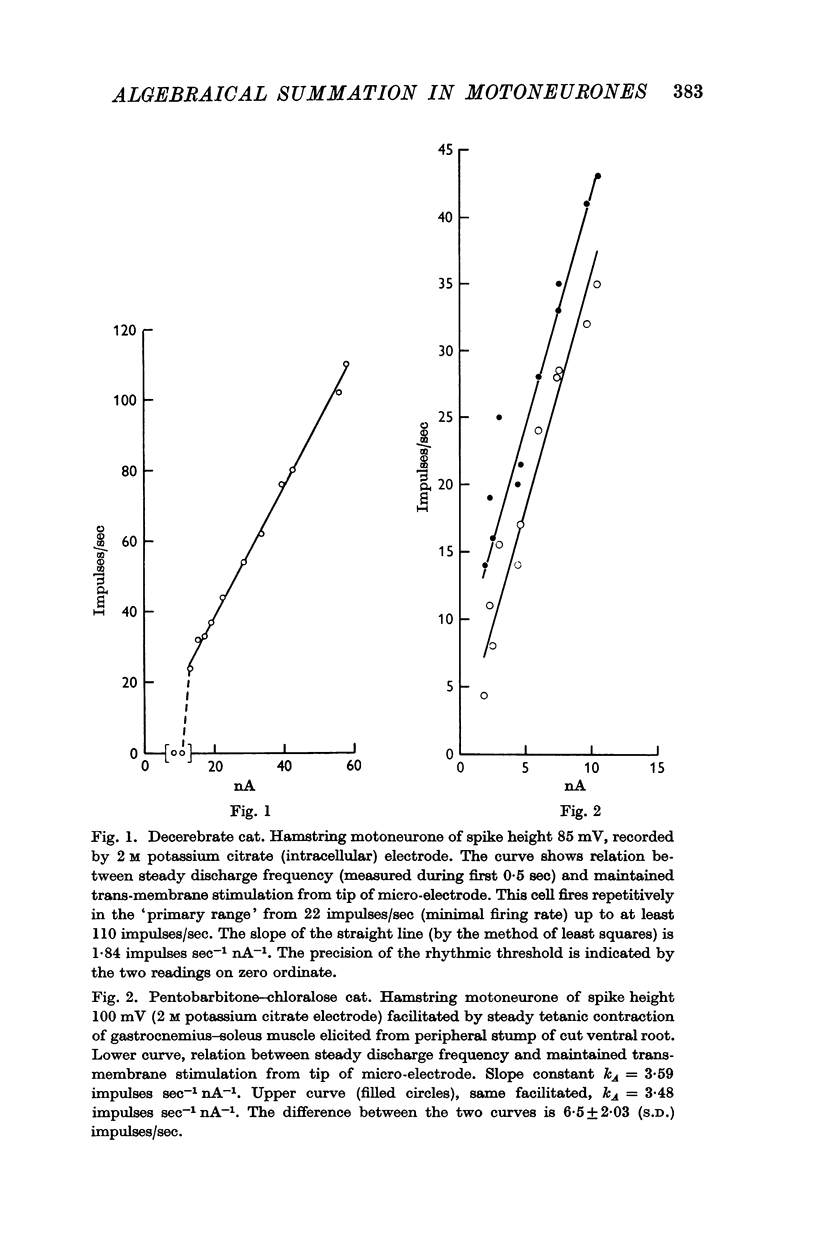
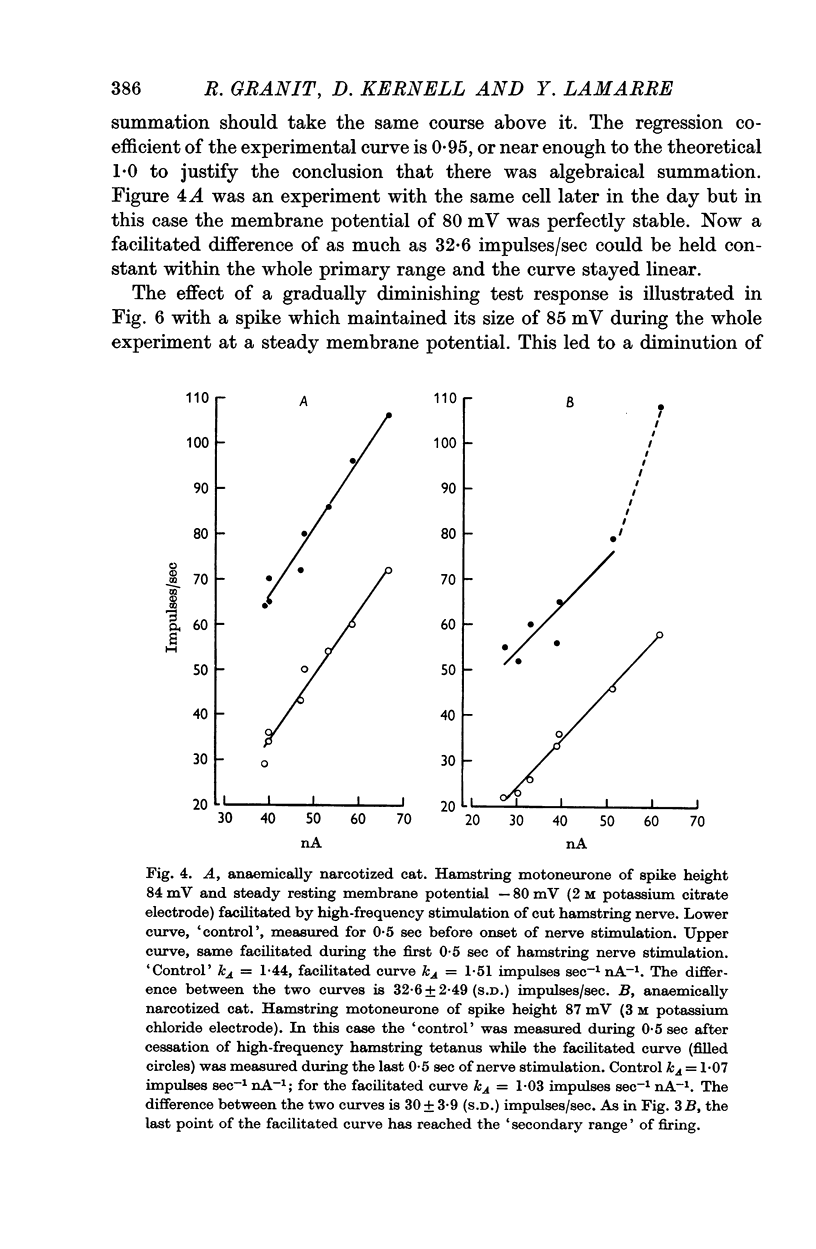
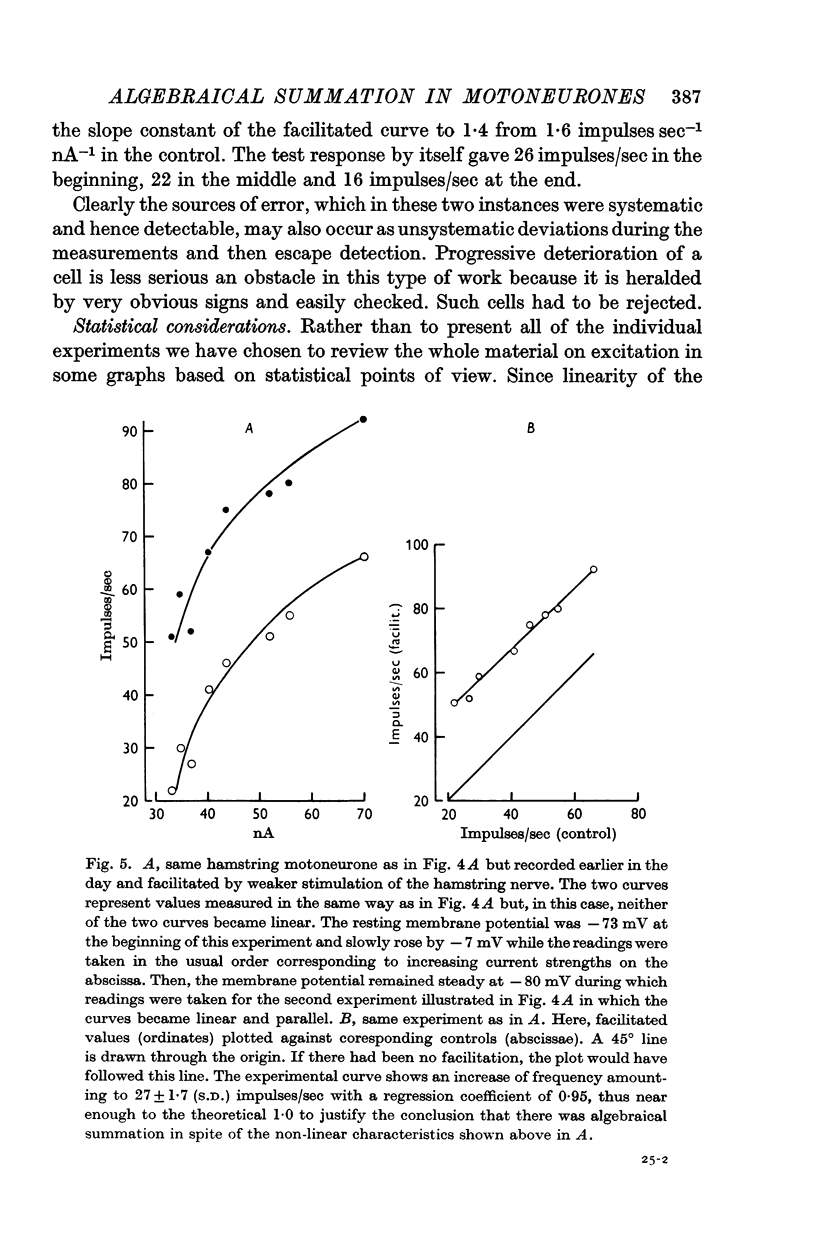
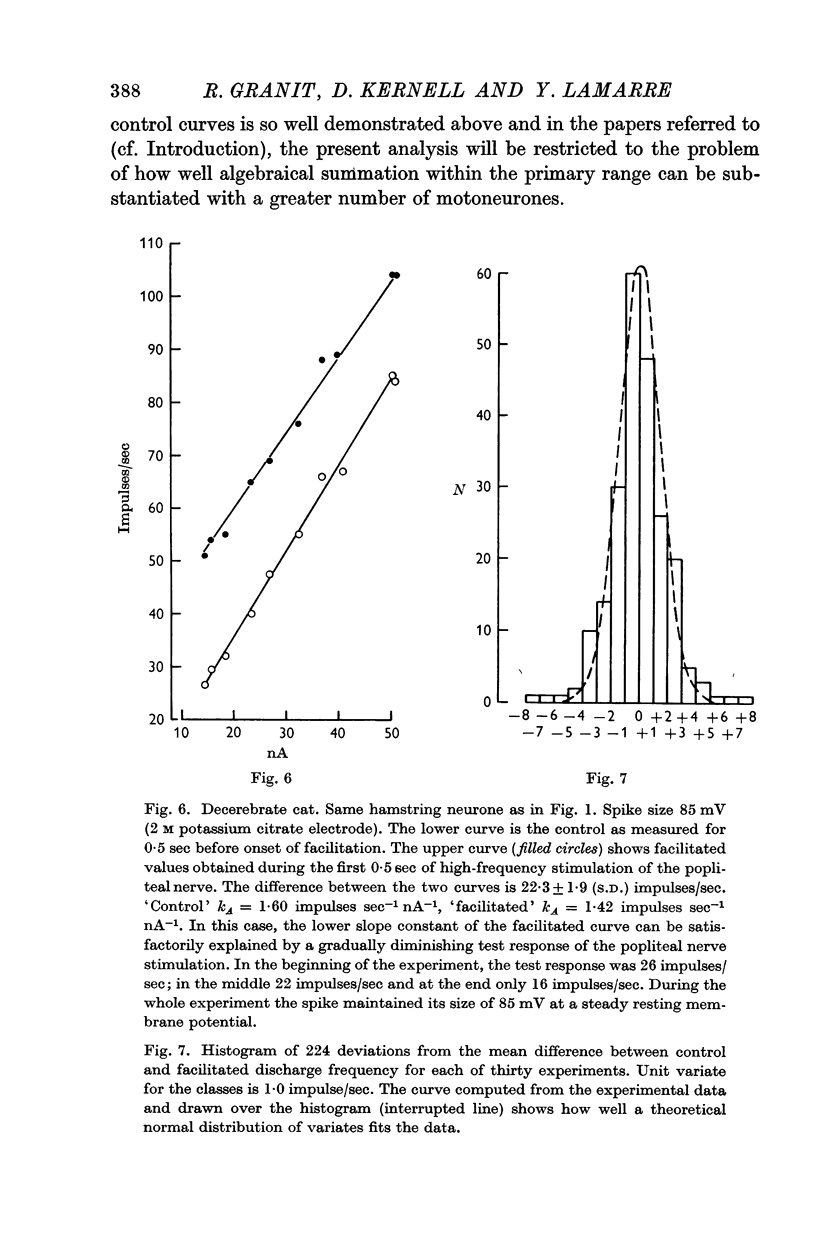
2. As long as the slope relating spike frequency to injected current remained constant, which by definition is the `primary range' of firing, algebraical summation of superimposed synaptic stimulation prevailed. Added quantities in these experiments were then between 2·0 and 56·2 impulses/sec for excitation, between -2·8 and -21·8 impulses/sec for inhibition.
3. Data were obtained correlating firing rates with amount of synaptic potential and current respectively.
4. Theoretical implications are dealt with in the Discussion.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COOMBS J. S., CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. The electrical constants of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 12;145(3):505–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., IGGO A., ITO M. Distribution of recurrent inhibition among motoneurones. J Physiol. 1961 Dec;159:479–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The action potentials of the alpha motoneurones supplying fast and slow muscles. J Physiol. 1958 Jul 14;142(2):275–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., VALLBO A. B. ACCOMMODATION IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS AS COMPUTED ON THE BASIS OF VOLTAGE CLAMP DATA. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Jan-Feb;63:1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Stimulation of spinal motoneurones with intracellular electrodes. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUORTES M. G. Initiation of impulses in visual cells of Limulus. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:14–28. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KELLERTH J. O., WILLIAMS T. D. INTRACELLULAR ASPECTS OF STIMULATING MOTONEURONES BY MUSCLE STRETCH. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:435–452. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KERNELL D., SHORTESS G. K. QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF REPETITIVE FIRING OF MAMMALIAN MOTONEURONES, CAUSED BY INJECTED CURRENTS. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:911–931. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KERNELL D., SMITH R. S. DELAYED DEPOLARIZATION AND THE REPETITIVE RESPONSE TO INTRACELLULAR STIMULATION OF MAMMALIAN MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:890–910. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., PASCOE J. E., STEG G. The behaviour of tonic alpha and gamma motoneurones during stimulation of recurrent collaterals. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):381–400. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., PHILLIPS C. G., SKOGLUND S., STEG G. Differentiation of tonic from phasic alpha ventral horn cells by stretch, pinna and crossed extensor reflexes. J Neurophysiol. 1957 Sep;20(5):470–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1957.20.5.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., RENKIN B. Net depolarization and discharge rate of motoneurones, as measured by recurrent inhibition. J Physiol. 1961 Oct;158:461–475. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granit R., Kernell D., Lamarre Y. Synaptic stimulation superimposed on motoneurones firing in the 'secondary range' to injected current. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(2):401–415. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M. Excitability following antidromic activation in spinal motoneurones supplying red muscles. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:374–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSHTON W. A. A theoretical treatment of Fuortes's observations upon eccentric cell activity in Limulus. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:29–38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERZUOLO C. A., WASHIZU Y. Relation between stimulus strength, generator potential and impulse frequency in stretch receptor of Crustacea. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Jan;25:56–66. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


