Abstract
Twenty-five patients were treated with a distal spleno-renal shunt modified after that of Warren. The operative mortality was 4/25. One patient had an early thrombosis. All post-operative angiography otherwise showed patent shunts. After a median observation time of 43 months, 10/20 patients included in the followup were dead. The chief cause of death was liver failure. Encephalopathy has been common although generally of minor degree. Hypersplenism, judged by thrombocyte count, was not significantly affected by the operation. Six of 21 patients have had gastrointestinal hemorrhage after the operation but no hemorrhage proved fatal. Postoperatively esophageal varices size was considerably diminished in most cases as judged by contrast x-ray. Ascites has not been a problem in this series. Postoperative angiography showed a marked and rapid reduction of portal blood flow to the liver with progressively more blood deviated through the coronary vein towards the shunt. This reduction in portal flow is a possible explanation of the high frequency of postoperative liver failure. This version of the distal spleno-renal shunt has probably no advantages over the portacaval shunt.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRICK I. B., PALMER E. D. ONE THOUSAND CASES OF PORTAL CIRRHOSIS OF THE LIVER. IMPLICATIONS OF ESOPHAGEAL VARICES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT. Arch Intern Med. 1964 Apr;113:501–511. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1964.00280100009003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengmark S. Surgical management of portal hypertension. Clin Gastroenterol. 1975 May;4(2):395–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN R., BLAISDELL F. W. The natural history of the patient with cirrhosis of the liver with esophageal varices following the first massive hemorrhage. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1958 Jun;106(6):699–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn H. O., Lindenmuth W. W., May C. J., Ramsby G. R. Prophylactic portacaval anastomosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1972 Jan;51(1):27–40. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197201000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet N. L'anastomose spléno-rénale distale dans le traitement de l'hypertension portale chez le cirrhotique. Acta Chir Belg. 1974 Sep;73(5):539–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCray R. S., Martin F., Amir-Ahmadi H., Sheahan D. G., Zamcheck N. Erroneous diagnosis of hemorrhage from esophageal varices. Am J Dig Dis. 1969 Nov;14(11):755–760. doi: 10.1007/BF02235964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen W. P. Therapeutic portacaval shunt. Preliminary data on controlled trial and morbid effects of acute hyaline necrosis. Arch Surg. 1974 Mar;108(3):302–305. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01350270036007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosimann R., Rausis C. La décompression élective des varices oeso-gastriques par anatomose spléno-rénale distale. Helv Chir Acta. 1974 Mar;41(1-2):89–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabseth D. C., Widrich W. C., O'Hara E. T., Johnson W. C. Flow and pressure characteristics of the portal system before and after splenorenal shunts. Surgery. 1975 Dec;78(6):739–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick R. H., Chalmers T. C., Ishihara A. M., Garceau A. J., Callow A. D., Schimmel E. M., O'Hara E. T. A controlled study of the prophylactic portacaval shunt. A final report. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Apr;70(4):675–688. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-4-675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick R. H., Iber F. L., Ishihara A. M., Chalmers T. C., Zimmerman H. A controlled study of the therapeutic portacaval shunt. Gastroenterology. 1974 Nov;67(5):843–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salam A. A., Warren W. D., LePage J. R., Viamonte M. R., Hutson D., Zeppa R. Hemodynamic contrasts between selective and total portal-systemic decompression. Ann Surg. 1971 May;173(5):827–844. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197105000-00022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver D., Puckett C. L., McNeer J. F., McLeod M. E., Sabiston D. C., Jr Evaluation of selective transsplenic decompression of gastroesophageal varices. Am J Surg. 1974 Jan;127(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(74)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira E. D., Yu H., Conn J., Jr, Bergan J. J. Selective decompression of esophagogastric varices. Arch Surg. 1968 Jan;96(1):4–8. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1968.01330190006002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomford N. R., Sirinek K. R., Martin E. W., Jr A series of 20 successful Warren shunts. Arch Surg. 1975 May;110(5):584–587. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1975.01360110130021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. D., Fomon J. J., Zeppa R. Further evaluation of selective decompression of varices by distal splenorenal shunt. Ann Surg. 1969 May;169(5):652–660. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196905000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
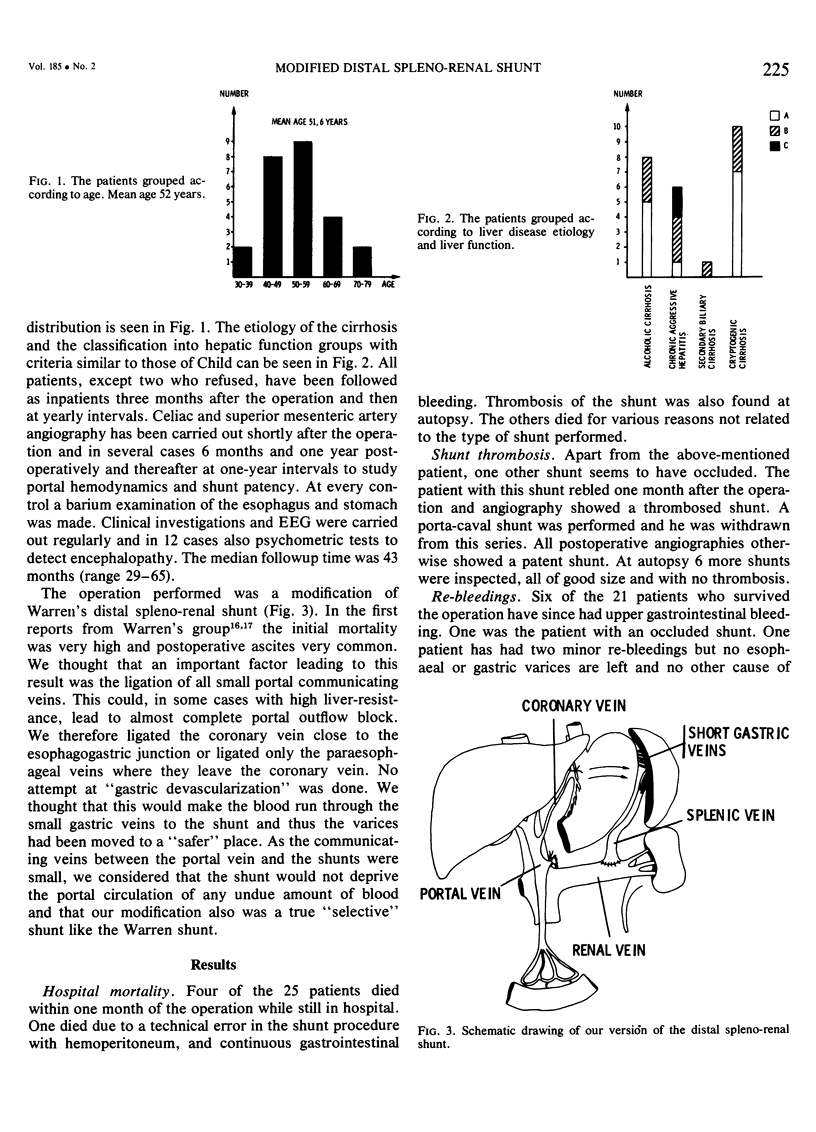
- Warren W. D., Salam A. A., Hutson D., Zeppa R. Selective distal splenorenal shunt. Technique and results of operation. Arch Surg. 1974 Mar;108(3):306–314. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01350270040008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. D., Zeppa R., Fomon J. J. Selective trans-splenic decompression of gastroesophageal varices by distal splenorenal shunt. Ann Surg. 1967 Sep;166(3):437–455. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196709000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]