Abstract
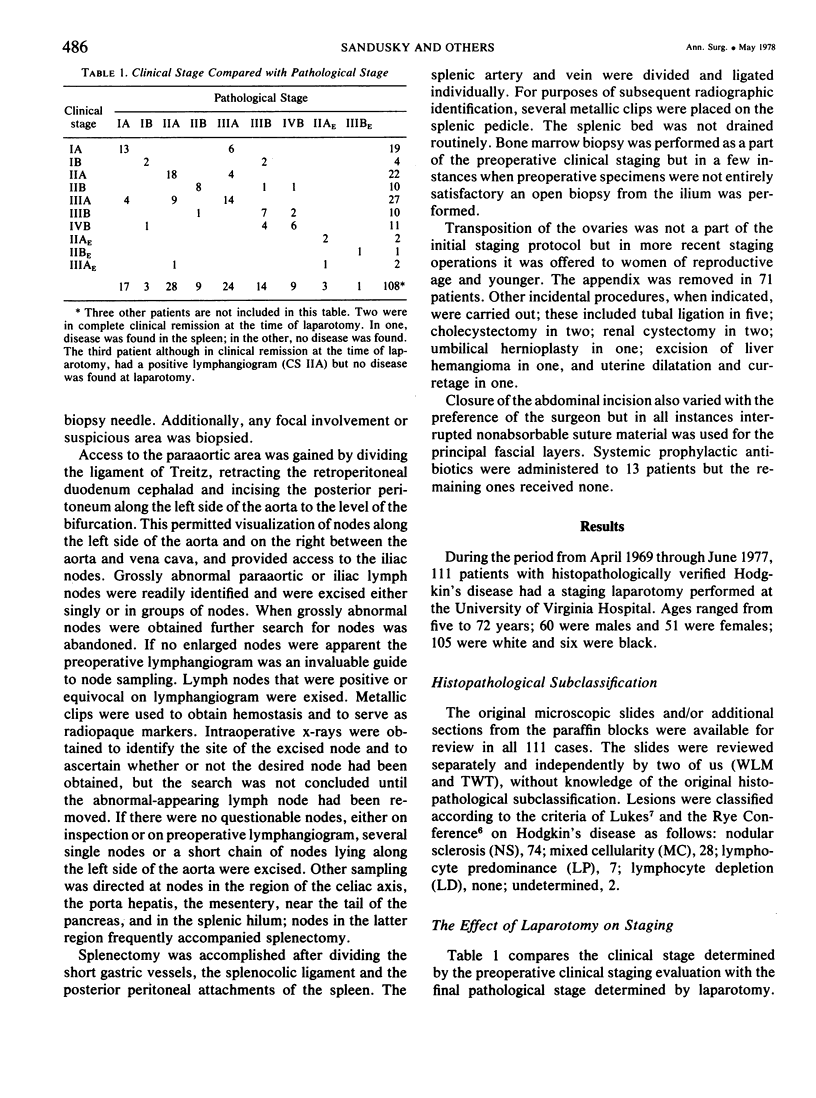
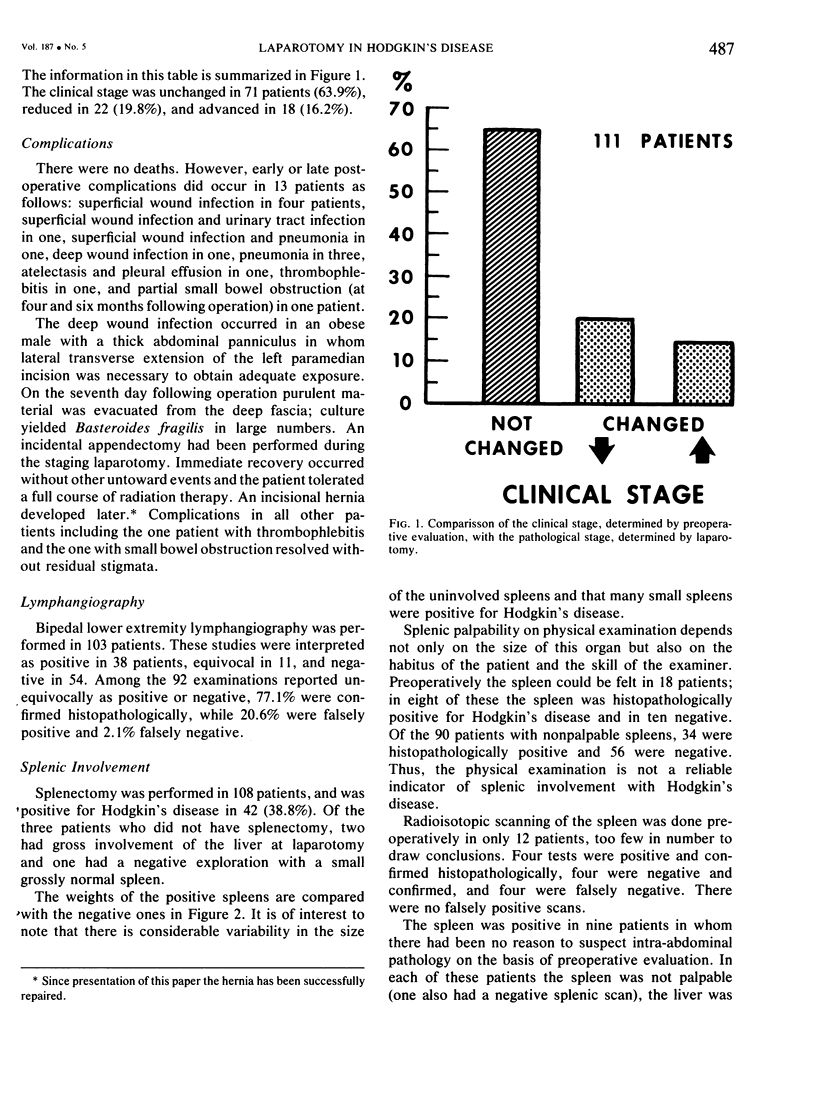
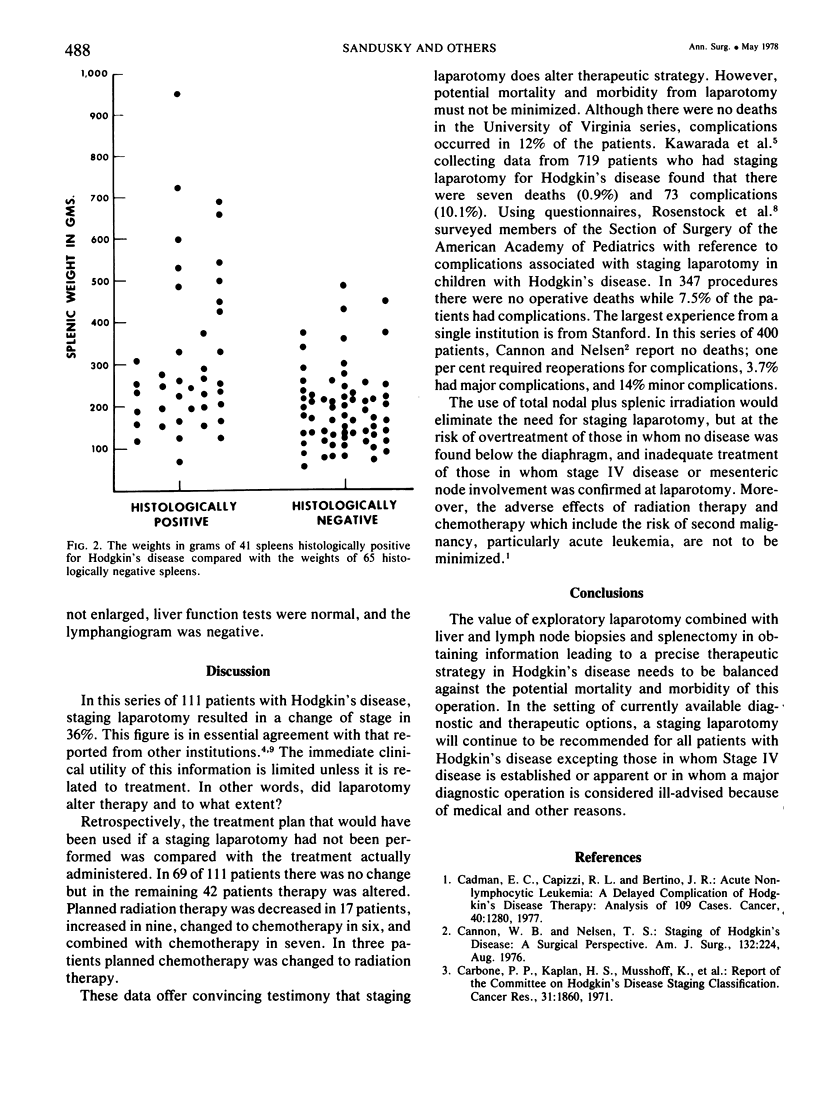
Staging laparotomy was performed at the University of Virginia Medical Center on 111 patients with Hodgkin's disease. The operation included multiple liver and lymph node biopsies and, excepting three patients, splenectomy. The histopathology was reviewed and the 111 patients were classified as follows: nodular sclerosis, 74; mixed cellularity, 28; lymphocyte predominance, 7; and undetermined, 2. There were no deaths. Wound, pulmonary or urinary tract complications occurred in 11 patients. One case of postoperative thrombophlebitis occurred and in another case small bowel obstruction developed, and resolved without reoperation. The pathologic stage (PS) following laparotomy was unchanged from the clinical stage (CS) in 64%, reduced in 20%, and advanced in 16%. The therapy, however, was altered in 38% of the patients. Lymphangiography in 103 patients was interpreted as showing lymph node involvement in 38, equivocal involvement in 11, and no involvement in 54. Among the 92 examinations reported as either positive or negative, 77% were confirmed histopathologically, 21% were falsely positive, and 2% were falsely negative. The spleen was positive for Hodgkin's disease in 39% of cases, and in these patients with positive spleens there was no reason to suspect intra-abdominal involvement preoperatively in 21%.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cadman E. C., Capizzi R. L., Bertino J. R. Acute nonlymphocytic leukemia: a delayed complication of Hodgkin's disease therapy: analysis of 109 cases. Cancer. 1977 Sep;40(3):1280–1296. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197709)40:3<1280::aid-cncr2820400343>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon W. B., Nelsen T. S. Staging of Hodgkin's disease: a surgical perspective. Am J Surg. 1976 Aug;132(2):224–230. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(76)90052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone P. P., Kaplan H. S., Musshoff K., Smithers D. W., Tubiana M. Report of the Committee on Hodgkin's Disease Staging Classification. Cancer Res. 1971 Nov;31(11):1860–1861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatstein E., Guernsey J. M., Rosenberg S. A., Kaplan H. S. The value of laparotomy and splenectomy in the staging of Hodgkin's disease. Cancer. 1969 Oct;24(4):709–718. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196910)24:4<709::aid-cncr2820240408>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawarada Y., Goldberg L., Brady L., Pavlides C., Matsumoto T. Staging laparotomy for Hodgkin's disease. Am Surg. 1976 May;42(5):332–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukes R. J. Criteria for involvement of lymph node, bone marrow, spleen, and liver in Hodgkin's disease. Cancer Res. 1971 Nov;31(11):1755–1767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstock J. G., D'Angio G. J., Kiesewetter W. B. Proceedings: The incidence of complications following staging laparotomy for Hodgkin's disease in children. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1974 Mar;120(3):531–535. doi: 10.2214/ajr.120.3.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe S. B., Wrigley P. F., Smyth J. F., Webb J. A., Tucker A. K., Beard M. E., Irving M., Stansfeld A. G., Malpas J. S., Crowther D. Intensive investigation in management of Hodgkin's disease. Br Med J. 1976 Dec 4;2(6048):1343–1347. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6048.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


