Abstract
Jejunoileal bypass surgery is fraught with many longterm complications, among which is hypovitaminosis D. The relationship, if any, of hypovitaminosis D to the skeletal disease which may occur following this operation is, however, unknown. Consequently, we studied eight patients with low circulating levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D who had undergone jejunoileal bypass at least two and one-half years previously. Despite the absence of skeletal symptoms, the bone biopsies of six of these patients were abnormal. The volume of trabecular bone was diminished in the group as a whole, and half the patients had an excess of unmineralized skeletal matrix. However, no noninvasive diagnostic technique identified those patients with skeletal disease. We therefore conclude that recognition of those jejunoileal bypass patients potentially at risk to develop clinically significant bone disease requires biopsy of the skeleton.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DeWind L. T., Payne J. H. Intestinal bypass surgery for morbid obesity. Long-term results. JAMA. 1976 Nov 15;236(20):2298–2301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood J. B., Bordier P. J., Clarkson E. M., Tun Chot S., de Wardener H. E. The contrasting effects on bone histology of vitamin D and of calcium carbonate in the osteomalacia of chronic renal failure. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Jul;47(1):23–42. doi: 10.1042/cs0470023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost H. M. Tetracycline-based histological analysis of bone remodeling. Calcif Tissue Res. 1969;3(3):211–237. doi: 10.1007/BF02058664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garn S. M., Poznanski A. K., Nagy J. M. Bone measurement in the differential diagnosis of osteopenia and osteoporosis. Radiology. 1971 Sep;100(3):509–518. doi: 10.1148/100.3.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J. G., Chyu K. J. Competitive protein-binding radioassay for 25-hydroxycholecalciferol. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Dec;33(6):992–995. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-6-992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J. G., Jr, Chyu K. J., Hahn T. J., Stamp T. C. Serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in sex-linked hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Jan;81(1):22–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halverson J. D., Wise L., Wazna M. F., Ballinger W. F. Jejunoileal bypass for morbid obesity. A critical appraisal. Am J Med. 1978 Mar;64(3):461–475. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90233-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meema H. E., Oreopoulos D. G., Meema S. A roentgenologic study of cortical bone resorption in chronic renal failure. Radiology. 1978 Jan;126(1):67–74. doi: 10.1148/126.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
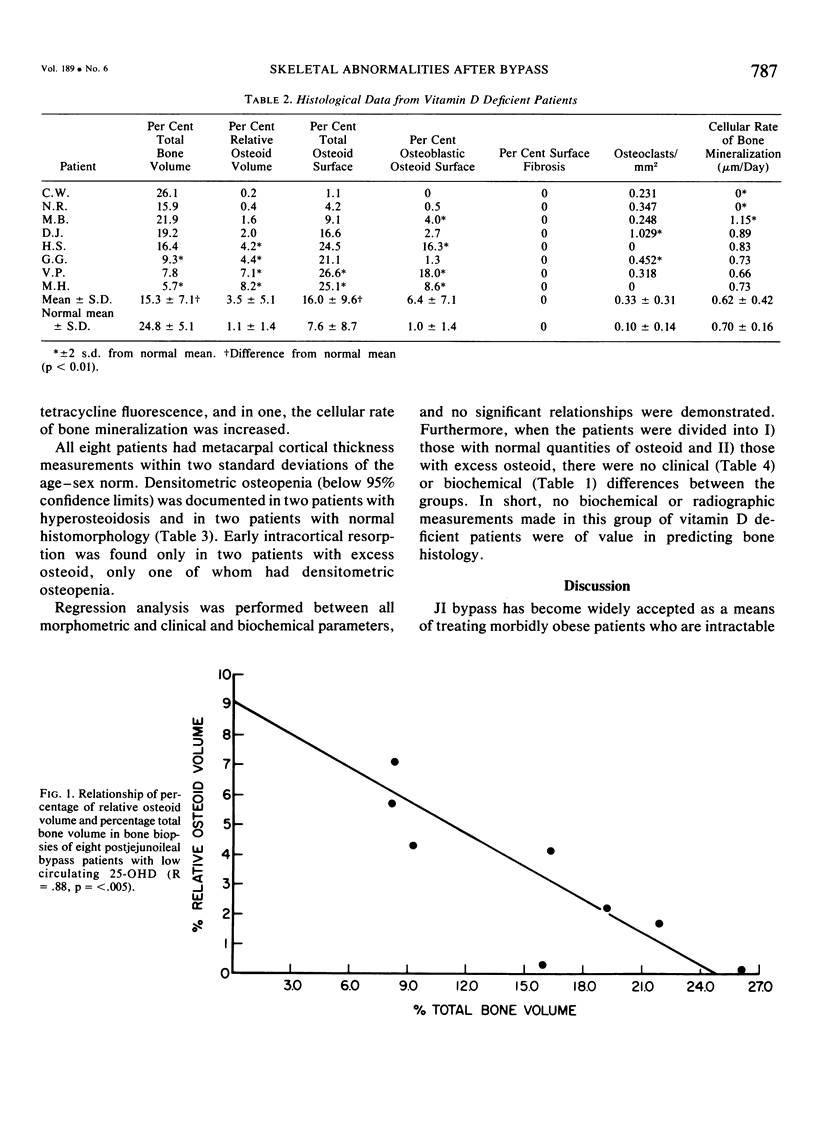
- Parfitt A. M., Miller M. J., Frame B., Villanueva A. R., Rao D. S., Oliver I., Thomson D. L. Metabolic bone disease after intestinal bypass for treatment of obesity. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Aug;89(2):193–199. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-2-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. W., Jr, Dean R., Shull H. J., Abram H. S., Webb W., Younger R. K., Brill A. B. Considerations in use of jejunoileal bypass in patients with morbid obesity. Ann Surg. 1973 Jun;177(6):723–735. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197306000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrard D. J., Baylink D. J., Wergedal J. E., Maloney N. A. Quantitative histological studies on the pathogenesis of uremic bone disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Jul;39(1):119–135. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson J. A., Cameron J. R. A reliable in vivo measurement of bone-mineral content. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1967 Apr;49(3):481–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamp T. C. Intestinal absorption of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol. Lancet. 1974 Jul 20;2(7873):121–123. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91553-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum S. L., Halverson J. D., Bates M., Wise L., Haddad J. G. Abnormalities of circulating 25-OH vitamin D after jejunal-lleal bypass for obesity: evidence of an adaptive response. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Mar;86(3):289–293. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-3-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum S. L., Hruska K. A., Shieber W., Debnam J. W., Nichols S. H. Tetracycline fluorescence in uremic and primary hyperparathyroid bone. Kidney Int. 1977 Nov;12(5):366–372. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]