Abstract
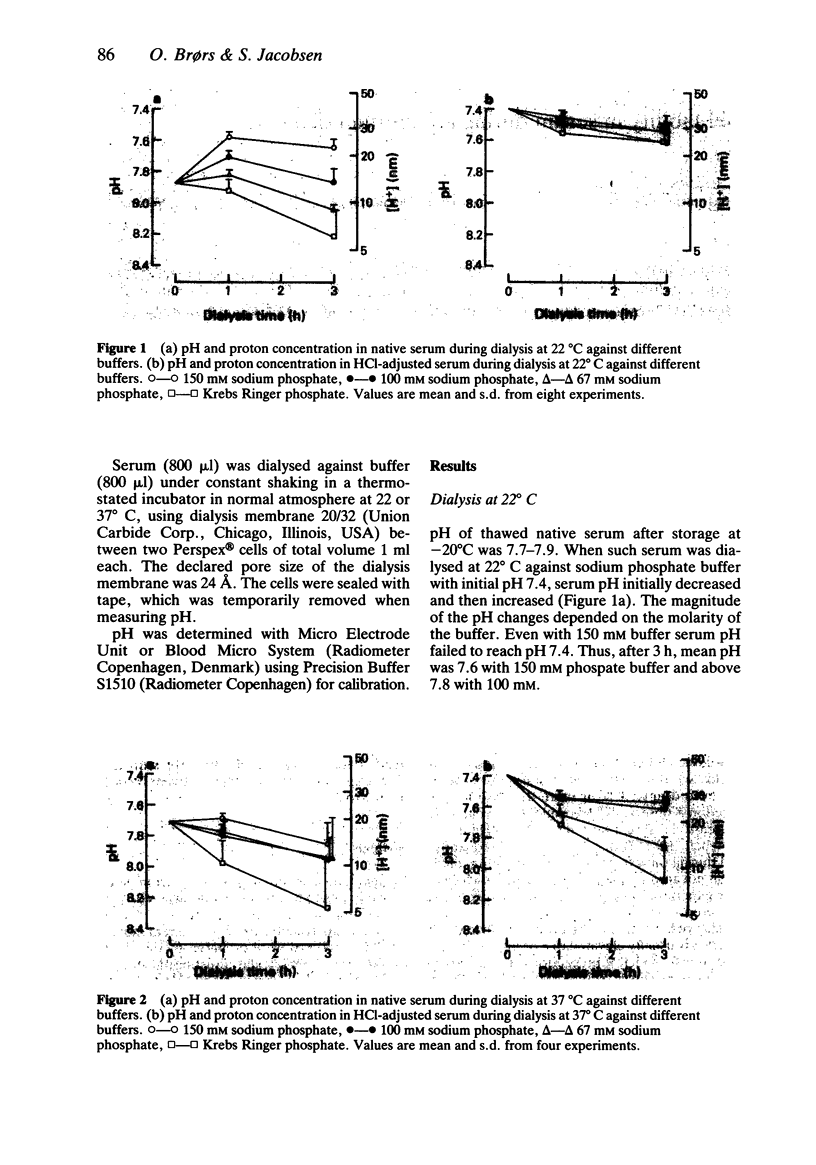
Changes in pH were determined in previously frozen normal human serum during dialysis against sodium phosphate, Krebs Ringer phosphate or Krebs Ringer bicarbonate buffers of pH 7.4. Serum was either untreated (native) or adjusted to pH 7.4 before dialysis. pH in native serum was 7.7-7.9 before dialysis, showed a decrease after 1 h, and an increase after 3 h. pH-adjusted serum showed a continuous pH increase during dialysis. The increase in serum pH during dialysis was larger at 37 degrees C than at 22 degrees C, larger at low than at high buffer molarity, and larger in native than in pH-adjusted serum. The observed changes in serum pH during dialysis are associated with unacceptably large errors in unbound fraction in serum for a number of important drugs. Drug binding determination in serum by equilibrium dialysis should be performed with buffers providing appropriate and stable pH level.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brørs O., Sager G., Sandnes D., Jacobsen S. Binding of theophylline in human serum determined by ultrafiltration and equilibrium dialysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Apr;15(4):393–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBAUM L. R., SMITH P. K. The interaction of barbiturates with serum albumin and its possible relation to their disposition and pharmacological actions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Jun;111(2):197–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry J. A., Dunlop A. W., Mitchell S. N., Turner P., Adams P. A model for the pH dependence of drug-protein binding. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;33(3):179–182. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen C. B., Gram L. F. Equilibrium dialysis for determination of protein binding or imipramine--evaluation of a method. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1982 Feb;50(2):130–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1982.tb00954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Rosa C., Mather L. E., Morgan D. J. Pethidine binding in plasma: effects of methodological variables. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Apr;17(4):411–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw L. M., Fields L., Mayock R. Factors influencing theophylline serum protein binding. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Oct;32(4):490–496. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallner J. J., Speir W. A., Jr, Kolbeck R. C., Harrison G. N., Bransome E. D., Jr Effect of pH on the binding of theophylline to serum proteins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jul;120(1):83–86. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilting J., van der Giesen W. F., Janssen L. H., Weideman M. M., Otagiri M., Perrin J. H. The effect of albumin conformation on the binding of warfarin to human serum albumin. The dependence of the binding of warfarin to human serum albumin on the hydrogen, calcium, and chloride ion concentrations as studied by circular dichroism, fluorescence, and equilibrium dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3032–3037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


