Abstract
1 The evidence for the presence of postjunctional α1- and α2-adrenoceptor subtypes in human blood vessels is reviewed.
2 Experiments in healthy subjects are described that show that α1- as well as α2-adrenoceptor mediated vasoconstriction contribute to vascular smooth muscle tone and that adrenaline and noradrenaline have similar affinities for each subtype. In addition, evidence is presented for a preferential intrajunctional location of α1-adrenoceptors and a preferential extrajunctional location of α2-adrenoceptors in human blood vessels.
3 It is concluded that at present postjunctional α-adrenoceptors in human blood vessels can be classified as α1 and α2. Despite the fact that both subtypes mediate vasoconstriction, these receptors are likely to subserve different physiological functions.
Keywords: α-adrenoceptors, catecholamines, forearm blood flow, human blood vessels
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abboud F. M., Schmid P. G., Eckstein J. W. Vascular responses after alpha adrenergic receptor blockade: I. Responses of capacitance and resistance vessels to norepinephrine in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1172/JCI105699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariëns E. J., Simonis A. M. Physiological and pharmacological aspects of adrenergic receptor classification. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 May 15;32(10):1539–1545. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcroft H., Bonnar W. M., Edholm O. G., Effron A. S. On sympathetic vasoconstrictor tone in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1943 Jun 30;102(1):21–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1943.sp004010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli P., Erne P., Kiowski W., Amman F. W., Bühler F. R. The adrenaline-alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated vasoconstrictor axis. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;68 (Suppl 10):141s–146s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M., Whiting S. B. Evidence for two distinct types of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;67(2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott H. L., Reid J. L. Evidence for postjunctional vascular alpha 2-adrenoceptors in peripheral vascular regulation in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Sep;65(3):237–241. doi: 10.1042/cs0650237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan N. A., McGrath J. C. Are human vascular alpha-adrenoceptors atypical? J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):208–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. R., Robertson D. Evidence for the existence of vascular alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in humans. Hypertension. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):551–556. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.6.4.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo J., Jr Cardiovascular hormonal effects of circulating norepinephrine. Hypertension. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):787–789. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.5.5.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauernig R. A., Moulds R. F., Shaw J. The action of prazosin in human vascular preparations. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1978 Jan;231(1):81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
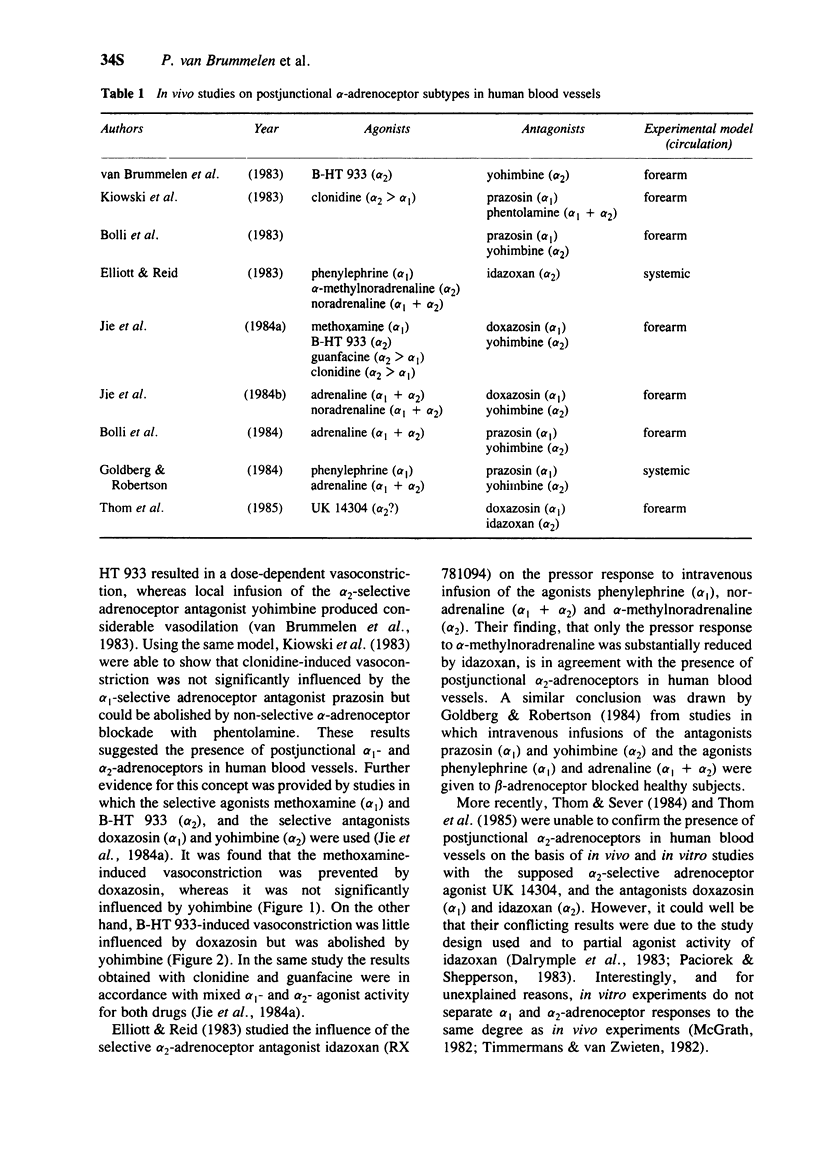
- Jie K., van Brummelen P., Vermey P., Timmermans P. B., van Zwieten P. A. Identification of vascular postsynaptic alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors in man. Circ Res. 1984 Apr;54(4):447–452. doi: 10.1161/01.res.54.4.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiowski W., Bühler F. R., van Brummelen P., Amann F. W. Plasma noradrenaline concentration and alpha-adrenoceptor-mediated vasoconstriction in normotensive and hypertensive man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 May;60(5):483–489. doi: 10.1042/cs0600483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiowski W., Hulthén U. L., Ritz R., Bühler F. R. Alpha 2 adrenoceptor-mediated vasoconstriction of arteries. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Nov;34(5):565–569. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWE R. D., ROBINSON B. F. EFFECT OF DIFFERENTIAL ADRENERGIC BLOCKADE ON RESPONSE OF FOREARM BLOOD FLOW TO INFUSED CATECHOLAMINES. Clin Sci. 1964 Feb;26:81–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z., Hicks P. E. Alpha-adrenoreceptor subtypes in blood vessels: physiology and pharmacology. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984;6 (Suppl 4):S547–S558. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198406004-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Presynaptic regulation of the release of catecholamines. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Dec;32(4):337–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Sixth gaddum memorial lecture, National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill, January 1977. Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):481–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Evidence for more than one type of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulds R. J., Jauernig R. A. Mechanism of prazosin collapse. Lancet. 1977 Jan 22;1(8004):200–201. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91808-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman R. A., Jr, Coleman T. G., Dent A. C. Continuous monitoring of arterial pressure indicates sinoaortic denervated rats are not hypertensive. Hypertension. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):119–125. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paciorek P. M., Shepperson N. B. alpha 1-Adrenoceptor agonist activity of alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists in the pithed rat preparation. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):12–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom S., Calvete J., Hayes R., Martin G., Sever P. Human vascular smooth muscle responses mediated by alpha 2 mechanisms in vivo and in vitro. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;68 (Suppl 10):147s–150s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., van Zwieten P. A. alpha 2 adrenoceptors: classification, localization, mechanisms, and targets for drugs. J Med Chem. 1982 Dec;25(12):1389–1401. doi: 10.1021/jm00354a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Brummelen P., Jie K., Vermey P., Timmermans P. B., van Zwieten P. A. Vascular alpha-adrenoceptors in man: interactions with adrenaline and noradrenaline. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;68 (Suppl 10):151s–153s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


