Abstract
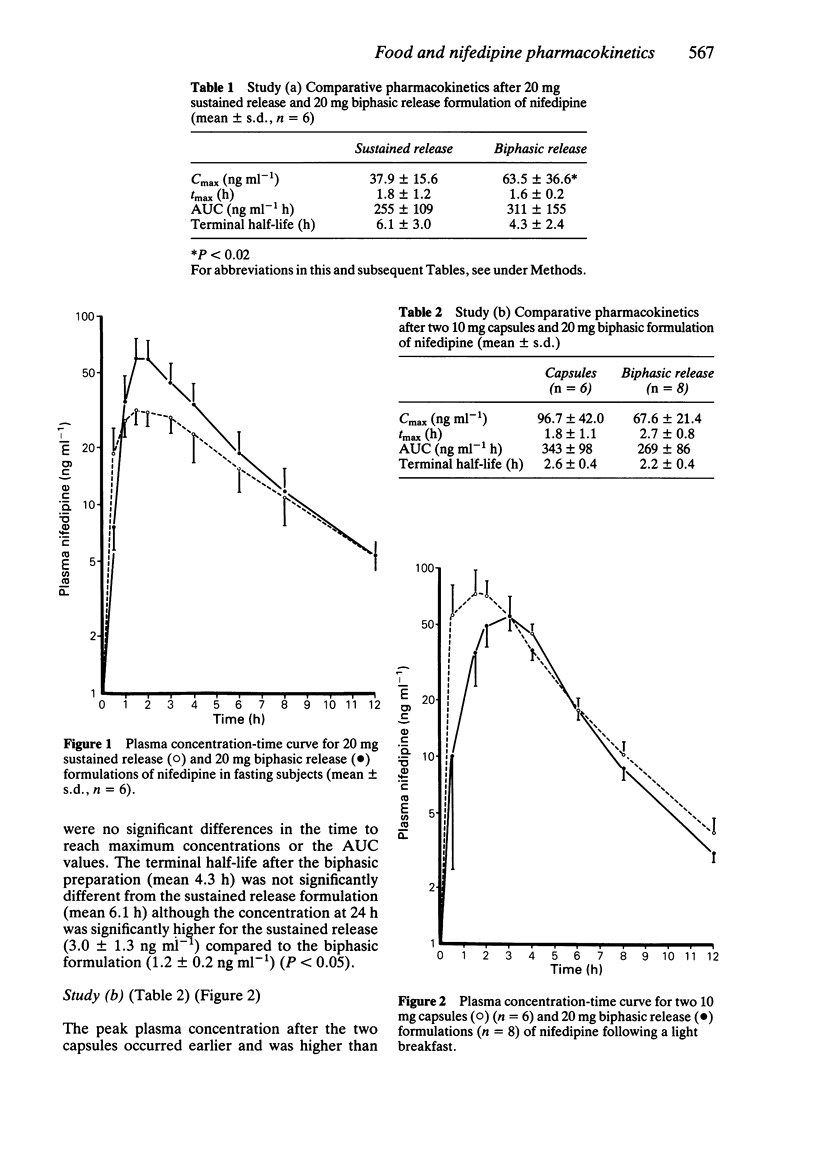
The pharmacokinetics of a novel 20 mg biphasic release tablet of nifedipine were compared with the conventional 10 mg capsule and 20 mg sustained release preparations in healthy volunteers. The influence of food and posture on the pharmacokinetics of the biphasic tablet were studied. In the fasting state, the time to peak concentration of nifedipine was not significantly different between the 20 mg biphasic and 20 mg sustained release tablets, but plasma concentrations were higher between 2 and 4 h after the biphasic tablet. The terminal elimination half-lives of the two formulations were similar. In subjects who fed prior to nifedipine administration there was no significant difference between either the peak plasma concentration or terminal half-life of the biphasic tablet and two 10 mg capsules of nifedipine. When the biphasic preparation was given after a standard breakfast, the time to peak plasma concentration was significantly longer and the terminal half-life shorter than when given in the fasting state. The dissolution characteristics of the biphasic tablet were influenced by prior administration of food to an extent which may be of clinical significance during twice daily administration.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki K., Sato K., Kawaguchi Y., Yamamoto M. Acute and long-term hypotensive effects and plasma concentrations of nifedipine in patients with essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1982;23(3):197–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00547553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banzet O., Colin J. N., Thibonnier M., Singlas E., Alexandre J. M., Corvol P. Acute antihypertensive effect and pharmacokinetics of a tablet preparation of nifedipine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;24(2):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00613808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brügmann U., Blasini R., Rudolph W. Antiischämische Wirkung von Nifepidin in Retard-Form. Ergebnisse einer doppelblind, randomisiert, cross-over durchgeführten, placebokontrollierten Akutstudie. Herz. 1983 Aug;8(4):206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. S., Hamann S. R., Richards V. R., Bryant P. J., Graves D. A., McAllister R. G. Nifedipine kinetics and bioavailability after single intravenous and oral doses in normal subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Apr;23(4):161–170. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1983.tb02720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. F. Drug kinetics and hepatic blood flow. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1979 Nov-Dec;4(6):433–448. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197904060-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills M., Armitage P. The two-period cross-over clinical trial. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;8(1):7–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb05903.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornung R. S., Gould B. A., Jones R. I., Sonecha T., Raftery E. B. Nifedipine tablets for hypertension: a study using continuous ambulatory intra-arterial recording. Postgrad Med J. 1983;59 (Suppl 2):95–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmark K. Antihypertensive and metabolic effects of long-term therapy with nifedipine slow-release tablets. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):12–17. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198501000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund-Johansen P., Omvik P. Haemodynamic effects of nifedipine in essential hypertension at rest and during exercise. J Hypertens. 1983 Aug;1(2):159–163. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198308000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch P., Dargie H., Krikler S., Krikler D. Objective assessment of antianginal treatment: a double-blind comparison of propranolol, nifedipine, and their combination. Br Med J. 1980 Jul 19;281(6234):184–187. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6234.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander A., McLean A. Influence of food intake on presystemic clearance of drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1983 Jul-Aug;8(4):286–296. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198308040-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller H. S., Chahine R. A. Interim report of multicenter double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of nifedipine in chronic stable angina. Am J Med. 1981 Oct;71(4):645–657. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs H. R., Rämsch K. D., Verburg-Ochs B., Greenblatt D. J., Gerloff J. Nifedipine: kinetics and dynamics after single oral doses. Klin Wochenschr. 1984 May 2;62(9):427–429. doi: 10.1007/BF01742301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibonnier M., Bonnet F., Corvol P. Antihypertensive effect of fractionated sublingual administration of nifedipine in moderate essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980;17(3):161–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00561894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller D. G., Renwick A. G., Gruchy B. S., George C. F. The first pass metabolism of nifedipine in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;18(6):951–954. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02569.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


