Abstract
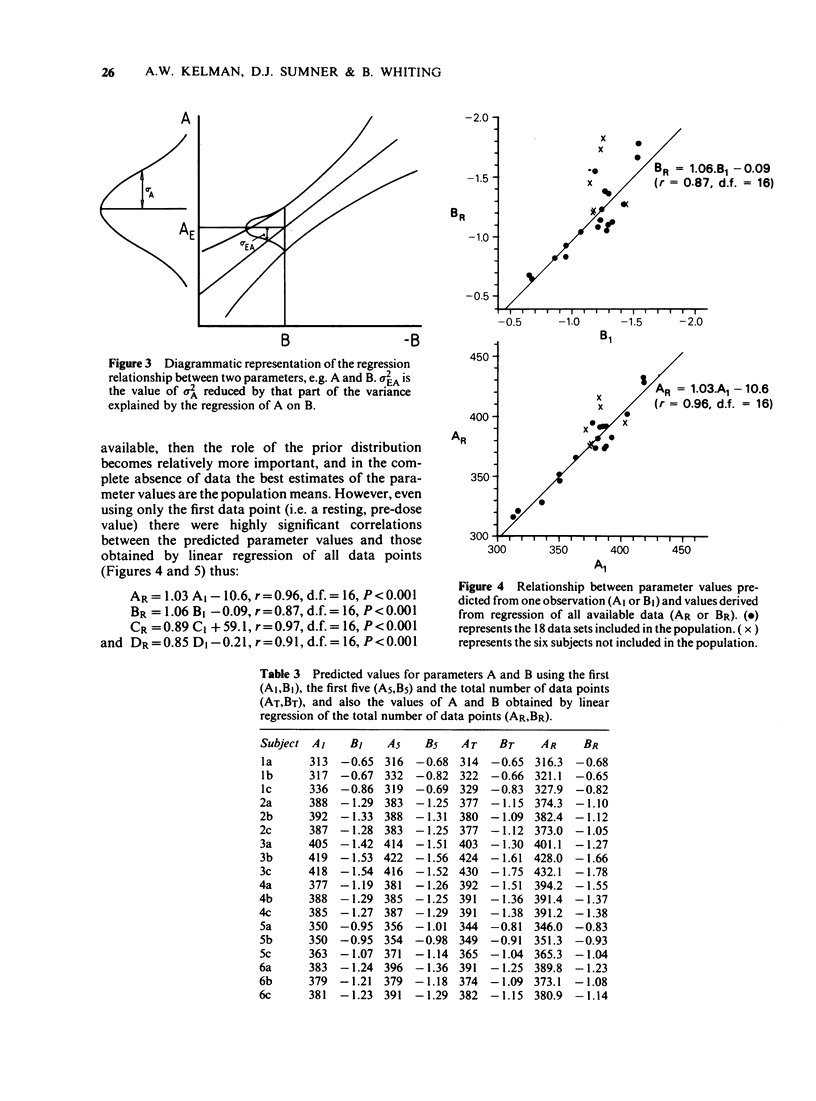
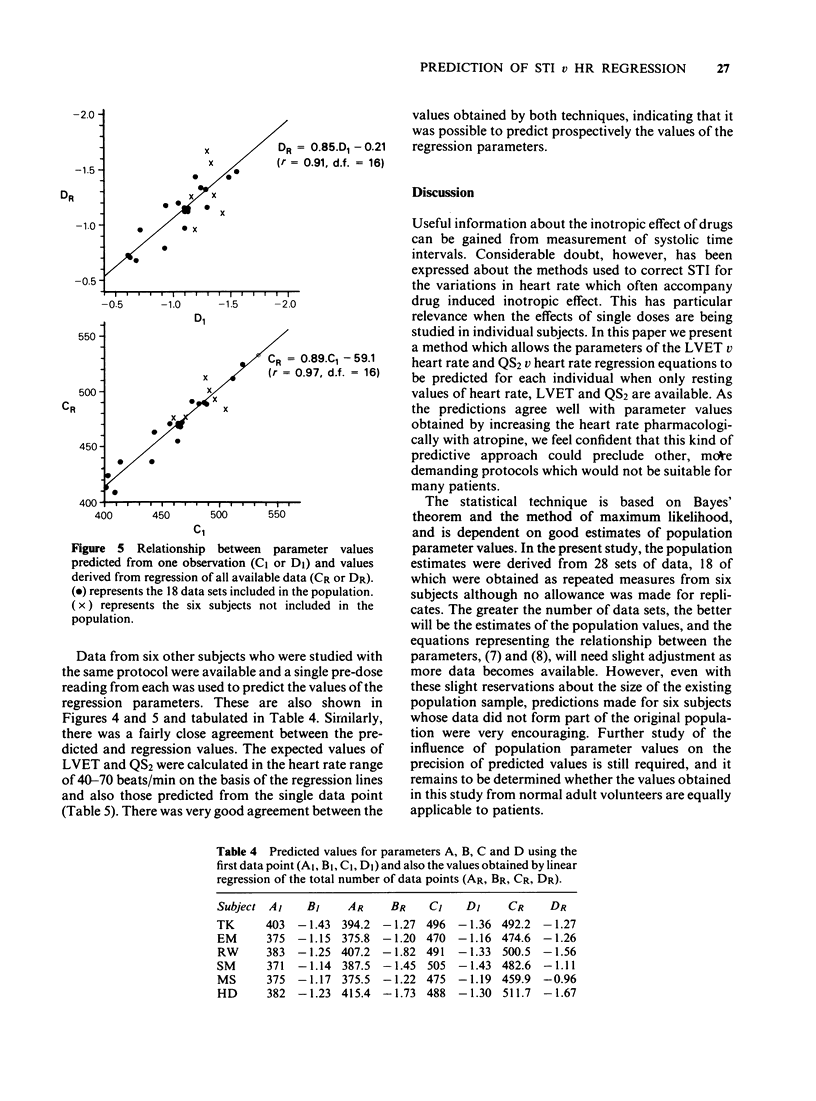
1. Twenty-eight sets of systolic time interval (STI) and heart rate (HR) data were available from studies in which small bolus doses of atropine had been given to alter heart rate. 2. Regression lines of the form LVET = A+B.HR and QS2 = C+D.HR were calculated. There was no significant relationship between PEP and HR. The values of the parameters A-D were normally distributed. 3. The maximum likelihood Estimation was used to obtain the most likely values of the parameters A-D for individual subjects. 4. The technique proved to be highly satisfactory and was subsequently validated with a further six sets of data.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess C. D., Wadsworth J., Warrington S. J. Evaluation of some non-invasive indices of cardiovascular function [proceedings]. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;7(4):436P–437P. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb00980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G. P., Talmers R. N., Weissler A. M. Comparative pharmacodynamics of betamethyl digoxin and digoxin in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Sep;22(3):280–285. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977223280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinderling P. H., Garrett E. R. Pharmacokinetics of beta-methyldigoxin in healthy humans III: Pharmacodynamic correlations. J Pharm Sci. 1977 Mar;66(3):326–329. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600660305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelman A. W., Sumner D. J., Lonsdale M., Lawrence J. R., Whiting B. Comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cardiac glycosides. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;10(2):135–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb01730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelman A. W., Sumner D. J., Whiting B. Systolic time interval v heart rate regression equations using atropine: reproducibility studies. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;12(1):15–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kligfield P. Systolic time intervals in atrial fibrillation and mitral stenosis. Br Heart J. 1974 Aug;36(8):798–805. doi: 10.1136/hrt.36.8.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. S., Armstrong T. G., Everson R. C., Gotsman M. S. Predictive value of the systolic time intervals in primary myocardial disease. Chest. 1973 Oct;64(4):431–438. doi: 10.1378/chest.64.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. S., Milne F. J., Goldberg B. Left ventricular function in chronic renal failure. Br Heart J. 1976 Dec;38(12):1229–1239. doi: 10.1136/hrt.38.12.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiner L. B., Beal S., Rosenberg B., Marathe V. V. Forecasting individual pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Sep;26(3):294–305. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979263294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes C. A., Wright A. D., Malins J. M., Pentecost B. L. Changes in systolic time intervals during treatment of diabetes mellitus. Br Heart J. 1977 Mar;39(3):255–259. doi: 10.1136/hrt.39.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Hoeven G. M., Clerens P. J., Donders J. J., Beneken J. E., Vonk J. T. A study of systolic time intervals during uninterrupted exercise. Br Heart J. 1977 Mar;39(3):242–254. doi: 10.1136/hrt.39.3.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waagstein F., Hjalmarson A. C., Wasir H. S. Apex cardiogram and systolic time intervals in acute myocardial infarction and effects of practolol. Br Heart J. 1974 Nov;36(11):1109–1121. doi: 10.1136/hrt.36.11.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissler A. M., Harris W. S., Schoenfeld C. D. Systolic time intervals in heart failure in man. Circulation. 1968 Feb;37(2):149–159. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.37.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissler A. M., Schoenfeld C. D. Effect of digitalis on systolic time intervals in heart failure. Am J Med Sci. 1970 Jan;259(1):4–20. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197001000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


