Abstract
1 The rates of noradrenaline spillover to, and removal from, plasma were measured in ten patients with essential hypertension treated with propranolol, to ascertain if long-term administration of this drug reduces sympathetic nervous system tone. 2 The plasma clearance of noradrenaline fell with propranolol, leading to a small rise in the mean plasma noradrenaline concentration. Sympathetic nervous activity in treated patients cannot be reliably gauged from plasma noradrenaline values because these are distorted by the reduction in noradrenaline clearance. 3 There was no consistent effect on noradrenaline spillover rates, which fell in six patients, but rose in the remaining four. The magnitude of the antihypertensive response was unrelated to these changes in noradrenaline release. During propranolol treatment, noradrenaline spillover rates were in every case within the normal range, much higher than in patients treated with the known sympathetic nervous systems suppressant, clonidine. 4 The principal mode of antihypertensive action of propranolol is something often than central suppression of sympathetic tone or pre-synaptic inhibition of noradrenaline release.
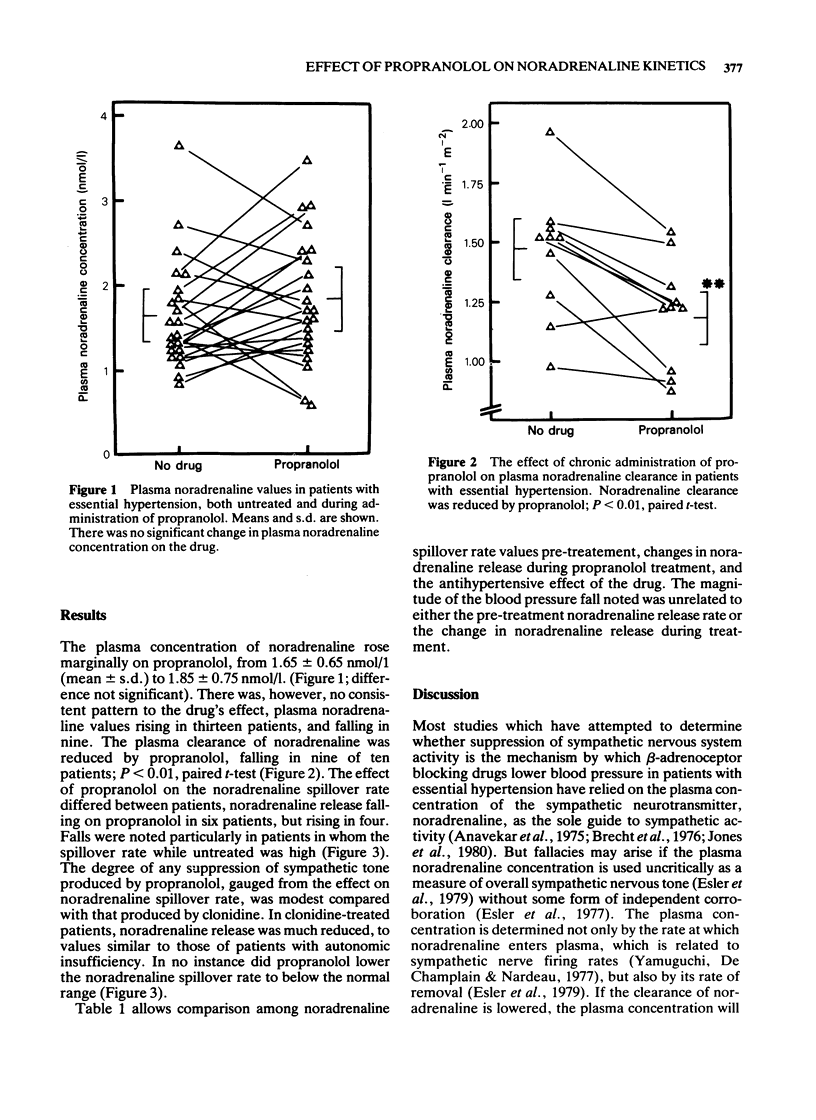
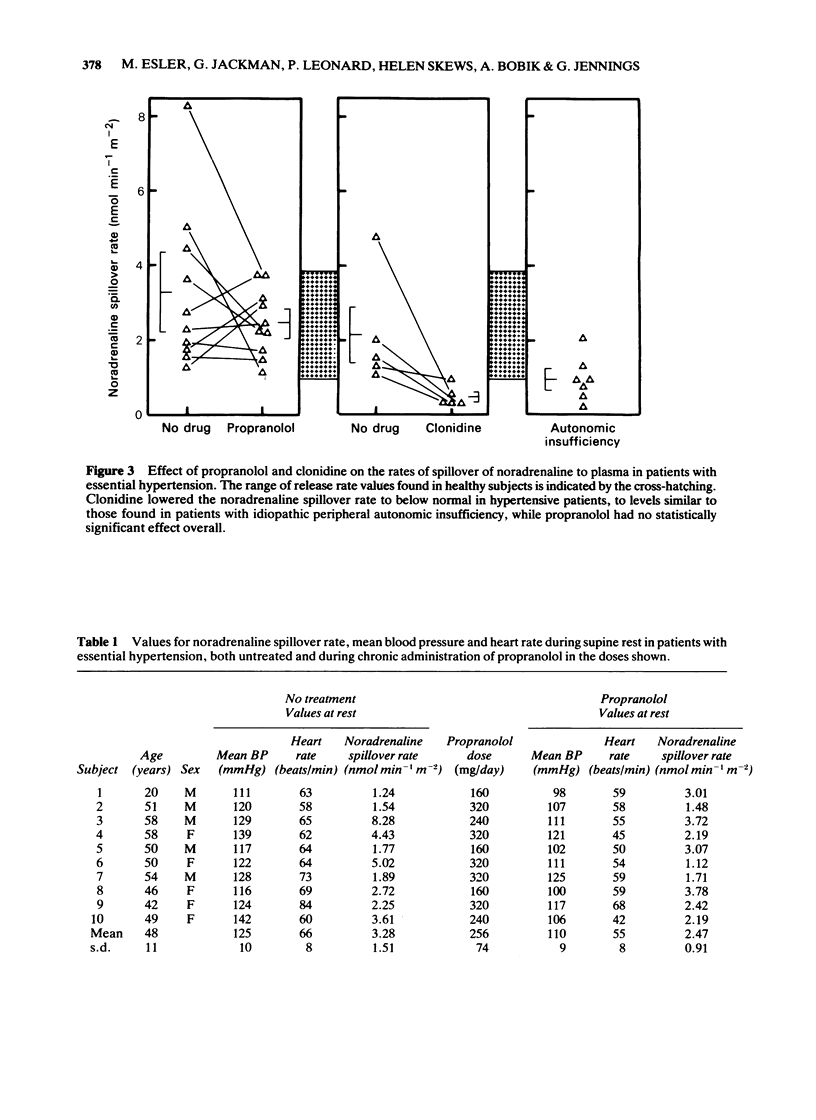
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anavekar S. N., Louis W. J., Morgan T. O., Doyle A. E., Johnston C. I. The relationship of plasma levels of pindolol in hypertensive patients to effects on blood pressure, plasma renin and plasma noradrenaline levels. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1975 May-Jun;2(3):203–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1975.tb03026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecht H. M., Banthien F., Ernst W., Schoeppe W. Increased plasma noradrenaline concentrations in essential hypertension and their decrease after long-term treatment with a beta-receptor-blocking agent (prindolol). Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1976 Dec;3:485S–488S. doi: 10.1042/cs051485s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distler A., Keim H. J., Cordes U., Philipp T., Wolff H. P. Sympathetic responsiveness and antihypertensive effect of beta-receptor blockade in essential hypertension. Am J Med. 1978 Mar;64(3):446–451. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90231-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop D., Shanks R. G. Inhibition of the carotid sinus reflex by the chronic administration of propranolol. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 May;36(1):132–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M. D., Nestel P. J. Evaluation of practolol in hypertension. Effects on sympathetic nervous system and renin responsiveness. Br Heart J. 1973 May;35(5):469–474. doi: 10.1136/hrt.35.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M., Jackman G., Bobik A., Kelleher D., Jennings G., Leonard P., Skews H., Korner P. Determination of norepinephrine apparent release rate and clearance in humans. Life Sci. 1979 Oct 22;25(17):1461–1470. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90371-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M., Jackman G., Leonard P., Skews H., Bobik A., Korner P. Effect of norepinephrine uptake blockers on norepinephrine kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Jan;29(1):12–20. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M., Julius S., Zweifler A., Randall O., Harburg E., Gardiner H., DeQuattro V. Mild high-renin essential hypertension. Neurogenic human hypertension? N Engl J Med. 1977 Feb 24;296(8):405–411. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197702242960801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M., Zweifler A., Randall O., DeQuattro V. Pathophysiologic and pharmacokinetic determinants of the antihypertensive response to propranolol. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Sep;22(3):299–308. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977223299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M., Zweifler A., Randall O., Julius S., DeQuattro V. Agreement among three different indices of sympathetic nervous system activity in essential hypertension. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 Jun;52(6):379–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier A., Hardin J. M., Alexandre J. M., Lombaert M., Ronco G., Bezoc J. F., Desmet G., Quichaud J. Anti-hypertensive effect of acebutolol: its relation to sympathetic nervous system responsiveness and to plasma renin and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activities. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1976 Dec;3:477s–480s. doi: 10.1042/cs051477s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTING G., AXELROD J., WHITBY L. G. Effect of drugs on the uptake and metabolism of H3-norepinephrine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Nov;134:146–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Daniel J., Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L. Plasma noradrenaline concentration in essential hypertension during long-term beta-adrenoceptor blockade with oxprenolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;9(1):27–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb04792.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelliher G. J., Buckley J. P. Central hypotensive activity of dl- and d-propranolol. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Sep;59(9):1276–1280. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. J., Haeusler G. Reduction in sympathetic nervous activity as a mechanism for hypotensive effect of propranolol. Nature. 1975 Jul 31;256(5516):440–440. doi: 10.1038/256440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt J. H., Grim C. E., Parkinson C. A. Effects of propranolol on aldosterone plasma concentration and aldosterone metabolic clearance in hypertensive patients. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 May;95(5):693–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing L. M., Reid J. L., Hamilton C. A., Sever P., Davies D. S., Dollery C. T. Effects of clonidine on biochemical indices of sympathetic function and plasma renin activity in normotensive man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Jul;53(1):45–53. doi: 10.1042/cs0530045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi N., de Champlain J., Nadeau R. A. Regulation of norepinephrine release from cardiac sympathetic fibers in the dog by presynaptic alpha- and beta-receptors. Circ Res. 1977 Jul;41(1):108–117. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler M. G., Lake C. R., Kopin I. J. The sympathetic-nervous-system defect in primary orthostatic hypotension. N Engl J Med. 1977 Feb 10;296(6):293–297. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197702102960601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Champlain J. The sympathetic system in hypertension. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Nov;6(3):633–655. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(77)80074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


