Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndts D., Stähle H., Struck C. J. A newly developed precise and sensitive radioimmunoassay for clonidine. Arzneimittelforschung. 1979;29(3):532–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett A. J., Cantor S. Observations on the hypotensive action of "Catapres" (ST 155) in man. Med J Aust. 1968 Jan 20;1(3):87–91. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1968.tb27492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthelsen S., Pettinger W. A. A functional basis for classification of alpha-adrenergic receptors. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 1;21(5):595–606. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. C., Elliott H. L., Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L. Changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and sympathetic activity on abrupt withdrawal of tiamenidine (HOE 440) in essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;18(6):449–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00874654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
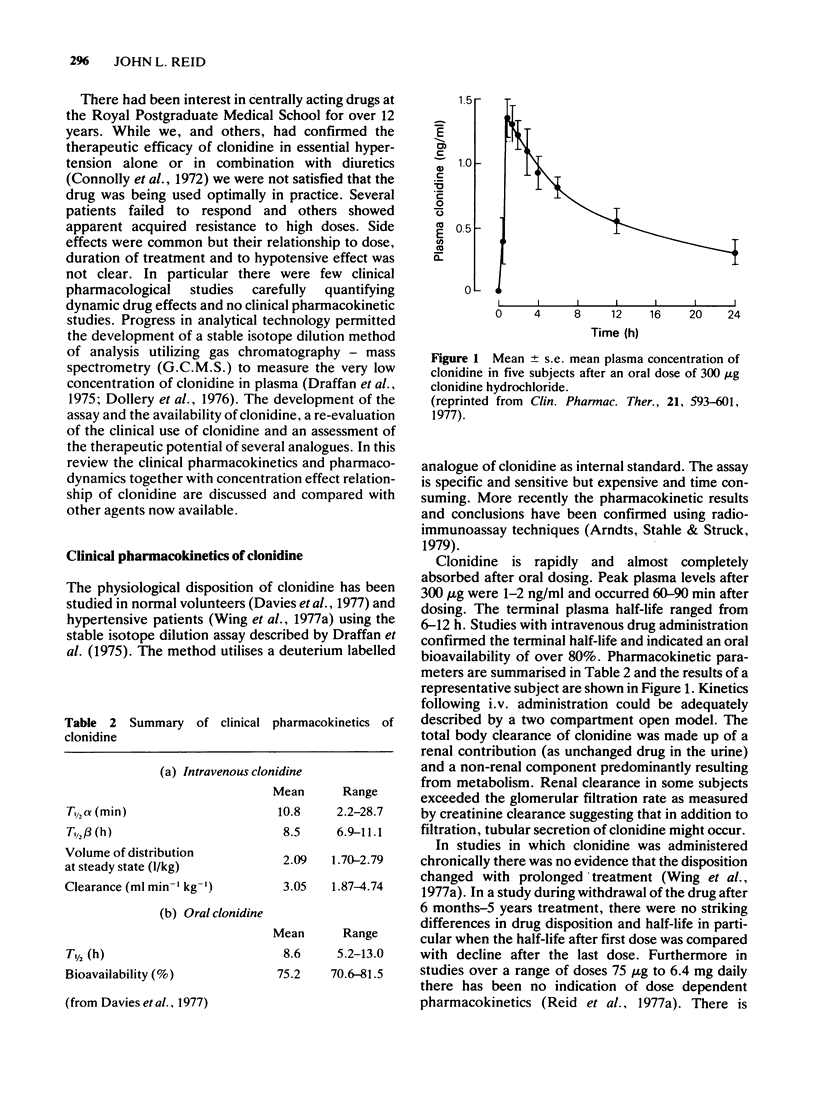
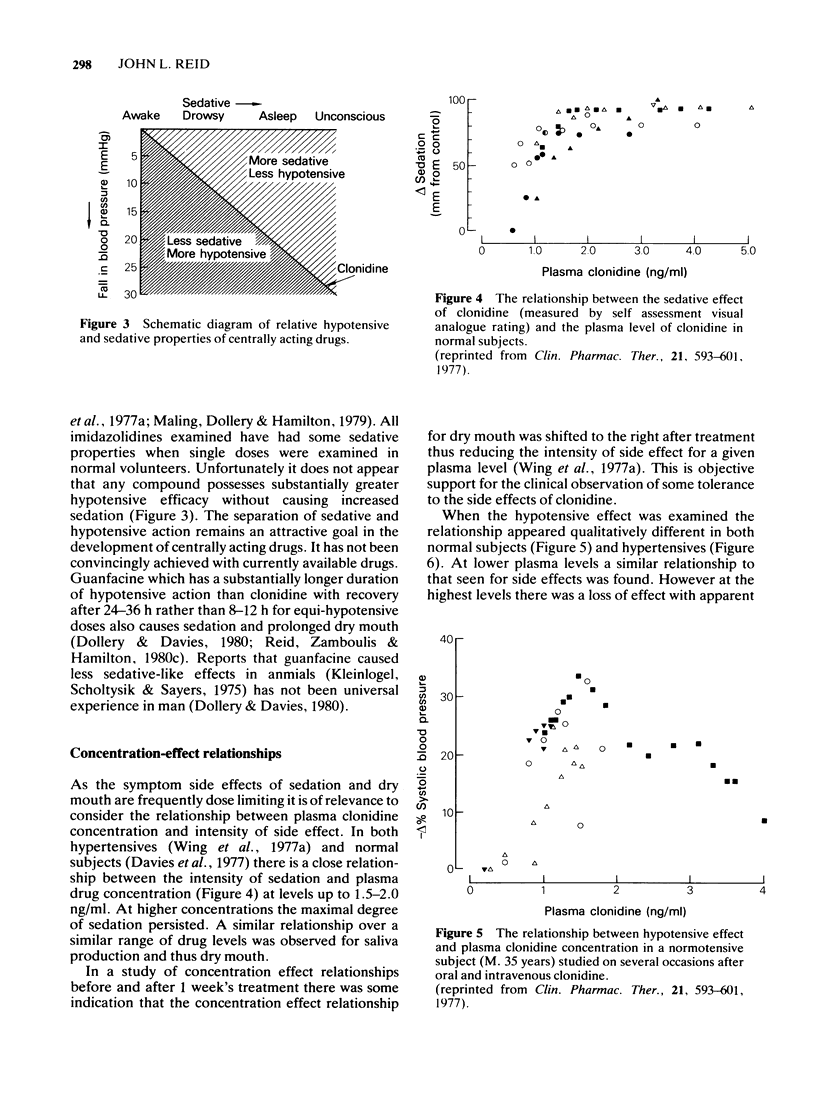
- Davies D. S., Wing A. M., Reid J. L., Neill D. M., Tippett P., Dollery C. T. Pharmacokinetics and concentration-effect relationships of intervenous and oral clonidine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 May;21(5):593–601. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977215593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollery C. T., Davies D. S., Draffan G. H., Dargie H. J., Dean C. R., Reid J. L., Clare R. A., Murray S. Clinical pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of clonidine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Jan;19(1):11–17. doi: 10.1002/cpt197619111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C. Pre- and postsynaptic effects of alpha-agonists in the anococcygeus muscle of the pithed rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Feb 15;54(1-2):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90423-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M., Whiting S. B. Evidence for two distinct types of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;67(2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisk-Holmberg M., Edlund P. O., Paalzow L. Pharmacokinetics of clonidine and its relation to the hypotensive effect in patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Sep;6(3):227–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb04589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisk-Holmberg M., Paalzow L. Relationship between clonidine kinetics and its blood pressure effects. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1979;625:68–73. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1979.tb00745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyskes G. G., Boer P., Dorhout Mees E. J. Clonidine withdrawal. Mechanism and frequency of rebound hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;7(1):55–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb00897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant J. A., Scrutton M. C. Novel alpha2-adrenoreceptors primarily responsible for inducing human platelet aggregation. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):659–661. doi: 10.1038/277659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graubner W., Wolf M. Kritische Betrachtungen zum Wirkungsmechanismus des 2-(2,6-Dichlorphenylamino)-2-imidazolin-hydrochlorids. Arzneimittelforschung. 1966 Aug;16(8):1055–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning M. Interaction of DOPA decarboxylase inhibitors with the effect of alpha-methyldopa on blood pressure and tissue monoamines in rats. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1969;27(2):135–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1969.tb00501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunyor S. N., Bradstock K., Somerville P. J., Lucas N. Clonidine overdose. Br Med J. 1975 Oct 4;4(5987):23–23. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5987.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunyor S. N., Hansson L., Harrison T. S., Hoobler S. W. Effects of clonidine withdrawal: possible mechanisms and suggestions for management. Br Med J. 1973 Apr 28;2(5860):209–211. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5860.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt B., Hedeland H., Hansson B. G. The effect of clonidine and penbutolol, respectively on catecholamines in blood and urine, plasma renin activity and urinary aldosterone in hypertensive patients. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1975 Feb;213(2):307–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerie P. Clinical experience with guanfacine in long-term treatment of hypertension. Part II: adverse reactions to guanfacine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980;10 (Suppl 1):157S–164S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb04924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinlogel H., Scholtysik G., Sayers A. C. Effects of clonidine and BS 100-141 on the EEG sleep pattern in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Aug;33(1):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger W., Walland A. Investigations into the mechanism of the hypotensive effect of 2-(2,6-dichlorphenylamino)-2-imidazoline-HCl. Eur J Pharmacol. 1967 Dec;2(3):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(67)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Sixth gaddum memorial lecture, National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill, January 1977. Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):481–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maling T. J., Dollery C. T., Hamilton C. A. Clonidine and sympathetic activity during sleep. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Dec;57(6):509–514. doi: 10.1042/cs0570509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mroczek W. J., Davidov M., Finnerty F. A., Jr Intravenous clonidine in hypertensive patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 Sep-Oct;14(5):847–851. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973145847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir A. L., Burton J. L., Lawrie D. M. Circulatory effects at rest and exercise of clonidine, an imidazoline derivative with hypotensive properties. Lancet. 1969 Jul 26;2(7613):181–184. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. L., Tangri K. K., Wing L. M. The central hypotensive action of clonidine and propranolol in animals and man. Prog Brain Res. 1977;47:369–383. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)62740-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. L., Wing L. M., Dargie H. J., Hamilton C. A., Davies D. S., Dollery C. T. Clonidine withdrawal in hypertension. Changes in blood-pressure and plasma and urinary noradrenaline. Lancet. 1977 Jun 4;1(8023):1171–1174. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92715-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. L., Wing L. M., Mathias C. J., Frankel H. L., Neill E. The central hypotensive effect of clonidine. Studies in tetraplegic subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Apr;21(4):375–381. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977214375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. L., Zamboulis C., Hamilton C. A. Guanfacine: effects of long-term treatment and withdrawal. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980;10 (Suppl 1):183S–188S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb04928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H., Boissier J. R., Giudicelli J. F. Centrally mediated decrease in sympathetic tone induced by 2(2,6-dichlorophenylamino)-2 imidazoline (S.T. 155, Catapresan). Eur J Pharmacol. 1967 Nov;2(2):147–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(67)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H., Fénard S. Action of -adrenergic blocking drugs on the sympathetic centres and their interactions with the central sympatho-inhibitory effect of clonidine. Arzneimittelforschung. 1973 Jan;23(1):40–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing L. M., Reid J. L., Davies D. S., Dargie H. J., Dollery C. T. Apparent resistance to hypotensive effect of clonidine. Br Med J. 1977 Jan 15;1(6054):136–138. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6054.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
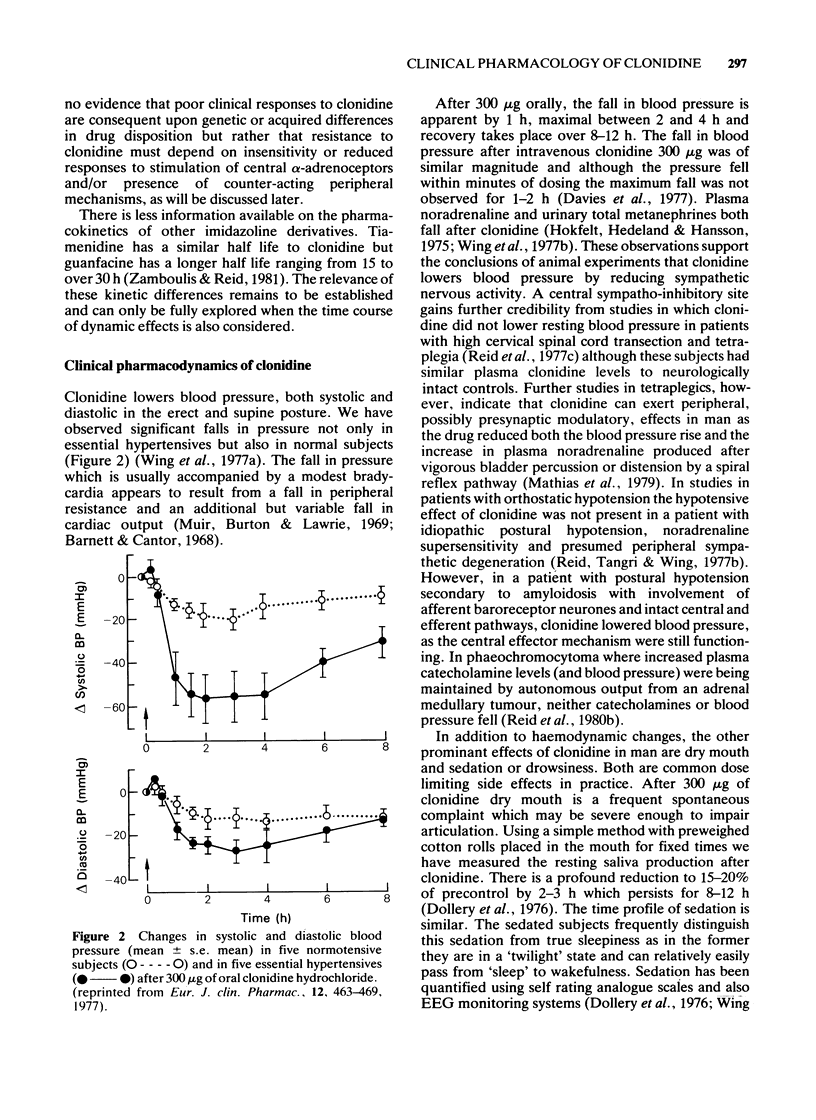
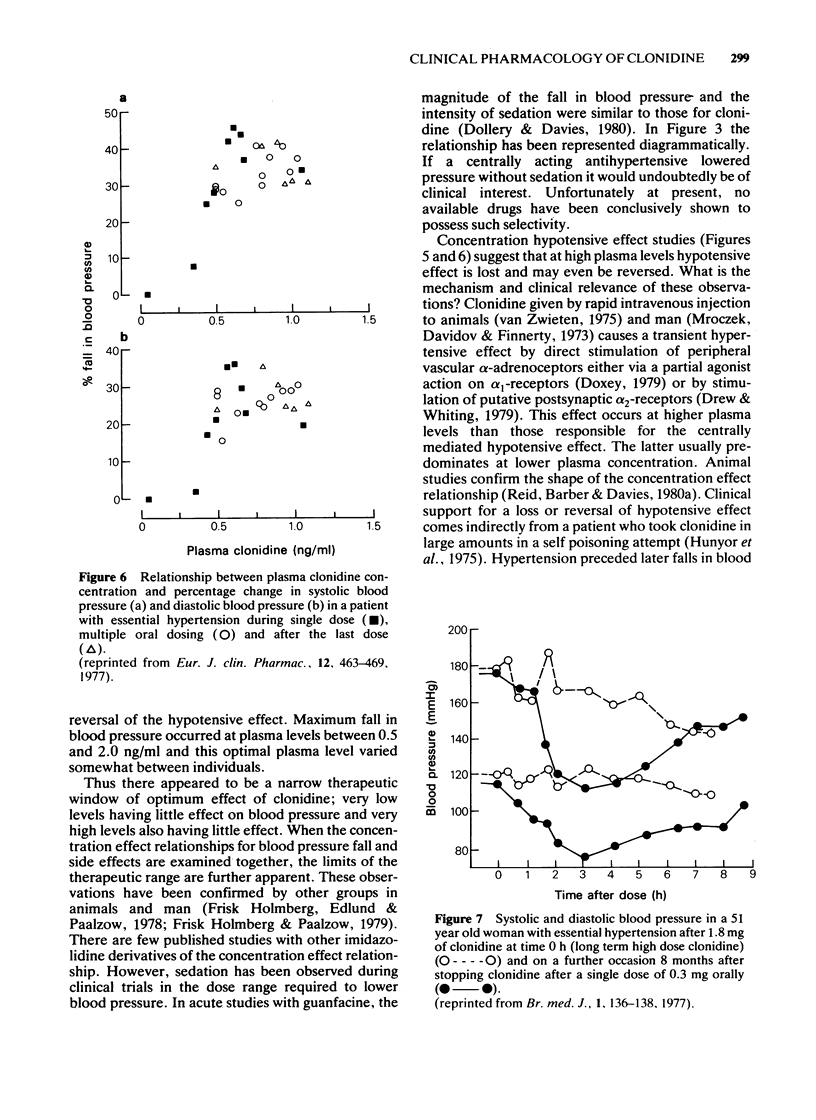
- Wing L. M., Reid J. L., Davies D. S., Neill E. A., Tippett P., Dollery C. T. Pharmacokinetic and concentration-effect relationships of clonidine in essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Dec 28;12(6):463–469. doi: 10.1007/BF00561067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing L. M., Reid J. L., Hamilton C. A., Sever P., Davies D. S., Dollery C. T. Effects of clonidine on biochemical indices of sympathetic function and plasma renin activity in normotensive man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Jul;53(1):45–53. doi: 10.1042/cs0530045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamboulis C., Reid J. L. Withdrawal of guanfacine after long-term treatment in essential hypertension. Observations on blood pressure and plasma and urinary noradrenaline. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;19(1):19–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00558376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


