Abstract
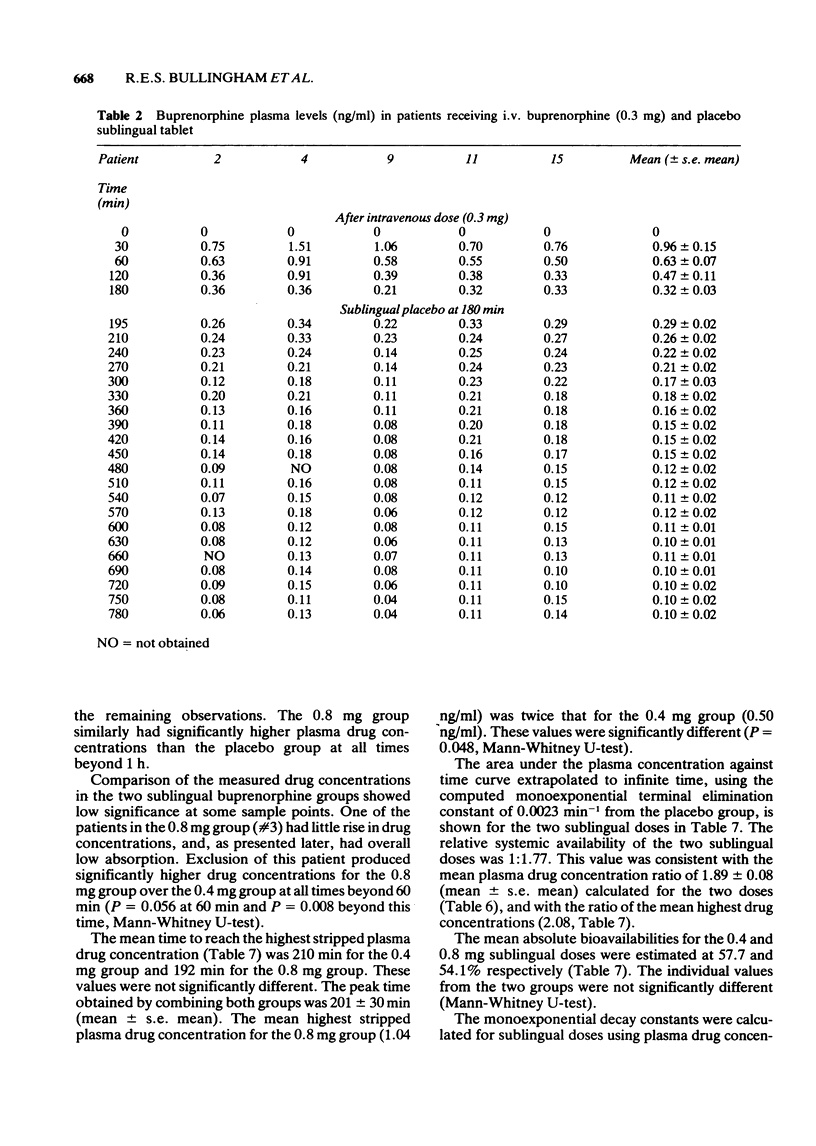
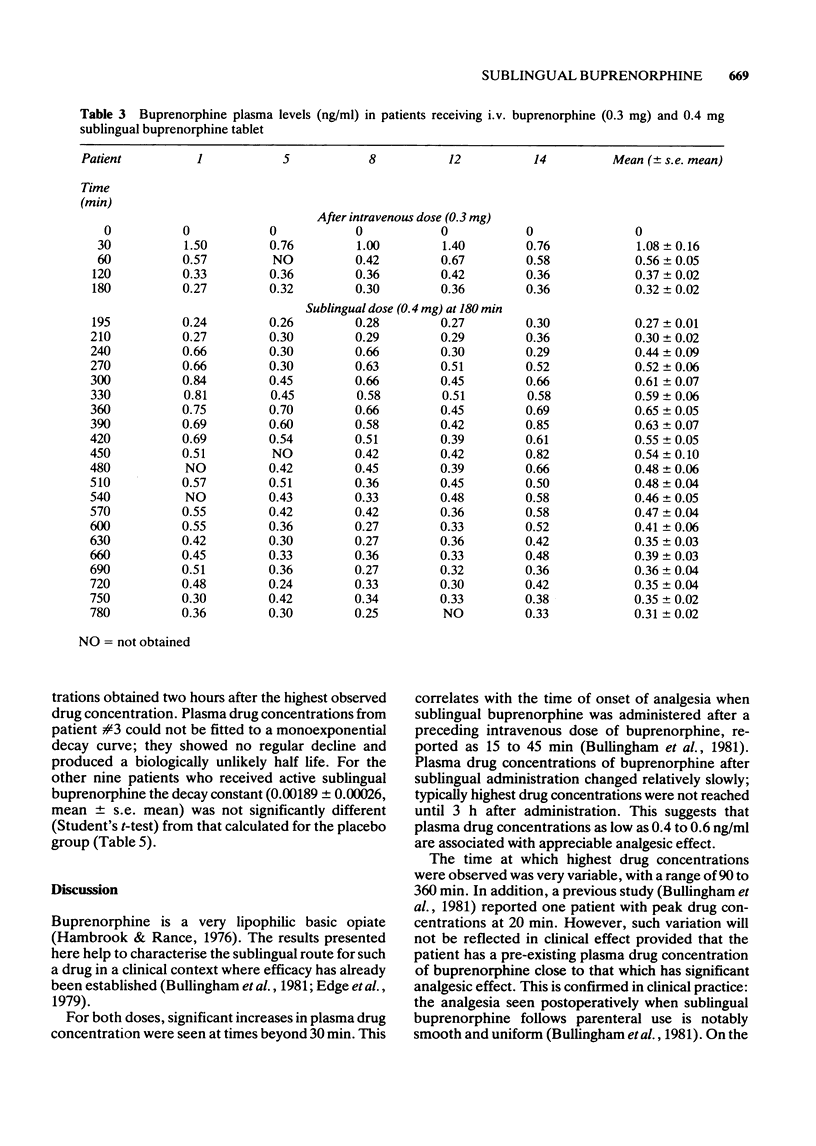
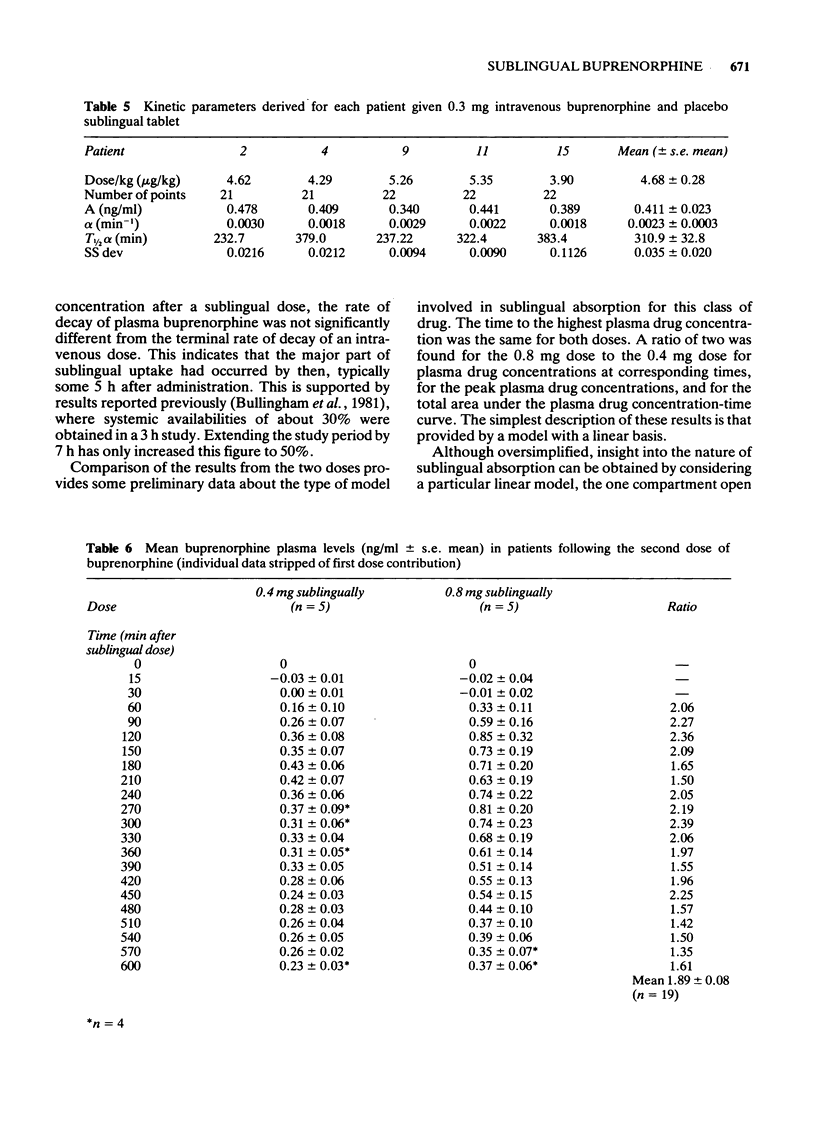
1 A 10 h study of plasma drug concentrations of the opiate buprenorphine after use was designed because a previous 3 h study had shown that peak plasma drug concentrations in some patients had not occurred by 3 h after the sublingual dose. 2 Fifteen postoperative patients were studied: at 3 h after a 0.3 mg intravenous dose five patients received a sublingual preparation of 0.4 mg of buprenorphine, five 0.8 mg of buprenorphine and five placebo. Plasma drug concentrations of buprenorphine were measured by specific radioimmuno-assay. 3 Plasma drug concentrations after sublingual buprenorphine were significantly higher than those in the placebo group by 1 h. They remained significantly higher over the succeeding nine hours. The mean time to peak plasma drug concentration was about 200 min in both the 0.4 mg and 0.8 mg groups (range 90-360 min). The plasma drug concentrations in the 0.8 mg group were approximately twice those in the 0.4 mg group; the ratio of the relative systemic availabilities was similarly 1.8:1. The absolute systemic availability was estimated at about 55% for both groups. Uptake of buprenorphine from the sublingual site was essentially complete by 5 h after the dose was given. 4 The implications for the timing of sublingual doses in clinical use are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett A. J., Lloyd-Jones J. G., Rance M. J., Flockhart I. R., Dockray G. J., Bennett M. R., Moore R. A. The radioimmunoassay of buprenorphine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Oct;18(4):339–345. doi: 10.1007/BF00561392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. S. Absorption of analgesics from the buccal mucous membrane. Practitioner. 1966 Jan;196(171):125–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullingham R. E., McQuay H. J., Dwyer D., Allen M. C., Moore R. A. Sublingual buprenorphine used postoperatively: clinical observations and preliminary pharmacokinetic analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;12(2):117–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01189.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullingham R. E., McQuay H. J., Moore A., Bennett M. R. Buprenorphine kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980 Nov;28(5):667–672. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1980.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K., Murray G. R., Ong G. C. A comparison of the physico-chemical properties and potency of pethidine and phenoperidine [proceedings]. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;9(1):122P–122P. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb04824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearden J. C., Tomlinson E. A new buccal absorption model. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Dec;23:68S–72S. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edge W. G., Cooper G. M., Morgan M. Analgesic effects of sublingual buprenorphine. Anaesthesia. 1979 May;34(5):463–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1979.tb06325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry E. N. Relief of pain after surgery. A comparison of sublingual buprenorphine and intramuscular papaveretum. Anaesthesia. 1979 Jun;34(6):549–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1979.tb06339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGDEN H. D. Sublingual ergotamine tablets. J La State Med Soc. 1963 Jan;115:23–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. A., Raw M., Jarvis M. J. Clinical use of nicotine chewing-gum. Br Med J. 1980 Jun 28;280(6231):1599–1602. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6231.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vora K. R., Higuchi W. I., Ho N. F. Analysis of human buccal absorption of drugs by physical model approach. J Pharm Sci. 1972 Nov;61(11):1785–1791. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600611119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G. Kinetics of pharmacologic response. I. Proposed relationships between response and drug concentration in the intact animal and man. J Theor Biol. 1968 Aug;20(2):173–201. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(68)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G. Linear pharmacokinetic equations allowing direct calculation of many needed pharmacokinetic parameters from the coefficients and exponents of polyexponential equations which have been fitted to the data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1976 Oct;4(5):443–467. doi: 10.1007/BF01062831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winsor T. Plethysmographic comparison of sublingual and intramuscular ergotamine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Jan;29(1):94–99. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


