Abstract
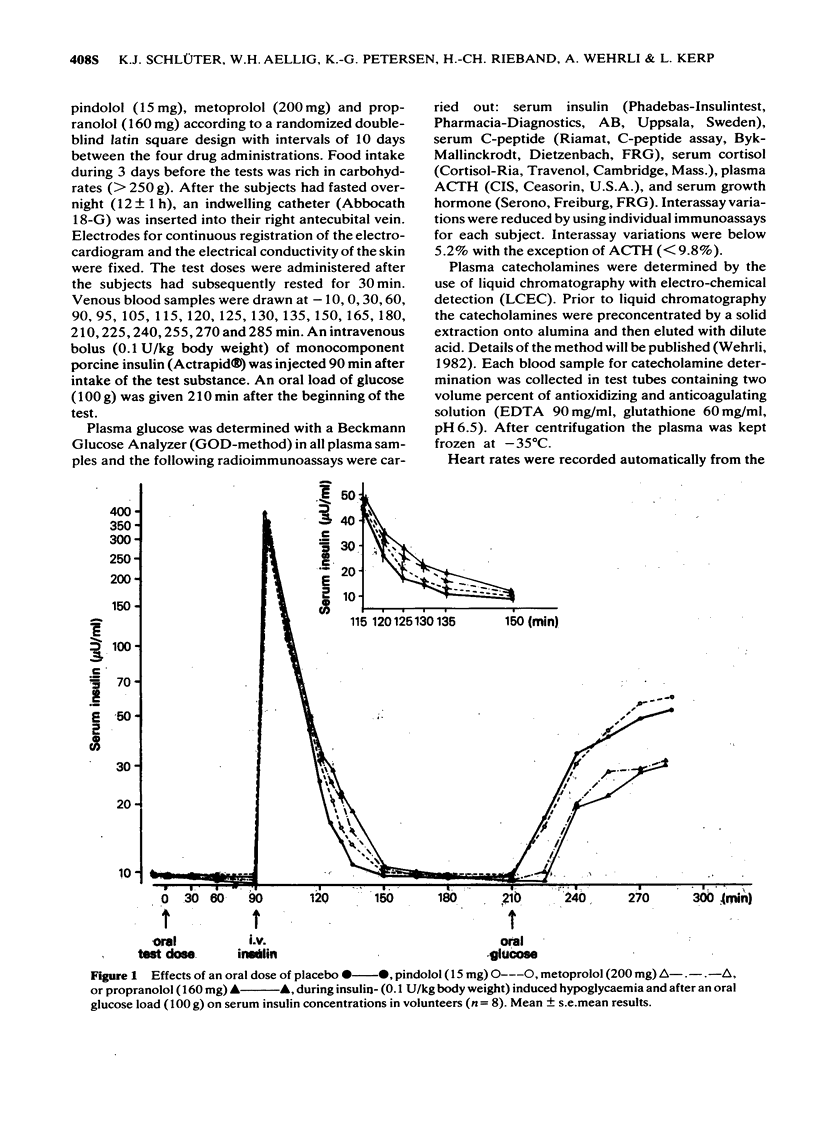
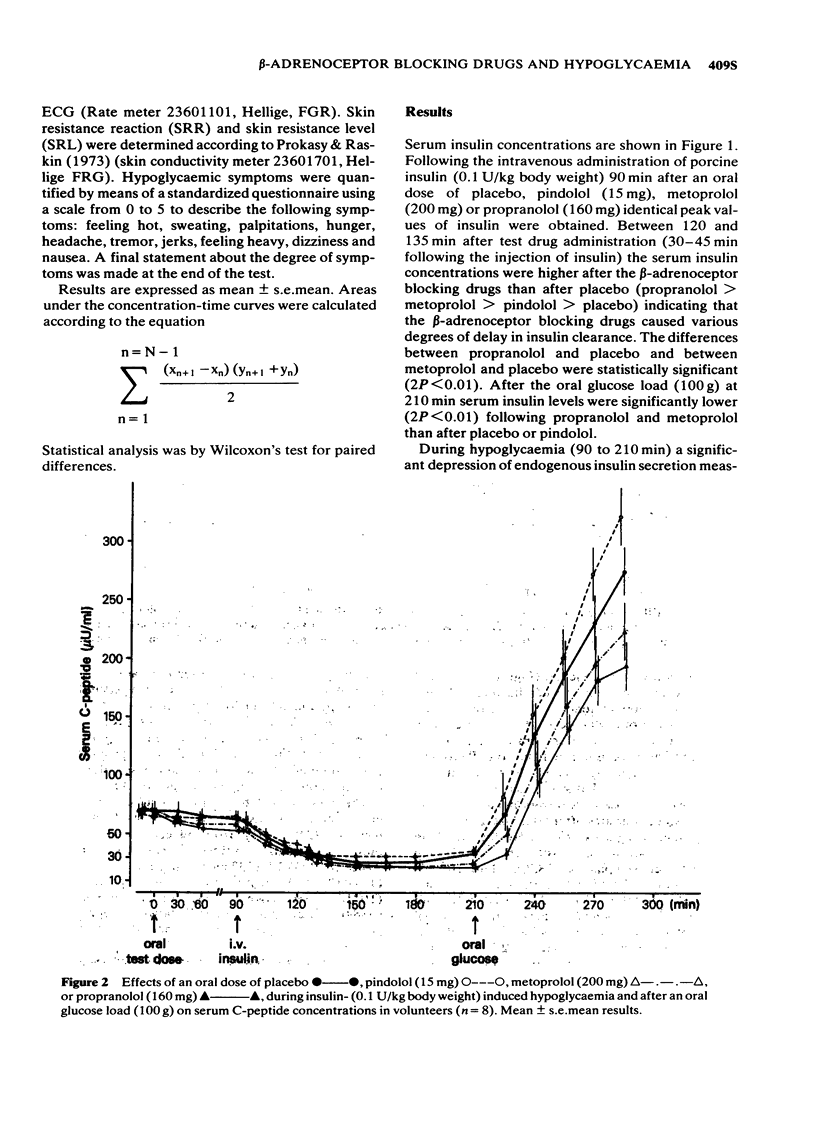
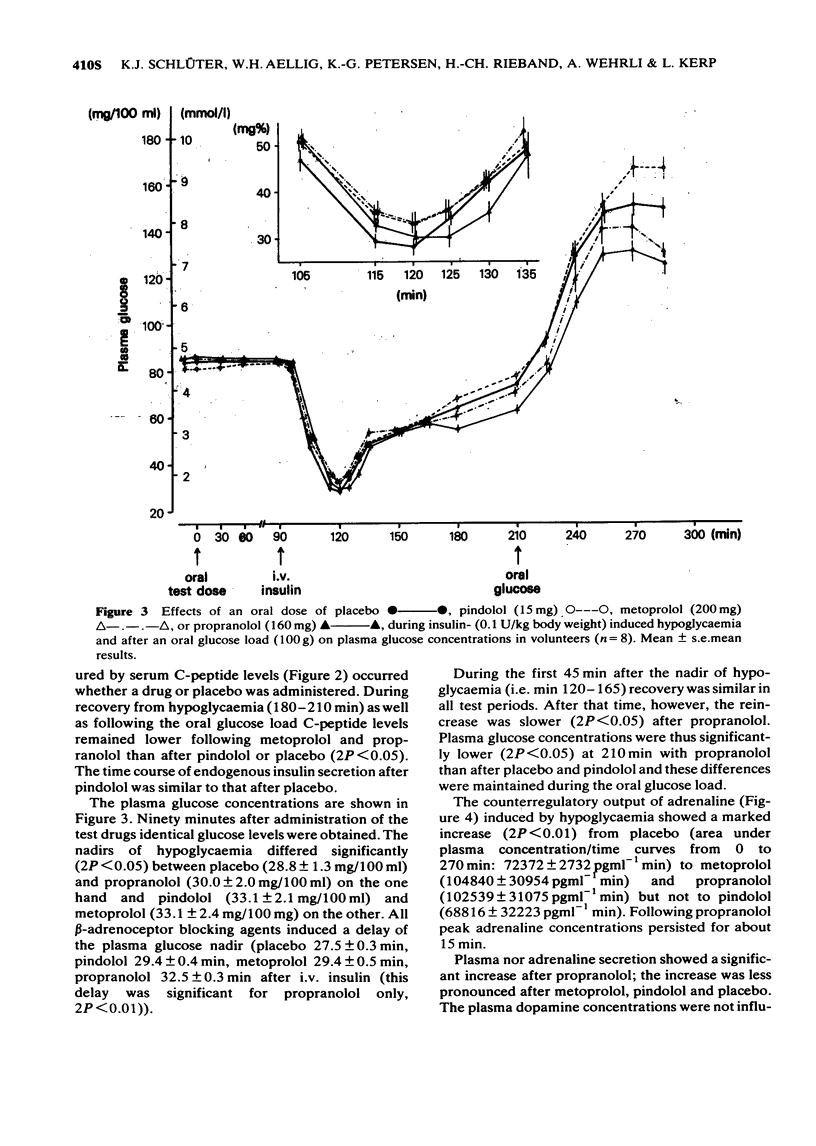
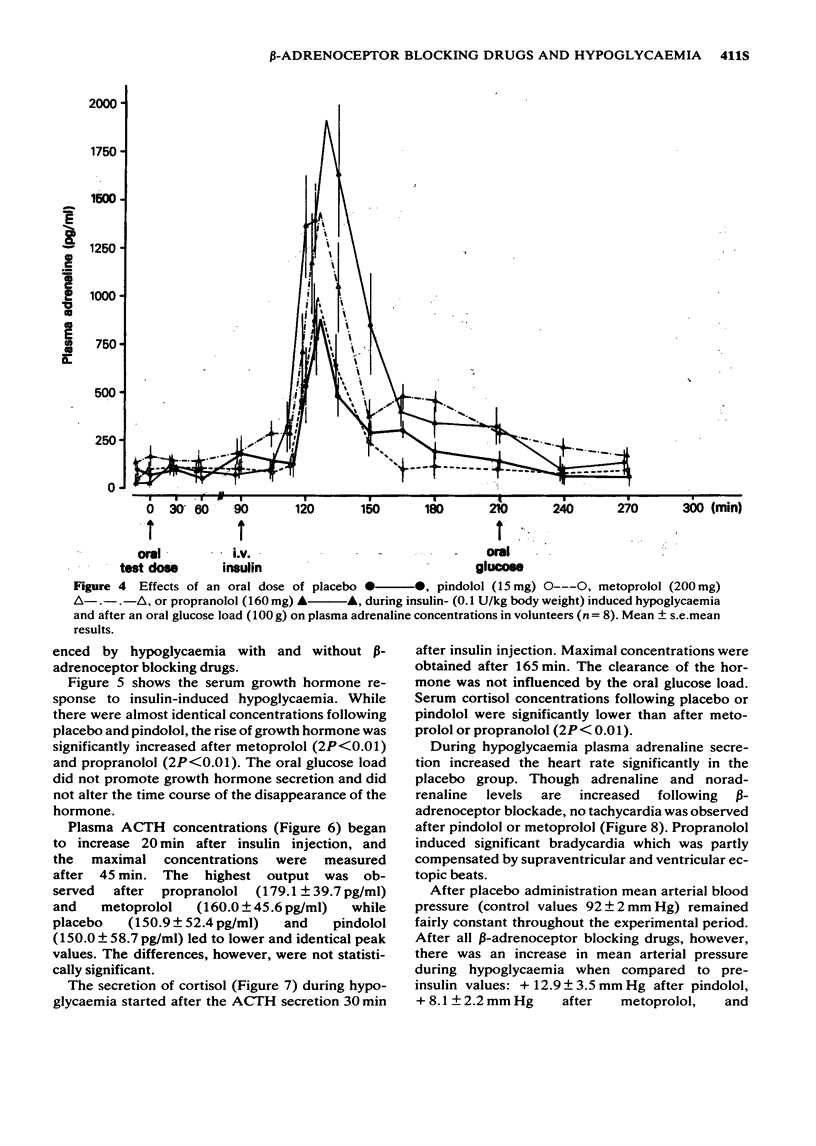
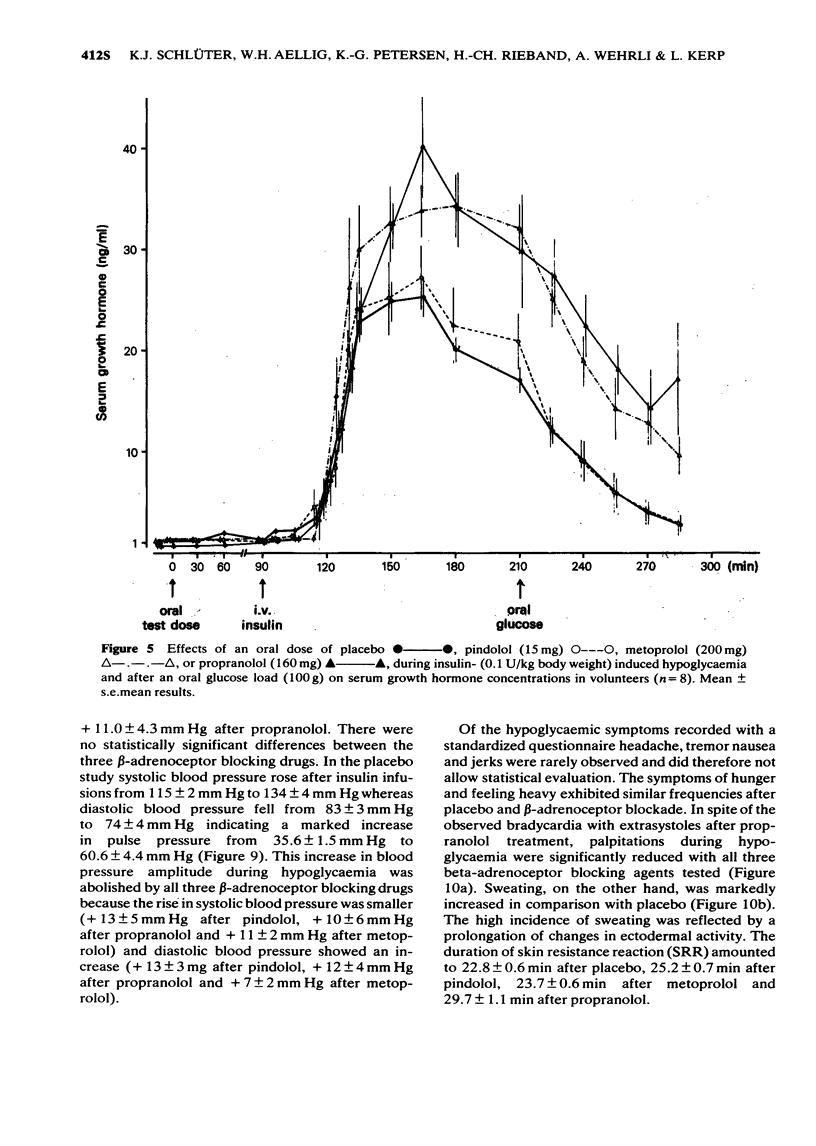
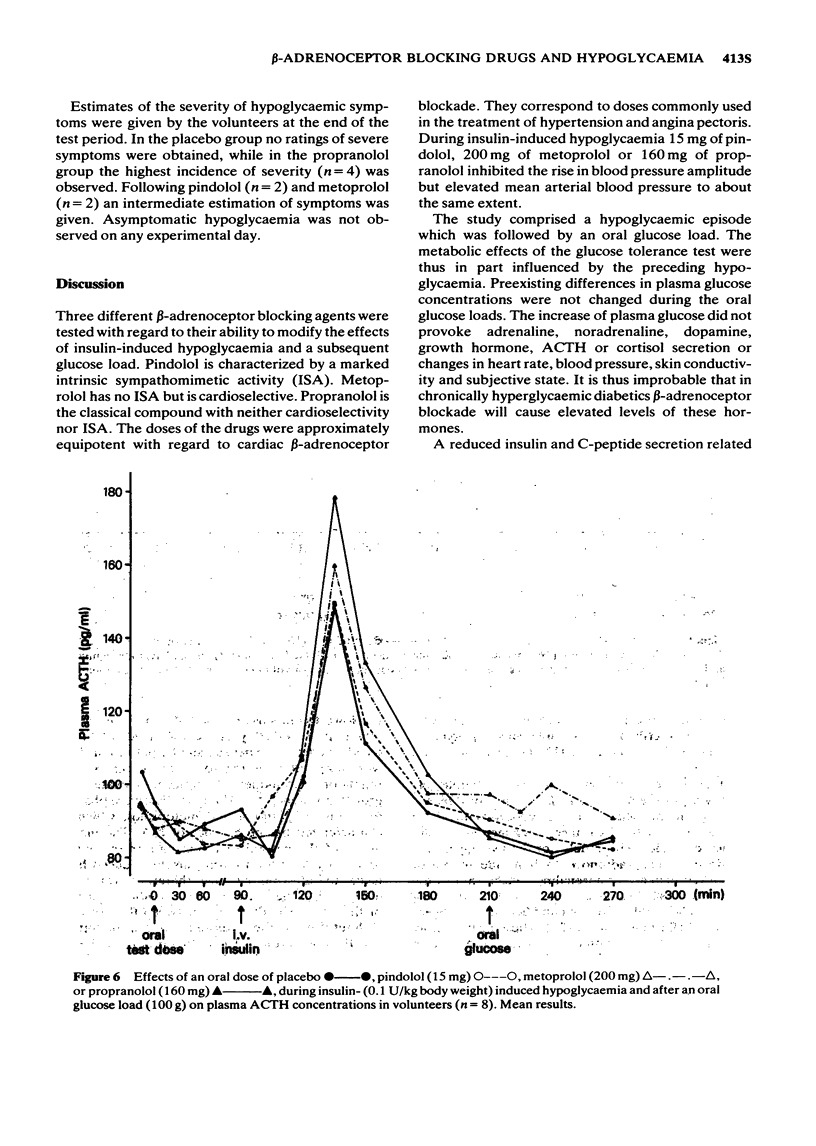
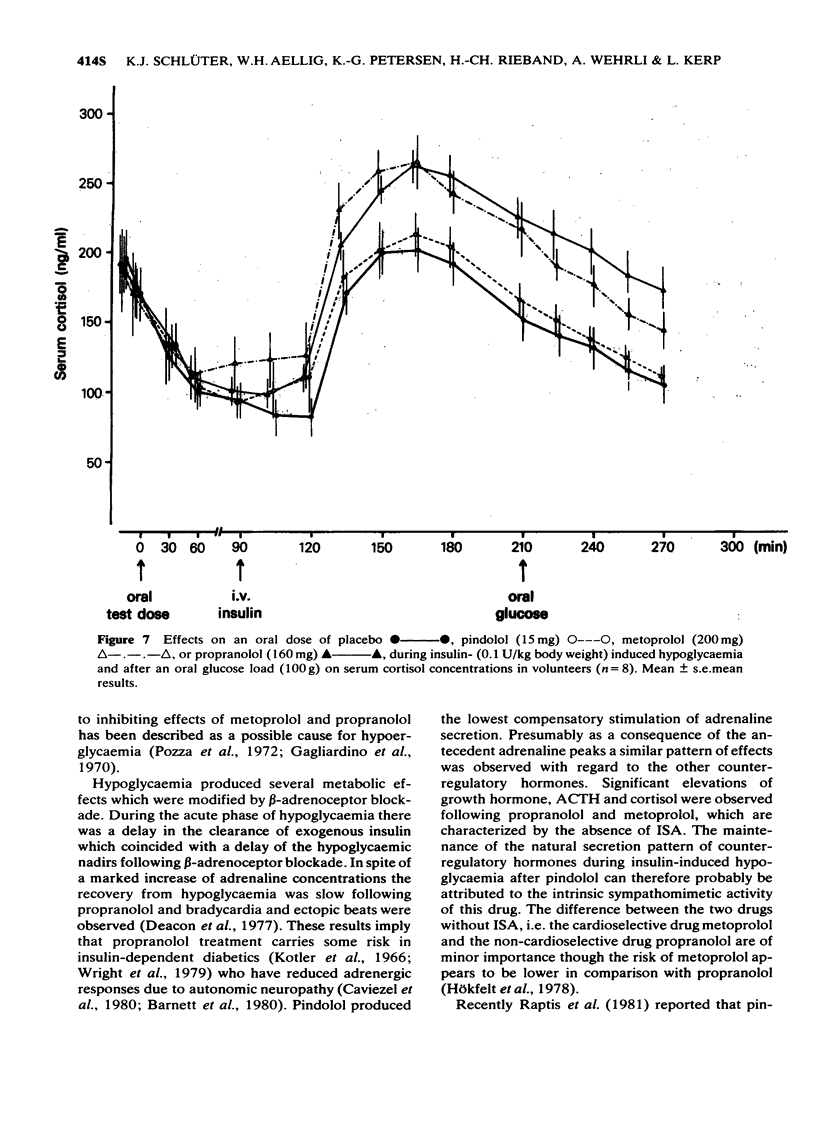
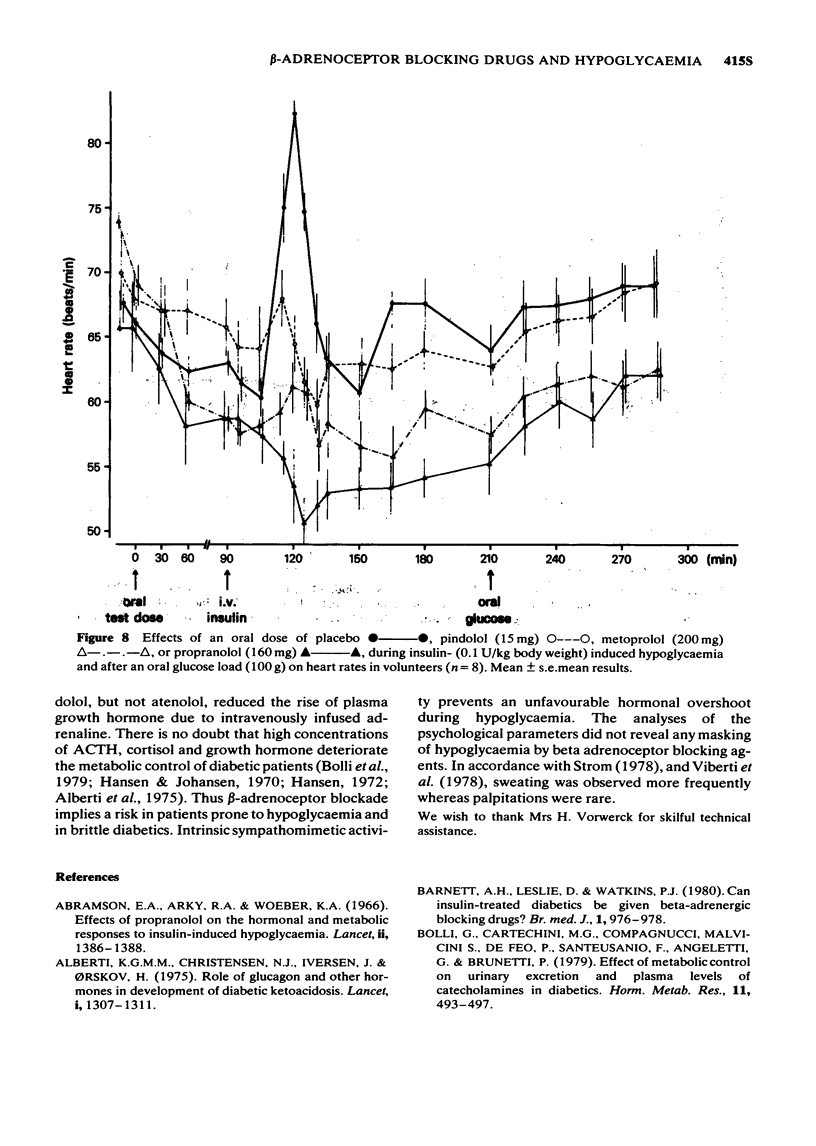
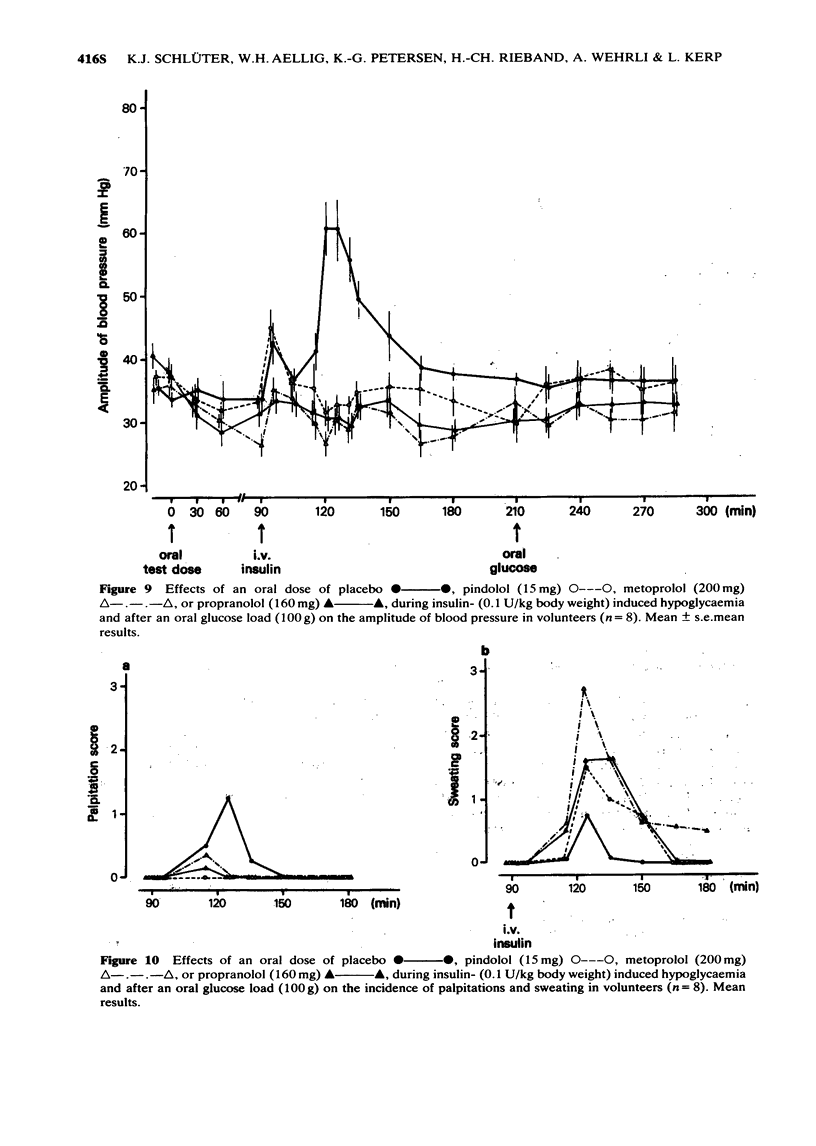
1 The effects of oral doses of pindolol (15 mg), metoprolol (200 mg) and propranolol (160 mg) on the response to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia and an oral glucose load were investigated. 2 Serum insulin and serum C-peptide secretion in response to a glucose load were inhibited (2P less than 0.01) by metoprolol and propranolol but not by pindolol. 3 During hypoglycaemia metoprolol and propranolol inhibited the clearance of insulin (2P less than 0.01) and caused a delay of glucose nadirs. 4 Adrenaline secretion during hypoglycaemia was markedly increased by metoprolol and propranolol but not by pindolol. 5 The counterregulatory response of growth hormone, ACTH and cortisol was increased following metoprolol and propranolol but not after pindolol. 6 The hypoglycaemic symptoms and signs showed a prevalence of sweating and prolonged changes in skin conductivity whereas palpitations were not observed during beta-adrenoceptor blockade. Asymptomatic hypoglycaemia did not occur. 7 The absence of unphysiological rises in adrenaline, growth hormone, ACTH and cortisol supports the use of a beta-adrenoceptor blocker with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson E. A., Arky R. A., Woeber K. A. Effects of propranolol on the hormonal and metabolic responses to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Lancet. 1966 Dec 24;2(7478):1386–1388. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett A. H., Leslie D., Watkins P. J. Can insulin-treated diabetics be given beta-adrenergic blocking drugs? Br Med J. 1980 Apr 5;280(6219):976–978. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6219.976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolli G., Cartechini M. G., Compagnucci P., Malvicini S., De Feo P., Santeusanio F., Angeletti G., Brunetti P. Effect of metabolic control on urinary excretion and plasma levels of catecholamines in diabetics. Horm Metab Res. 1979 Oct;11(9):493–497. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1092768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R., Efendić S. Effect of adrenergic blocking agents on insulin response to glucose infusion in man. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Feb;69(2):335–346. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0690335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day J. L. The metabolic consequences of adrenergic blockade: a reveiw. Metabolism. 1975 Aug;24(8):987–996. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon S. P., Barnett D. Comparison of atenolol and propranolol during insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Br Med J. 1976 Jul 31;2(6030):272–273. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6030.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon S. P., Karunanayake A., Barnett D. Acebutolol, atenolol, and propranolol and metabolic responses to acute hypoglycaemia in diabetics. Br Med J. 1977 Nov 12;2(6097):1255–1257. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6097.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardino J. J., Bellone C. F., Doria I., Sănchez J. J., Pereyra V. Adrenergic regulation of basal serum glucose, NEFA and insulin levels. Horm Metab Res. 1970 Nov;2(6):318–322. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen A. P., Johansen K. Diurnal patterns of blood glucose, serum free fatty acids, insulin, glucagon and growth hormone in normals and juvenile diabetics. Diabetologia. 1970 Feb;6(1):27–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00425888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen A. P. Serum growth hormone patterns in juvenile diabetes. Dan Med Bull. 1972 Apr;19(1 Suppl):3–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms H. H., Gooren L., Spoelstra A. J., Hesse C., Verschoor L. Blockade of isoprenaline-induced changes in plasma free fatty acids, immunoreactive insulin levels and plasma renin activity in healthy human subjects, by propranolol, pindolol, practolol, atenolol, metoprolol and acebutolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;5(1):19–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G., Johansson S., Vedin A., Wilhelmsson C., Smith U. The effect of beta-blockade on glucose tolerance and insulin release in adult diabetes. Acta Med Scand. 1980;208(3):187–191. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1980.tb01175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt B., Hansson B. G., Heding L. G., Nilsson K. O. Effect of insulin induced hypoglycaemia on the blood levels of catecholamines, glucagon, growth hormone, cortisol, C-peptide and proinsulin before and during medication with the cardioselective beta-receptor blocking agent metoprolol in man. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1978 Mar;87(3):659–667. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0870659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler M. N., Berman L., Rubenstein A. H. Hypoglycaemia precipitated by propranolol. Lancet. 1966 Dec 24;2(7478):1389–1390. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90423-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT R., OLIVECRONA H., SJOGREN B. Hypofysektomi på människa. Nord Med. 1952 Mar 14;47(11):351–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT R., OLIVECRONA H., SJOGREN B. Hypophysectomy in man: experiences in severe diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1955 Apr;15(4):391–408. doi: 10.1210/jcem-15-4-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lager I., Blohmé G., Smith U. Effect of cardioselective and non-selective beta-blockade on the hypoglycaemic response in insulin-dependent diabetics. Lancet. 1979 Mar 3;1(8114):458–462. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90821-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann F. W. Die Beeinflussung des Stoffwechsels durch Beta-Rezeptoren-Blocker. Klin Wochenschr. 1981 Jan 15;59(2):49–57. doi: 10.1007/BF01477283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J., Fineberg S. E., Hollander W. Vascular disease in the chronic HGH-deficient state. Diabetes. 1973 Nov;22(11):813–819. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.11.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raptis S., Rosenthal J., Welzel D., Moulopoulos S. Effects of cardioselective and non-cardioselective beta-blockade on adrenaline-induced metabolic and cardiovascular responses in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1981;20(1):17–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00554661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSSMAN K. E., CROUT J. R., MARBLE A. Failure of warning in insulin-induced hypoglycemic reactions. Diabetes. 1963 Jan-Feb;12:38–45. doi: 10.2337/diab.12.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandellari C., Zaccaria M., De Palo C., Sicolo N., Erle G., Federspil G. The effect of propranolol on hypoglycaemia. Observations in five insulinoma patients. Diabetologia. 1978 Oct;15(4):297–301. doi: 10.1007/BF02573822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staniforth D. H., Yorkston N. J., Gemidjioglu M. Propranolol and blood glucose: simultaneous measurements over a wide range of doses and the effect of propranolol on the glucose tolerance test. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;17(6):415–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00570157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom L. Propranolol in insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1978 Aug 31;299(9):487–487. doi: 10.1056/nejm197808312990917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waal-Manning H. J. Can beta-blockers be used in diabetic patients? Drugs. 1979 Mar;17(3):157–160. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197917030-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waal-Manning H. J. Metabolic effects of beta-adrenoreceptor blockers. Drugs. 1976;11(Suppl 1):121–126. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197600111-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. D., Barber S. G., Kendall M. J., Poole P. H. Beta-adrenoceptor-blocking drugs and blood sugar control in diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1979 Jan 20;1(6157):159–161. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6157.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


