Abstract
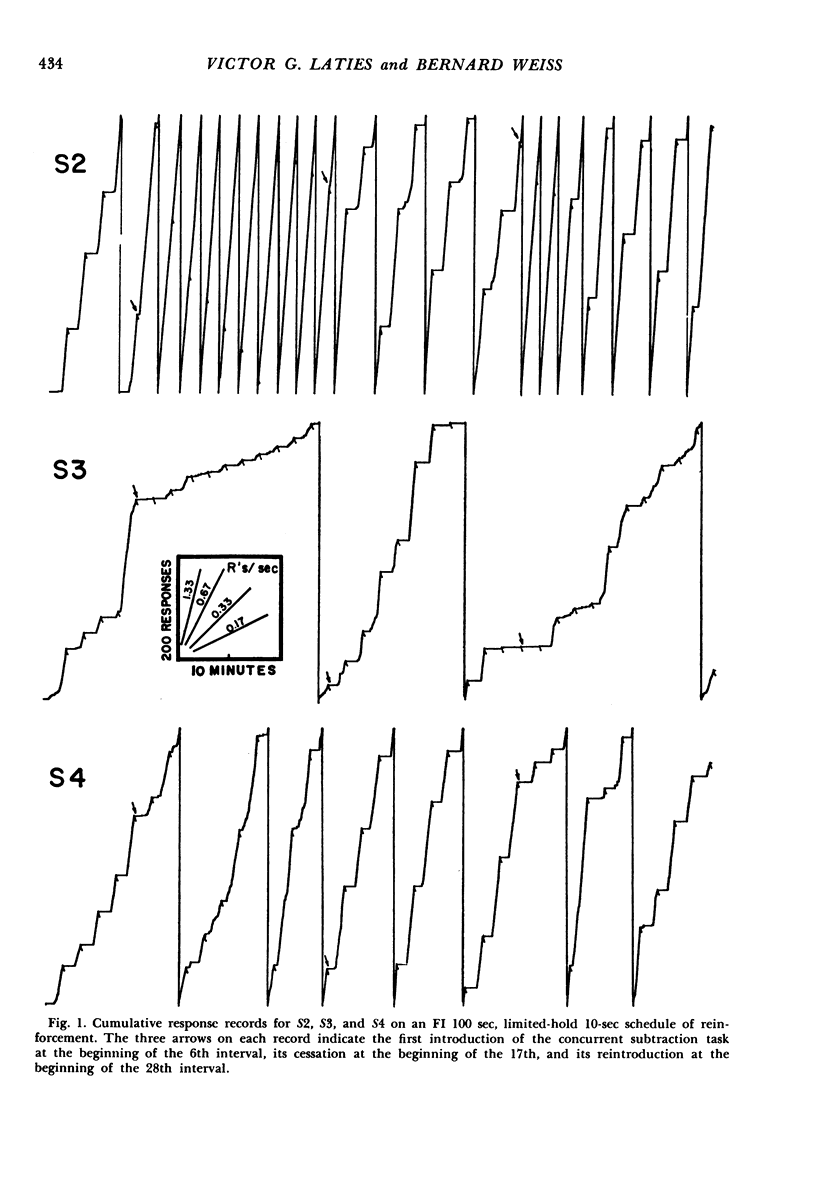
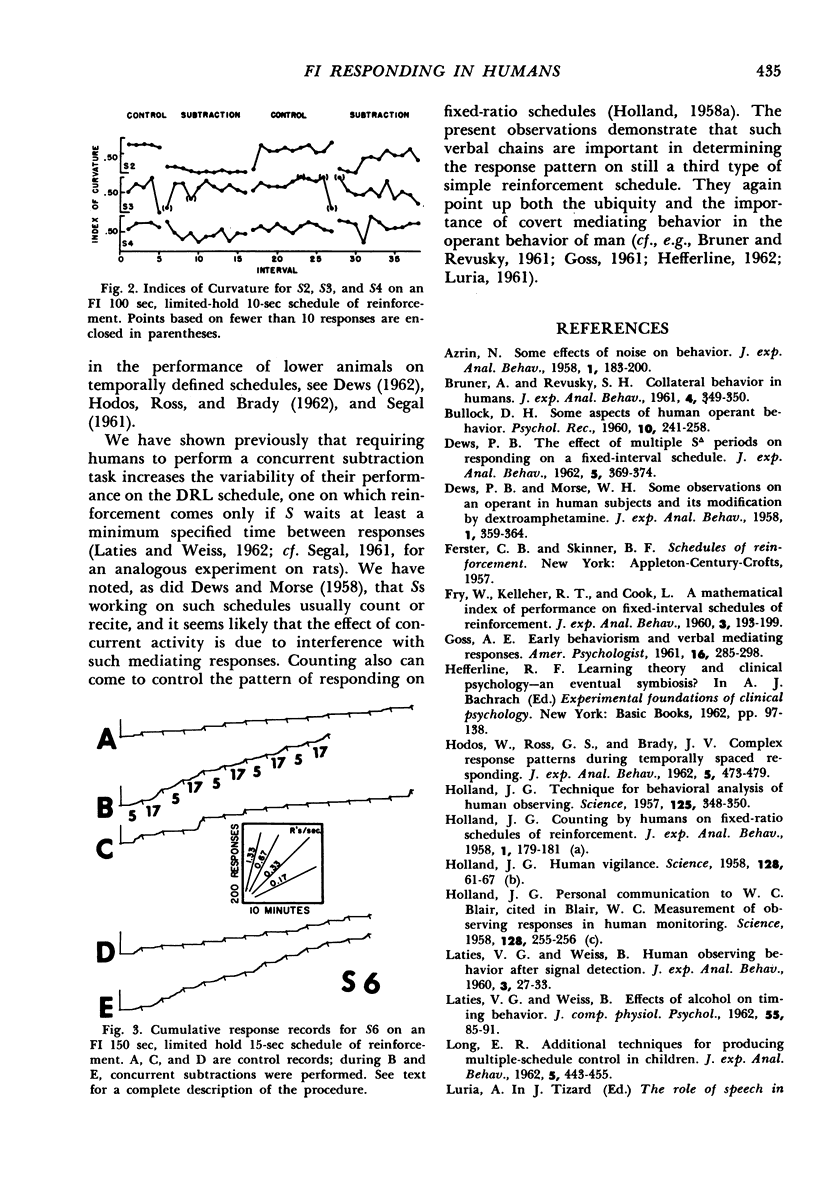
Subjects pressed a telegraph key to illuminate a meter dial on which pointer deflections appeared at fixed intervals. Upon detecting a deflection they were required to press another key to reset the pointer to zero. This detecting and resetting operation reinforced the behavior of pressing the light-flashing key (i.e., the observing responses). The usual pattern of responding on the light-flashing key was a long pause following the reinforcement and an abrupt transition to a steady response rate toward the end of the interval. When the subjects were required to perform a concurrent subtraction task, the pattern of responding changed in varying degrees, ranging from complete loss of typical fixed-interval behavior to a slight shortening of the post-reinforcement pause. These effects were attributed to the disruption of the self-produced verbal chains (counting or reciting) that ordinarily govern human behavior on this schedule.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azrin N. H. Some Effects of Noise on Human Behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):183–200. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAIR W. C. Measurement of observing responses in human monitoring. Science. 1958 Aug 1;128(3318):255–256. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3318.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUNER A., REVUSKY S. H. Collateral behavior in humans. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Oct;4:349–350. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWS P. B. The effect of multiple S delta periods on responding on a fixed-interval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jul;5:369–374. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dews P. B., Morse W. H. Some observations on an operant in human subjects and its modification by dextro amphetamine. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Oct;1(4):359–364. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRY W., KELLEHER R. T., COOK L. A mathematical index of performance on fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Jul;3:193–199. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODOS W., ROSS G. S., BRADY J. V. Complex response patterns during temporally spaced responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:473–479. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. G. Human vigilance: the rate of observing an instrument is controlled by the schedule of signal detections. Science. 1958 Jul 11;128(3315):61–67. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3315.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. G. Technique for behavioral analysis of human observing. Science. 1957 Feb 22;125(3243):348–350. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3243.348-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. G. Counting by Humans on a Fixed-ratio Schedule of Reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):179–181. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATIES V. G., WEISS B. Effects of alcohol on timing behavior. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1962 Feb;55:85–91. doi: 10.1037/h0046400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laties V. G., Weiss B. Human Observing Behavior after Signal Detection. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Jan;3(1):27–33. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. R. Additional techniques for producing multiple-schedule control in children. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5(4):443–455. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGAL E. F. Behavioral interaction under concurrent spaced-responding, variable-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:263–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E. F. Exteroceptive control of fixed-interval responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jan;5(1):49–57. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER H. Some effects of response cost upon human operant behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:201–208. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


