Abstract
Three hooded rats were trained to bar press for variable-ratio liquid reinforcement after which an electric shock was delivered following the response. Initially, the shock was presented on a FR 100 basis but the frequency was gradually increased until all responses were punished. Finally, a partial extinction procedure was conducted to determine if the shock resulted in increased bar pressing. No durable suppression of responding occurred, although one subject's rate was reduced during continuous shock. The overall trend for the three animals was one of increased responding. Changes in the pattern of responding were also observed suggesting that the suppressive effects of the punishment were largely restricted to the first response following reinforcement. Increased responding as a function of shock reintroduction during extinction was also observed.
Full text
PDF

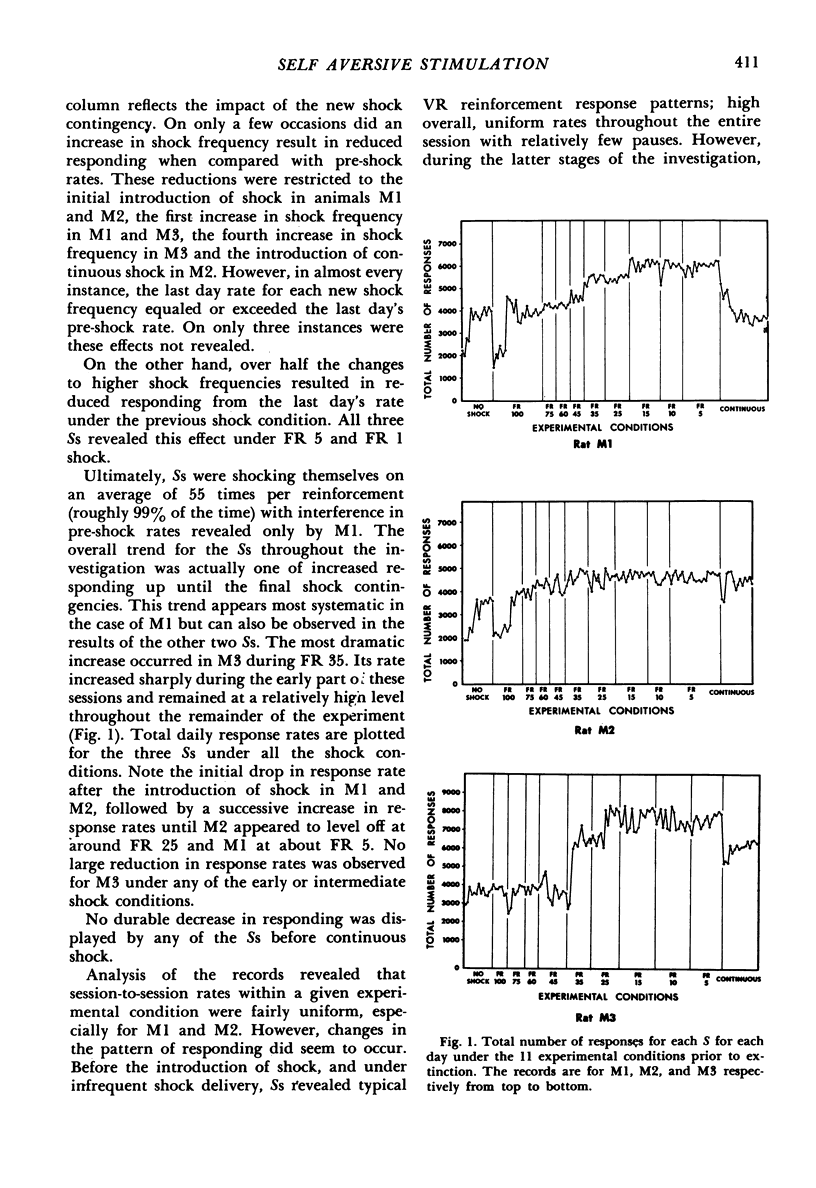

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMSEL A., MALTZMAN I. The effect upon generalized drive strength of emotionality as inferred from the level of consummatory response. J Exp Psychol. 1950 Oct;40(5):563–569. doi: 10.1037/h0061101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZ W. C., AZRIN N. H. Discriminative properties of punishment. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:225–232. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STORMS L. H., BOROCZI G., BROEN W. E., Jr Punishment inhibits an instrumental response in hooded rats. Science. 1962 Mar 30;135(3509):1133–1134. doi: 10.1126/science.135.3509.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULLMAN A. D. The experimental production and analysis of a "compulsive eating symptom" in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1951 Dec;44(6):575–581. doi: 10.1037/h0057260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


