Abstract
Posttranscriptional controls play a major role in eucaryotic gene expression. These controls are mediated by sequence-specific interactions of cis-acting determinants in target mRNAs with one or more protein factors. The positioning of a subset of these mRNA-protein (RNP) complexes within the 3′ untranslated region (3′ UTR) may allow them to remain associated with the mRNA during active translation. Robust expression of human α-globin mRNA during erythroid differentiation has been linked to formation of a binary complex between a KH-domain protein, αCP, and a 3′ UTR C-rich motif. Detection of this “α-complex” has been limited to in vitro studies, and the functional state of the α-globin mRNA targeted by αCP has not been defined. In the present study we demonstrate that a significant fraction of αCP is associated with polysomal mRNA. Targeted analysis of the polysomal RNP complexes revealed that αCP is specifically bound to actively translating α-globin mRNA. The bound αCP is restricted to the poly(C)-rich 3′ UTR motif and is dislodged when ribosomes are allowed to enter this region. These data validate the general importance of the 3′ UTR as a sheltered site for RNP complexes and support a specific model in which the stabilizing function of αCP is mediated on actively translating target mRNAs.
Posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression plays a pivotal role in developmental processes and in cellular differentiation (16). A prominent component of this control is exerted at the level of mRNA stability (35). The half-lives of mammalian mRNAs can be as short as 15 min or as long as several days. Generally speaking, mRNAs with short half-lives encode proteins that are tightly controlled over narrow time frames, while mRNAs with long half-lives often encode proteins expressed at high levels in terminally differentiated cells (3, 39). The stability of individual mRNAs reflects the interaction of general determinants, such as the 5′ m7Gppp cap and a 3′ terminal poly(A) tail, with transcript-specific regulatory elements. The latter determinants are often restricted to the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) (4) and are recognized by sequence- and structure-specific RNA binding proteins (23). The net contributions of general and specific stability determinants generate expression profiles unique to each mRNA species. Identifying the structures and compositions of these RNP complexes and determining how they mediate control over mRNA stability presents a major challenge to current research efforts.
Globin mRNAs accumulate to 95% of the total cellular mRNA during the 2- to 3-day window of terminal erythroid differentiation (36). This is a period at which these cells have already undergone global transcriptional arrest. Hence, the shift in mRNA complexity during terminal differentiation of the erythroblast reflects stabilization of globin mRNAs and selective destabilization of most nonglobin mRNAs (reviewed in reference 36). Due to the high-level stability of globin mRNAs and the numerous genetic and experimental model systems that are available for their study, these mRNAs constitute an ideal model for the study of stabilization mechanisms.
Initial insight into the mechanism of globin mRNA stabilization was gained from the study of α-Constant Spring (αCS) thalassemia. The αCS mutation, found at a high frequency in Southeast Asia, is a single base substitution at the translation stop codon (UAA → CAA) of the major α-globin gene (α2) (8, 29). This mutation results in ribosome read-through into the 3′ UTR with termination at an in-frame UAA within the poly(A) addition site AAUAAA. The αCS mutation results in greater than 95% loss of α-globin mRNA expression from the affected locus and a corresponding decrease in overall α-globin synthesis (8, 29). The dramatic loss of α-globin expression reflects instability of αCS mRNA (24). Studies further revealed that this destabilization is triggered by ribosome entry into the 3′ UTR (30, 44). The model that emerged from these studies was that one or more determinants within the 3′ UTR of human α-globin (hα-globin) mRNA are involved in maintenance of its stability; interference with the structure or function of this complex(es) by the elongating ribosome triggers accelerated mRNA decay.
Studies to define the determinants of hα-globin mRNA stability subsequently confirmed certain aspects of this model. Three discontinuous C-rich elements within the 3′ UTR of hα-globin mRNA were linked to its high-level accumulation in erythroid cells (44, 45). A corresponding set of high-affinity binding proteins was identified by in vitro analyses (42). Biochemical purification of these proteins (20) revealed that they comprised a set of proteins sharing a characteristic triple repeat of the 50-amino-acid KH domain RNA binding motif (37). Based on their binding to hα-globin mRNA and their poly(C) specificity, these proteins were named α-globin poly(C) binding proteins, or αCPs (20, 26). {αCPs are also referred to as PCBPs [poly(C)-binding proteins] and hnRNP Es (14, 22, 31).} Interaction of αCP with the C-rich 3′ UTR determinants forms an RNP “α-complex.” Mutations within the 3′ UTR that destroyed the ability of αCPs to form this complex in vitro resulted in a corresponding loss of mRNA accumulation in vivo (42). Studies carried out in transgenic mice and using in vitro decay systems further suggested that the α-complex protects the poly(A) tail from rapid shortening (30, 43). Using in vitro approaches it was possible to identify α-complexes on the 3′ UTRs of three additional stable mRNAs. These findings led to the hypothesis that the α-complex might constitute a general determinant of high-level mRNA stability (18).
While the model of α-complex-mediated mRNA stabilization is supported by experimental data, certain aspects remain speculative. Demonstration of the α-complex formation on α-globin mRNA has been limited to in vitro binding studies, and these studies have been restricted to the analysis of 3′ UTR sequences. Whether the α-complex forms in vivo and whether it is limited to the 3′UTR and/or binds to other regions of the target mRNA is not known. In addition, the provisional model assumes that αCP is normally present on actively translating mRNAs and that an antiterminated ribosome, as occurs in the αCS mutation, has the capacity to disrupt this RNP complex (45). Alternatively, the α-complex may be limited to mRNAs that are translationally inert or have cycled out of translation due to stochastic or age-related phenomena.
To further define the in vivo pathways of mRNA stabilization and the role(s) of αCP binding in this process, we tested a number of assumptions intrinsic to αCP binding and function. Significantly, these studies and others (S. Waggoner and S. A. Liebhaber, unpublished data) demonstrate a stable and selective in vivo association of αCP with α-globin mRNA. These studies also localize the binding site exclusively to the C-rich motif in the 3′ UTR. This association is dependent on the 3′ UTR positioning and is compatible with efficient polysome loading and active translation. These data support a model in which the RNP α-complex can exert a stabilizing effect on actively translating mRNAs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture.
Human erythroleukemia (K562) cells were grown in RPMI 1640 medium and mouse erythroleukemia (MEL) cells were cultured in minimal essential medium (MEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum containing 100 U of penicillin/ml and 100 μg of streptomycin sulfate/ml in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator. MEL cells stably transfected with the tet transactivator (MEL/tTA) (20a) were used for conditional expression of the hα-globin mRNA. For transfections, MEL/tTA cells supplemented with 500 ng of tetracycline (TET)/ml were split 1 day before electroporation, washed with cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pelleted by centrifugation at 4°C, and resuspended in cold serum-free MEM at a concentration of 5 × 107/ml (0.5 ml of cells). Two micrograms of plasmid and 18 μg of vector carrier were added to the cell suspension. Electroporation was performed with a BRL Cell-Porator system at 250 V, 1,180 μF, and low resistance. The cells were then plated in prewarmed complete MEM and maintained in the incubator for 24 h prior to analysis.
Expression plasmids.
The full-length hα2-globin gene cloned into pTet-splice vector (Gibco-BRL) was designated pTet-WT. pTet-CS was generated by replacing the termination codon of α2-globin with CS mutation, and pTet-Neu was generated by replacing the 42-bp protected region of the WT gene with a 42-bp neutral sequence which cannot form the α-complex (detailed by Kong et al. [20a]).
Preparation of cell extracts and polysome purification.
MEL and K562 cells grown under standard conditions (see above) were washed three times with cold PBS and resuspended in proteinase inhibitor buffer (1 mM potassium acetate, 1.5 mM magnesium acetate, 2 mM dithiothreitol [DTT], 10 mM Tris-Cl [pH 7.4], 100 mg of phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride [PMSF]/ml, 2 mg of aprotinin/ml, 2 mg of pepstatin A/ml) at a density of 2 × 107/ml. The cells were lysed with 25 strokes in a Dounce homogenizer. The lysate was clarified by centrifugation at 4°C for 10 min at 10,000 × g. The supernatant was layered onto a 30% sucrose cushion (in 1 mM potassium acetate, 1.5 mM magnesium acetate, 2 mM DTT, 10 mM Tris-Cl [pH 7.4]) and centrifuged for 2.5 h at 130,000 × g (32,500 rpm; SW41 rotor). The supernatant (S130) was harvested and the pellet (polysomes) was resuspended in protease inhibitor buffer (1 mM potassium acetate, 1.5 mM magnesium acetate, 2 mM DTT, 10 mM Tris-Cl [pH 7.4], 100 mg of PMSF/ml, 2 mg of aprotinin/ml, 2 mg of pepstatin A/ml). All fractions were stored at −80°C.
Sucrose gradients.
Ten-to-50% linear sucrose gradients containing 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM DTT, 20 mM HEPES (pH 7.4) were prepared in Beckman ultracentrifuge tubes by using a two-chamber gradient mixer. K562 cells were incubated with cycloheximide (100 μg/ml; freshly prepared in ethanol) for 15 min prior to harvesting. The cells were then transferred to a 50-ml tube containing 20 ml of frozen crushed PBS and 100 μg of cycloheximide/ml and centrifuged at 1,000 × g for 5 min at 4°C. The cell pellet was washed with ice-cold PBS twice and was lysed by repeated pipetting in 500 μl of ice-cold TMK100 lysis buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.4], 5 mM MgCl2, 100 mM KCl, 2 mM DTT, 1% Triton X-100, and RNase inhibitor [100 U/ml; Promega], in diethyl pyrocarbonate-treated water) for 5 min. The nuclei were cleared at 10,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C, and the supernatants (S10) were removed and layered onto the prepared gradients. The SW41 rotor and the ultracentrifuge were both precooled to 4°C, and the gradients were centrifuged at 40,000 rpm for 85 min at 4°C. The gradients were collected in 16 fractions (650 μl per fraction) from the top to the bottom by displacing them upwards with 60% sucrose, and the gradient profile was monitored via UV absorbance at 254 nm with an ISCO UA-5 detector (Lincoln, Nebr.). The fractions were collected into 1.5-ml microcentrifuge tubes containing 70 μl of 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Each sample was digested with 8 μl of protease K (20 mg/ml) solution at 37°C for 30 min. Samples were stored at −80°C prior to RNA extraction.
For αCP-polysome interaction studies, 25 optical density at 260 nm (OD260) units of redissolved polysomes was used as a starting material. For EDTA treatment, a polysome aliquot was brought to 20 mM EDTA and incubated at 4°C for 20 min before loading onto the gradient supplemented with 20 mM EDTA. For nuclease treatment, RNase A was added to a polysome aliquot to a final concentration of 100 μg/ml (9) and incubated for 15 min in a cold room before loading. For the salt sensitivity study, a polysome aliquot was adjusted to the desired final concentration of KCl (0.5 or 0.8 M) and loaded onto a gradient containing the same concentration of salt. After loading, each gradient was centrifuged at 40,000 rpm in a Beckman L8-m ultracentrifuge with an SW41 rotor for 150 min at 4°C. Fractions were collected as described above, and proteins were precipitated with a fourfold excess of cold acetone prior to SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and Western blotting.
Antibodies.
Primary antibodies to the αCP isoforms have been previously detailed and characterized (7). PK antibody (Biodesign International) was used at 1:3,000. Polyclonal anti-L7a rabbit serum was raised against epitope residues 253 to 266 in the human L7a sequence as originally described by Ziemiecki et al. (47) and used without further purification at 1:1,000. Secondary antibodies were as follows: donkey anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG)-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) (used at 1:5,000; Amersham) and donkey anti-goat IgG-HRP (used at 1:5,000; Santa Cruz).
SDS-PAGE and analysis.
For Western and Northwestern analysis, proteins were separated on SDS-12.5% PAGE and electroblotted to nitrocellulose membranes (Protran BA 85; Schleicher & Schuell) for 1 h at 150 mA in transfer buffer (20 mM Tris, 150 mM glycine, 20% methanol) using a Semi-phor transfer apparatus (Hoefer). For Western analysis, the membranes were blocked in 3% nonfat milk in 1× PBS for 1 h at room temperature, followed by an additional hour with appropriate antisera. Signals were developed by incubation with HRP-labeled secondary antibodies (Amersham) as detailed by the supplier (ECL reagents; Boehringer Mannheim).
RPA.
Probes used for the RNase protection assay (RPA) were generated by in vitro transcription of plasmids containing cDNA inserts for hα-globin and hζ-globin (25), human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and mouse GAPDH (Ambion, Austin, Tex.), or direct transcription from a human γ-globin genomic DNA PCR template containing a contiguous region extending from intron 1 through intron 2. This 320-nucleotide (nt) antisense γ-globin RNA probe generated from an SP6 promoter element in the 5′ amplification primer yields a 223-nt protected fragment corresponding to exon 2 of the γ-globin mRNA (a kind gift from J. E. Russell, University of Pennsylvania). In vitro transcriptions were carried out in the presence of α[32P]CTP (400 Ci/mmol, 10 mCi/ml; Amersham, Arlington Heights, Ill.) using a Maxiscript SP6 kit under conditions recommended by the manufacturer (Ambion). Final concentrations of ATP, GTP, and UTP were 0.5 mM, and that of CTP was 0.06 mM.
RNA was phenol extracted from sucrose fractions and ethanol precipitated with 1 μl of glycogen (15 μg/μl) as a carrier. The precipitated RNA was redissolved in 21 μl of hybridization buffer (40 mM piperazine-N,N′-bis(2-ethanesulfonic acid) [pH 6.4], 1 mM EDTA [pH 8.0], 0.4 M NaCl, 80% formamide) supplemented with probes. Samples were heated at 84°C for 15 min, incubated overnight at 50°C, and digested for 15 min at room temperature in 200 μl of RNase assay buffer (300 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris Cl [pH 7.5], 5 mM EDTA [pH 8.0]) containing 1 μl of RNase cocktail (500 mg of RNase A/ml, 20,000 U of RNase T1/ml; Ambion). Digestions were terminated by addition of 18 μl of an SDS-protease K (10%:2 mg/ml) mixture to each sample followed by incubation for 20 min at 37°C. RNA was extracted, precipitated, dissolved in loading buffer, and resolved onto a 6% acrylamide-8 M urea gel. Radioactivity in bands of interest was quantified by PhosphorImager analysis (Storm 840; Molecular Dynamics).
Immunoprecipitation.
Ten microliters of anti-CP rabbit serum or preimmune rabbit serum was incubated with 200 μl of a 50% protein A-Sepharose slurry in 600 μl of PBS for 1 h at 4°C with gentle rocking. S130 and the polysome fraction (150 μl) were diluted in 600 μl of IP binding buffer (20 mM HEPES [pH 7.9], 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Triton X-100, 100 U of RNase inhibitor/ml). The diluted S130 or polysome fraction was incubated with antibody-coupled protein A-Sepharose for 2 h at 4°C. The immunoprecipitated complexes were pelleted by brief low-speed centrifugation and washed five times with IP binding buffer. A 400-μl aliquot of IP elution buffer (0.1 M Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 12.5 mM EDTA, 0.15 M NaCl, 1% SDS) was added to the protein A-Sepharose-RNP complex pellet and the complex was disrupted by boiling for 3 min. RNA was then extracted and ethanol precipitated prior to RPA analysis.
RESULTS
Globin gene expression is restricted to erythroid cells and is developmentally specified. The human-derived K562 cell line expresses abundant levels of a fetal or adult α-globin, as well as its embryonic precursor, ζ-globin. This phenotype makes these cells an optimal model for analysis of hα-globin gene expression. To characterize in vivo interactions between hα-globin mRNA and αCP proteins and relate these interactions to α-complex function, we asked whether hα-globin mRNA and αCPs colocalize on ribosomes.
hα-globin mRNA is quantitatively loaded on polysomes.
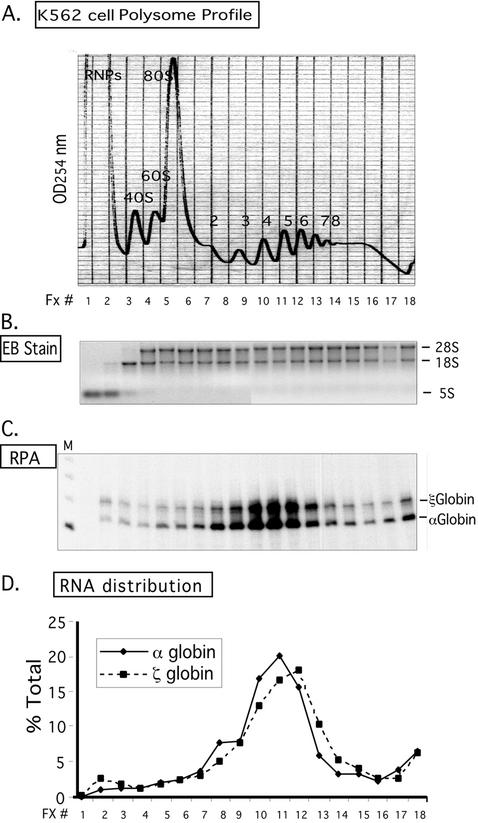
The distribution of α-globin mRNA in K562 cells was studied by cell fractionation and sucrose gradient analyses. In the initial experiment, a clarified K562 cytoplasmic extract was fractionated into preribosomal and ribosomal fractions by sedimentation at 130,000 × g through a 30% sucrose cushion. The content of hα-globin mRNA in these fractions was assessed by RPA (Fig. 1). The data revealed that α-globin mRNA quantitatively fractionated with the polysomal pellet. To confirm and extend this observation, the distribution of hα-globin mRNA was assessed across a polysome gradient. A clarified K562 cytosolic extract was applied to a linear 10-to-50% sucrose gradient (Fig. 2A). RNA extracted from each fraction was resolved on an agarose gel (Fig. 2B), and the distributions of hα-globin and ζ-globin mRNAs were determined across the gradient by RPA (Fig. 2C). hα-globin and ζ-globin mRNAs both have 142-codon open reading frames. Consistent with the data in Fig. 1, α-globin mRNA was quantitatively incorporated in the polysomal fractions. The distributions of hα- and ζ-globin mRNAs peaked at the 4-5 polysome region (Fig. 2D). Higher-molecular-weight polysomes are involved in translation of various nonglobin mRNAs in the K562 cells. The positioning of the ζ-globin mRNA peak slightly to the right of the α-globin peak was reproducible and may indicate a slightly higher translation efficiency of ζ-globin mRNA in this embryonic erythroid cell environment. We conclude from these data that hα-globin is quantitatively incorporated on polysomes in K562 cells.
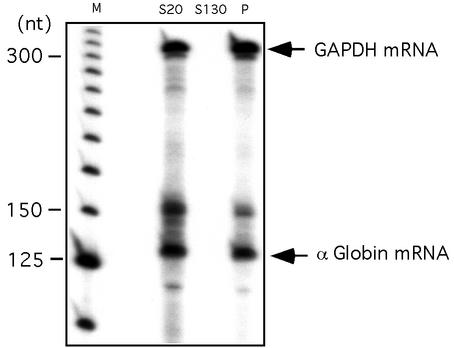
FIG. 1.
hα-globin mRNA localizes to the polysome fraction of K562 cells. A clarified (S20) cytoplasmic extract from log-growth K562 was pelleted through a 30% sucrose cushion to separate prepolysome supernatant (S130) and polysomal (P) pellet fractions. hα-globin and GAPDH mRNAs were detected by RPA. The positions of the protected bands corresponding to GAPDH and α-globin are noted. The band above α-globin corresponds in size to the primary α-globin transcript and may be detecting contaminant genomic DNA. A 25-nt DNA ladder is shown (M).
FIG. 2.
Distribution of hα- and ζ-globin mRNAs across a K562 cell polysome gradient. (A) Sucrose gradient profile of K562 cytosolic extract. The absorbance profile (OD254) of the gradient is shown. The top of the gradient is to the left; the positions of absorbance peaks corresponding to preribosomal RNPs, 40S, 60S, and 80S, and polysomes (2-, 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-somes) are indicated. The 18 fractions (Fx #) collected for subsequent analysis are identified below the tracing. (B) Agarose gel electrophoresis of RNA extracted from the polysome gradient fractions. A 2-μg RNA sample from each fraction (in panel A) was applied to the gel and electrophoresed, and the abundant 28S, 18S, and 5S rRNAs were directly visualized by ethidium bromide staining. The distributions of these RNAs were consistent with the OD peak assignment (in panel A). (C) Detection of globin mRNAs across the K562 polysome gradient. Each gradient fraction was assessed for hα-globin and hζ-globin mRNAs by RPA with corresponding 32P-labeled probes. hα-globin and hζ-globin mRNAs protected probe fragments of 132 and 150 bp, respectively. (D) Distribution of globin mRNAs across the K562 polysome gradient. The contents of hα-globin and ζ-globin mRNAs in each fraction (in panel C) were quantified by PhosphorImager analysis. The amount of each mRNA species in each fraction is depicted as a percentage (ordinate) of the total for the corresponding species across the gradient.
A fraction of αCP proteins is polysome associated.
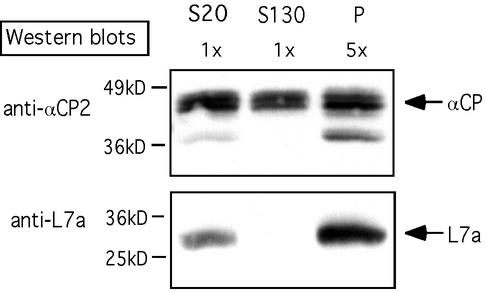
Direct association of αCP with polysomes was tested. Equal aliquots of S20 and S130 and a fivefold-concentrated aliquot of polysome proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and probed with a series of antisera (Fig. 3). As expected, the large ribosome subunit protein L7a was restricted to the polysome pellet. In contrast, the αCP2 isoforms were present in both the supernatant and polysomal fractions. On the basis of relative intensity of signals and the relative loading on each lane, it was estimated that 10 to 20% of the total cytoplasmic αCP2 isoforms was localized to the polysome pellet.
FIG. 3.
αCP proteins are ribosome associated. A clarified K562 cell cytoplasmic extract (S20) was fractionated into prepolysomal (S130) and polysomal (P) fractions by sedimentation through a 30% sucrose cushion. Each of the three preparations was resolved on an SDS-PAGE gel; equal aliquots of S20 and S130 fractions and fivefold-concentrated aliquots of the polysome fraction were separated by SDS-PAGE. αCP2/KL and ribosomal L7a proteins were detected by Western blotting with corresponding antisera. The band at 37 kDa represents an isoform of αCP2 (αCP2KL). The positions of the molecular mass markers (not shown) are indicated on the left.
The observation that a fraction of cytoplasmic αCPs was enriched in the polysome pellet suggested that these proteins might be polysome associated. To test this possibility, polysome gradients were probed for αCP. An initial study was carried out on a native polysome preparation (Fig. 4A). The distribution of L7a protein was appropriately limited to the 60S, 80S, and polysome regions of the gradient. In contrast, the αCP2 signal extended from the pre-40S region through the entire polysome region. Since it is possible that a certain amount of the prepolysomal αCP2 signal may result from dissociation during handling, the αCP content in the polysome-associated fraction of the gradient is considered as a minimal estimate. These data, in combination with those in Fig. 3, demonstrate that a substantial population of cytoplasmic αCP is associated with polysomes.
FIG. 4.
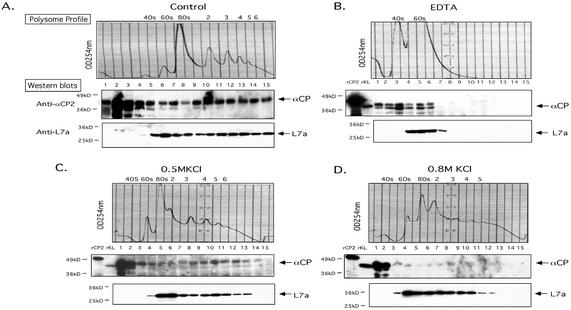
Characterization of the αCP-polysome interaction. Polysome aliquots (as in Fig. 3) were treated in the indicated manners and analyzed on 10-to-50% sucrose gradients. (A) No additional treatment. The OD254 is indicated (upper panel; Polysome Profile). Proteins in each fraction were precipitated, separated by SDS-12% PAGE, transferred to membranes, and probed with the indicated antibodies (Western blots). See the legend to Fig. 3 for details. (B) EDTA treatment. The polysome sample was resuspended in 20 mM EDTA (final concentration) prior to sucrose gradient fractionation. This treatment dissociates polysomes into 40S and 60S ribosome subunits. The splitting of the αCP signal seen in this Western blot is occasionally observed. (C) Treatment with 0.5 M KCl. The polysome fraction was brought to 0.5 M KCl (final concentration) prior to sucrose gradient fractionation. This treatment removes proteins loosely associated with the polysomes. (D) Treatment with 0.8 M KCl. The polysome fraction was supplemented with 0.8 M KCl (final concentration) prior to sucrose gradient fractionation. This treatment removes almost all proteins from the polysomes that are not intrinsic ribosomal proteins.
The interaction of αCP with polysomes was further characterized. Ribosome stability is dependent on the presence of Mg2+ (5). Treatment of the K562 polysome preparation with EDTA caused the predicted collapse of the polysome profile to 40S and 60S peaks (Fig. 4B). L7a was appropriately localized to the 60S peak. The release of αCPs from EDTA-dissociated polysomes to the top of the gradient (Fig. 4B, lower panel) indicated that the αCPs, although associated with polysomes, are not directly bound to either of the two ribosomal subunits.
The basis for the αCP-polysome association was assessed for salt resistance. An aliquot of the polysome preparation was brought to a final KCl concentration of 0.5 or 0.8 M. Under these high salt conditions, most protein-protein interactions are interrupted while the structure of the core ribosomal complex remains intact (46). As expected, the polysome profile and the distribution of L7a were maintained under the high-salt treatment (Fig. 4C and D, upper panels). The distribution of αCPs was only minimally altered at the 0.5 M KCl concentration (Fig. 4C) but changed significantly at 0.8 M KCl, with a shift to the lighter, prepolysome fractions (Fig. 4D). This level of salt resistance clearly distinguishes αCP from intrinsic ribosomal proteins (e.g., L7a) and defines αCP as a tightly bound polysome accessory protein.
Association of αCP with polysomes is RNA dependent.
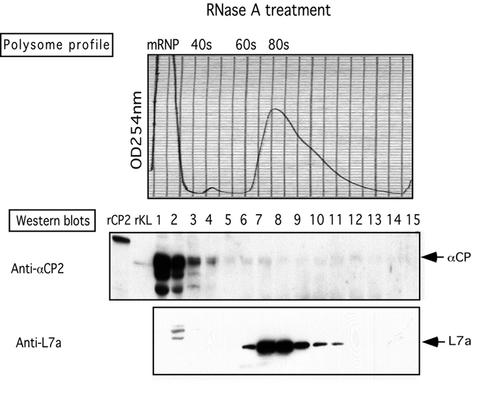
The tight association of αCP with polysomes might reflect a direct interaction of αCP with the 80S ribosome per se. Alternatively, this association might be mediated indirectly via binding to actively translating mRNAs. To distinguish between these two models, an aliquot of the K562 polysomes was treated with RNase A prior to sucrose gradient fractionation. RNase A will digest exposed regions of the mRNA and in so doing will sever linkages between ribosomes in the polysome complex. RNase digestion resulted in the expected collapse of the polysome profile to a single monosome peak (80S) (Fig. 5, top panel). A second distinct peak, generated at the top of the gradient, most likely represented mRNP fragments released by the RNase digestion. L7a protein appropriately localized to the 80S peak (Fig. 5, bottom panel). In contrast, αCP was restricted to the preribosomal mRNP peak at the top of the gradient (Fig. 5, middle panel). Of particular note, αCP was not represented in the monosome region. These data demonstrate that the association of αCPs with polysomes is indirect and RNA dependent.
FIG. 5.
Association of αCP with polysomes is RNA dependent. The polysome fraction was prepared as detailed in the legend for Fig. 3, and an aliquot was treated with RNase A prior to sucrose gradient fractionation. Details of the analysis are as in the legend to Fig. 4.
αCP binds to actively translating α-globin mRNA.
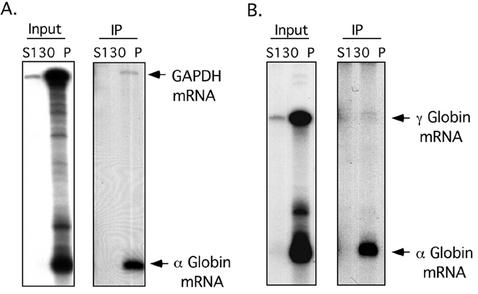
The partial overlap in the distributions of αCP and hα-globin mRNA on the polysome gradient (Fig. 2 and 4) and the RNA dependence of αCP association with ribosomes (Fig. 5) suggested that αCP might be directly bound to actively translating hα-globin mRNA. To test this model, αCP-containing complexes were immunoprecipitated from S130 and polysome fractions of a K562 cytosolic extract; RNAs isolated from the immunoprecipitates were assayed for hα-globin mRNA and for two mRNAs that do not associate with αCP, GAPDH and γ-globin (Fig. 6). The input polysomal RNA preparation contained equivalent amounts of all three mRNAs, while αCP2 complexes contained abundant amounts of hα-globin mRNA with only trace levels of the two control mRNAs. These data demonstrate a specific in vivo association of αCPs with actively translating, polysomal hα-globin mRNA.
FIG. 6.
In vivo association of αCP with polysome-bound hα-globin mRNA. Equal amounts of the prepolysomal (S130) and polysomal (P) fractions of K562 cytoplasmic extracts were individually immunoprecipitated with an antibody specific to the αCP2 and αCP2-KL isoforms. RNA extracted from the immunoprecipitates was assessed for specific mRNA content by RPA. This study was carried out independently four times with consistent results. (A) RPA using probes to hα-globin and GAPDH mRNAs. (B) RPA using probes to hα-globin and γ-globin mRNAs.
In vivo binding of αCP to hα-globin mRNA is restricted to the 3′ UTR.
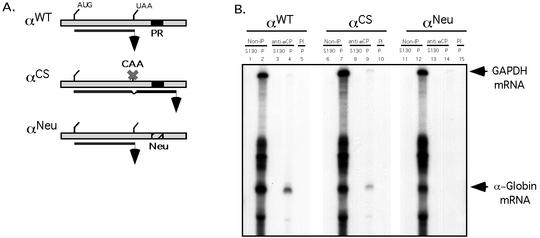
Prior work from our laboratory has defined a C-rich motif within the 3′ UTR of hα-globin mRNA that serves as a high-affinity binding site for αCP (7). Of note, these studies relied on in vitro binding analyses and were limited to the study of 3′ UTR target sequences. The immunoprecipitation studies detailed in the present report demonstrate in vivo binding of αCP to polysomal hα-globin mRNA, but they did not define the site of this interaction on the target mRNA. This binding may be uniquely mediated by the previously defined 3′ UTR poly(C)-rich motifs. Alternatively, αCP could bind to one or more additional sites elsewhere in the full-length GC-rich hα-globin mRNA. To resolve this issue, MEL cells expressing a tet-transactivator fusion protein (MEL/tTA cells) were transfected with wild-type hα-globin mRNA (αWT) and with a derivative RNA in which the 3′ UTR αCP binding site has been replaced by a comparably sized “neutral” sequence (αNeu) (Fig. 7A). Both constructs were under the control of the tet operator and cytomegalovirus promoter. The neutral sequence substitution in αNeu destroys αCP binding to the 3′ UTR when assayed in vitro and destabilizes the mRNA when assessed in vivo (20a). Twenty-four hours posttransfection in TET-deficient medium, the MEL cells were harvested and polysomes were isolated. Immunoprecipitation of αCP complexes from the polysome (P) and prepolysomal (S130) fractions was performed along with a control preimmune immunoprecipitation (Fig. 7B). Analysis of the two fractions prior to immunoprecipitation confirmed robust representation of both hα-globin mRNAs in the polysome fraction. Immunoprecipitation of αCP-containing polysomal RNPs resulted in selective isolation of the wild-type hα-globin mRNA but failed to bring down the mutant (αNeu) mRNA. These data demonstrated that the αCP binding site in the 3′ UTR is the unique in vivo binding site for αCP on translating hα-globin mRNA.
FIG. 7.
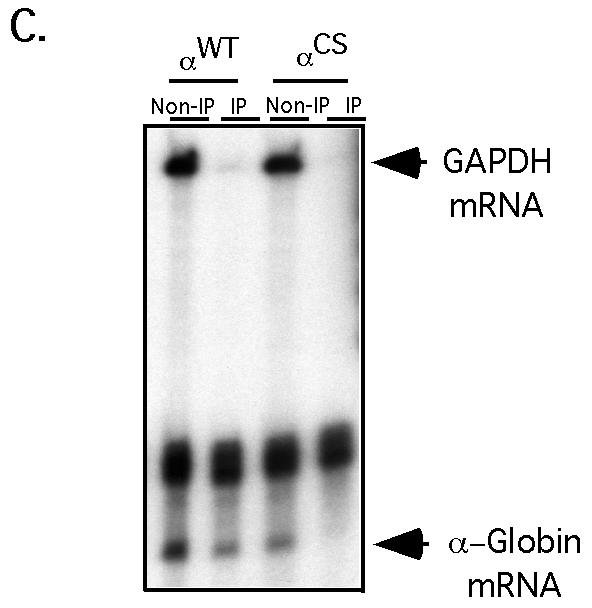
Interaction of αCP2 with α-globin mRNA is uniquely dependent on the 3′ UTR poly(C)-rich region and is sensitive to displacement by an antiterminated 80S. (A) Expression of hα-globin mRNAs with distinct 3′ UTRs (WT, Neu, and CS) in MEL/tTA cells. The structures of the three encoded mRNAs under the control of a tet promoter are shown. The positions of the translation start site (AUG), termination site (UAA), αCP binding site (protected region [PR]), and the antitermination mutation in the αCS (UAA → CAA) are shown. The cross-hatched box represents the substitution of a neutral sequence for the PR motif. (B) αCP binding on hα-globin mRNA is restricted to the C-rich 3′ UTR stability motif. Each of the indicated α-globin mRNAs was expressed in transfected cells from a corresponding plasmid. After 24 h of induction of expression in TET-deficient medium, the cells were lysed and the clarified cytoplasmic (S20) extracts were layered onto a 30% sucrose cushion. The isolated prepolysomal (S130) and polysomal (P) fractions were separately immunoprecipitated with antibody to αCP2 and αCP2-KL or with preimmune serum (PI). RNA was extracted from the starting material and from each immunoprecipitate. hα-globin and GAPDH mRNAs were detected by RPA. The origin of each sample is indicated above its respective lane. The positions of the RPA probes are indicated to the right of the gel. (C) Selective dissociation of αCP from the antiterminated αCS mRNA. MEL/tTA cells were separately transfected with pTet-WT and pTet-CS plasmids. The transfected genes were transcriptionally induced for 24 h in TET-deficient medium. TET was then added back to the medium at a concentration of 500 ng/ml for an additional 2 h. The cells were subsequently lysed and clarified (S10), and RNP complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-αCP2 sera. mRNA content in the precipitate was analyzed by RPA as described for panel B. These studies were carried out independently three times with consistent results.
The α-complex is displaced by ribosome extension into the 3′ UTR.
Analysis of αCS mRNA was carried out to further characterize the association of αCP with hα-globin mRNA. αCS mRNA has a single base substitution at the translation termination codon (UAA → CAA) that allows the translating ribosome to enter the 3′ UTR and translate 31 additional amino acids. This translational extension traverses the αCP binding site (Fig. 7A). MEL/tTA cells were transfected with the αWT and αCS expression vectors, and transcription was induced for 24 h by transferring the cells to TET-deficient medium. αCP complexes were immunoprecipitated from the respective polysome pellets (Fig. 7B). RPA revealed that αWT and αCS mRNAs were both present in the α-complexes. Of note, the efficiency of αCS mRNA recovery in the α-complex precipitate was somewhat lower than that of the αWT mRNA (Fig. 7B). This would be consistent with displacement of αCP by the antiterminated ribosome. However, the continued association of a substantial amount of αCS mRNA with αCP suggested that this displacement was either not efficient or that, once displaced, the αCP could readily reassociate with the mRNA. A third possibility was that the αCP-bound αCS mRNA represented the subset of newly synthesized mRNA that had not been fully translated. To decide among these models, the α-complex immunoprecipitation study was repeated on cells pulsed with αWT or αCS mRNAs followed by a 2-h chase in which the expression of the transfected genes was shut off by transfer of the cells into TET-containing medium. The content of α-globin mRNA in the αCP-containing RNPs from these pulse-chased cells was determined by RPA (Fig. 7C). Consistent with the known instability of αCS mRNA, the total level of αCS mRNA in these cells at the end of the chase was lower than that of αWT mRNA. Significantly, αCS mRNA could no longer be detected in the α-complex pellet. These results suggest that the antiterminated ribosome can efficiently and permanently displace αCP from the 3′ UTR of α-globin mRNA.
DISCUSSION
The present report addresses questions central to the formation and function of 3′ UTR RNP complexes. The particular complex being studied comprises a single molecule of αCP bound to a C-rich motif (7). The resultant 3′ UTR α-complex is a major determinant of hα-globin mRNA expression. The impact of αCP binding on hα-globin mRNA expression is most likely mediated via mRNA stabilization (44). The data in the present report demonstrate that a fraction of cytosolic αCP is polysome associated (Fig. 3 and 4) and that this association is RNA dependent (Fig. 5). Coimmunoprecipitation of polysomal mRNPs from cell extracts directly demonstrates specific binding of αCP to hα-globin mRNA (Fig. 6). The in vivo association of αCP with hα-globin mRNA was demonstrated to be restricted to the 3′ UTR C-rich motif and was subject to displacement by antiterminated ribosomes that read through the αCP binding site (Fig. 7). We conclude from these data that αCP is bound to actively translating mRNAs in vivo and that the maintenance of the α-complex is dependent on its positioning in the 3′ UTR.
Lines of evidence, both in vivo and in vitro, support a role for the α-complex in maintaining the high-level expression of hα-globin mRNA (see the introduction). Based on the presence of poly(C)-rich cis elements in the 3′ UTRs of additional highly stable mRNAs and the ability of these elements to form high-affinity mRNP complexes containing αCP, it has been further suggested that the α-complex may constitute a general determinant of mRNA stabilization (18, 34, 38). However, formation of these RNP complexes in vivo has not been tested, and the mode of α-complex action remains to be fully defined. Here, we show that a fraction of the cytoplasmic αCPs is polysome associated and is bound to an actively translating target mRNA. These data extend our understanding of αCP action and can be used to refine models of α-complex-mediated alterations in mRNA stability and/or function.
While a subpopulation of αCPs in K562 cells are polysome associated, approximately 80% are prepolysomal (Fig. 3). A similar estimate has been reported for αCPs in HeLa cells (1, 15). These data suggest that αCPs may be involved in functional interactions with nontranslating as well as translating mRNAs. This suggestion is consistent with prior studies demonstrating that the α-complex contributes to the stability of translationally blocked as well as translationally active hα-globin mRNAs (44, 45).
The relationship of subcellular αCP localization with its functions can be inferred from studies of 15-lipoxygenase (LOX) mRNA. LOX mRNAs are maintained in a stable and translationally silent state over a several-day span of erythroid differentiation (17, 40). This stored LOX mRNA is present on free cytoplasmic mRNP particles (41). Translational silencing of LOX mRNA has been linked to binding of αCP, as well as hnRNP K (28), to a pyrimidine-rich differentiation control element determinant in its 3′ UTR (31-33). Based upon the function of α-complexes in a subset of stable mRNAs, it has been proposed that the same αCP-containing complex that mediates the translational silencing of LOX mRNA may also mediate its stable storage in erythroid cells (18). Therefore, the observation in the present report that αCP is present in both polysomal and nonpolysomal cytosolic fractions is consistent with studies implicating the α-complex, or α-like complexes, in control over the stability and function of both translationally active and translationally silenced mRNAs.
The association of αCP with polysomes occurs via binding to mRNAs. This was indicated by the release of αCP from the polysomes after RNase treatment (Fig. 5) and confirmed by coimmunoprecipitation studies (Fig. 6). The stability of this interaction at 0.5 M KCl (Fig. 4C) suggested that this interaction is quite stable at physiologic salt concentrations (0.15 M NaCl). In comparison, association of the closely related KH domain FMRP with polysomes is significantly more salt sensitive (9). This tight association of αCP with polysomal mRNAs is consistent with the high binding affinity that has been previously determined for the interaction of αCP with its target hα-globin mRNA (Kd(app), 0.5 nM [7]).
Several members of the KH domain family of RNA binding proteins have been shown to be associated with polysomes. One of the best-characterized is FMRP. This protein contains three RNA binding elements: two KH domains and an RGG box. Silencing of the X-linked FMR1 gene by pathological expansion of a 5′ UTR trinucleotide CGG repeat results in the highly prevalent fragile X mental retardation (FMR) syndrome (reviewed in reference 19). Early studies aimed at defining a role for the FMR protein demonstrated that it was polysome associated and that it bound a subset of brain RNAs (2, 10). More recent studies have defined a restricted subset of FMR-targeted mRNAs and further demonstrated that loss of FMR expression results in a selective shift in the polysome distribution of a subset of these binding targets (6). Thus, the FMR protein appears to control as-yet-undefined aspects of translation. Whether FMR associates with nontranslating mRNAs is not known, although some FMRP is prepolysomal (12). SCP160p, a 160-kDa protein containing 14 KH domains with an undefined role, may target a subset of polysomal mRNAs (13, 21). CRD-BP, a four-KH domain protein that binds to the c-myc mRNA coding region stability determinant is also ribosome associated (11). Thus, a number of KH proteins have been implicated in various aspects of posttranscriptional control. In each case, the mechanisms and pathways are now under study but appear in at least a subset of their actions to overlap in targeting polysomal mRNAs.
While the present study demonstrates an association of αCP with α-globin mRNA, the data do not address where and when the α-complex forms in vivo. Some insight into the question of where α-complex assembly can occur may be gleaned from the analysis of αCS mRNA. Newly synthesized αCS mRNA is bound by αCP, while αCS mRNAs that have spent several hours in the cytoplasm are excluded from the α-complex (Fig. 7). The data suggest that the majority of αCP loading occurs in the nucleus or at least prior to cytoplasmic translation; once displaced by the translating ribosome, the α-complex cannot efficiently reform in the cytoplasmic compartment. The dislocation of αCP from the αCS mRNA in the cytoplasm may be sufficient to expose these mRNAs to rate-limiting steps in mRNA decay and contribute to its dramatic destabilization.
Although αCP is present on the same set of polysomes as hα-globin mRNA, αCP is present elsewhere in the polysome profile as well and its distribution clearly extends on polysomes too large to accommodate α-globin mRNA (Fig. 4A). This extensive distribution of αCP throughout the polysome gradient and the RNA dependence of the entire αCP polysome profile (Fig. 5) suggest that αCP is binding to a wide range of cellular mRNAs. This broad range of target mRNAs is consistent with the suggested role of the α-complex as a general determinant of mRNA stabilization (18) as well as contributing to translational controls (reviewed in reference 27). A broad-based approach to the identification of the full spectrum of target mRNAs, based upon the high affinity and structural specificity of αCP-mRNA interactions, may afford further insight into the role(s) that this family of RNA binding proteins plays in gene regulation.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grants HL 65449 and CA72765 to S.A.L. and by the generous support of the Doris Duke Foundation.
REFERENCES
- 1.Andino, R., G. E. Rieckhof, P. L. Achacoso, and D. Baltimore. 1993. Poliovirus RNA synthesis utilizes an RNP complex formed around the 5′-end of viral RNA. EMBO J. 12:3587-3598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ashley, C. T., K. D. Wilkinson, D. Reines, and S. T. Warren. 1993. FMR1 protein: conserved RNP family domains and selective RNA binding. Science 262:563-566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Atwater, J. A., R. Wisdom, and I. M. Verma. 1990. Regulated mRNA stability. Annu. Rev. Genet. 24:519-541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bernstein, P. L., D. J. Herrick, R. D. Prokipcak, and J. Ross. 1992. Control of c-myc mRNA half-life in vitro by a protein capable of binding to a coding region stability determinant. Genes Dev. 6:642-654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Blobel, G., and D. Sabatini. 1971. Dissociation of mammalian polyribosomes into subunits by puromycin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68:390-394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brown, V., P. Jin, S. Ceman, J. C. Darnell, W. T. O'Donnell, S. A. Tenenbaum, X. Jin, Y. Feng, K. D. Wilkinson, J. D. Keene, R. B. Darnell, and S. T. Warren. 2001. Microarray identification of FMRP-associated brain mRNAs and altered mRNA translational profiles in fragile X syndrome. Cell 107:477-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chkheidze, A. N., D. L. Lyakhov, A. V. Makeyev, J. Morales, J. Kong, and S. A. Liebhaber. 1999. Assembly of the alpha-globin mRNA stability complex reflects binary interaction between the pyrimidine-rich 3′ untranslated region determinant and poly(C) binding protein αCP. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:4572-4781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Clegg, J. B., D. J. Weatherall, and P. F. Milner. 1971. Haemoglobin Constant Spring—a chain termination mutant? Nature 234:337-340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Corbin, F., M. Bouillon, A. Fortin, S. Morin, F. Rousseau, and E. W. Khandjian. 1997. The fragile X mental retardation protein is associated with poly(A)+ mRNA in actively translating polyribosomes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 6:1465-1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Darnell, J. C., K. B. Jensen, P. Jin, V. Brown, S. T. Warren, and R. B. Darnell. 2001. Fragile X mental retardation protein targets G quartet mRNAs important for neuronal function. Cell 107:489-499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Doyle, G. A., N. A. Betz, P. F. Leeds, A. J. Fleisig, R. D. Prokipcak, and J. Ross. 1998. The c-myc coding region determinant-binding protein: a member of a family of KH domain RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 26:5036-5044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Feng, Y., D. Absher, D. E. Eberhart, V. Brown, H. Malter, and S. T. Warren. 1997. FMRP associates with polyribosomes as an mRNP, and the I304N mutation of severe fragile X syndrome abolishes this association. Mol. Cell 1:109-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Frey, S., M. Pool, and M. Seedorf. 2001. Scp160p, an RNA-binding, polysome-associated protein, localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a microtubule-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 276:15905-15912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Funke, B., B. Zuleger, R. Benavente, T. Schuster, M. Goller, J. Stevenin, and I. Horak. 1996. The mouse poly(C)-binding protein exists in multiple isoforms and interacts with several RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 24:3821-3828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gamarnik, A. V., and R. Andino. 1997. Two functional complexes formed by KH domain containing proteins with the 5′ noncoding region of poliovirus RNA. RNA 3:882-892. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hazelrigg, T. 1998. The destinies and destinations of RNAs. Cell 95:451-460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hohne, M., B. J. Thiele, S. Prehn, E. Giessmann, B. Nack, and S. M. Rapoport. 1988. Activation of translationally inactive lipoxygenase mRNP particles from rabbit reticulocytes. Biomed. Biochim. Acta 47:75-78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Holcik, M., and S. A. Liebhaber. 1997. Four highly stable eukaryotic mRNAs assemble 3′ untranslated region RNA-protein complexes sharing cis and trans components. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:2410-2414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kaytor, M. D., and H. T. Orr. 2001. RNA targets of the fragile X protein. Cell 107:555-557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kiledjian, M., X. Wang, and S. A. Liebhaber. 1995. Identification of two KH domain proteins in the alpha-globin mRNP stability complex. EMBO J. 14:4357-4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20a.Kong, J., et al. Mol. Cell. Biol., in press.
- 21.Lang, B. D., A. M. Li, H. D. Black-Brewster, and J. L. Fridovich-Keil. 2001. The brefeldin A resistance protein Bfr1p is a component of polyribosome-associated mRNP complexes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:2567-2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Leffers, H., K. Dejgaard, and J. E. Celis. 1995. Characterization of two major cellular poly(rC)-binding human proteins, each containing three K-homologous (KH) domains. Eur. J. Biochem. 230:447-453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liebhaber, S. A. 1997. mRNA stability and the control of gene expression. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 36:29-32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liebhaber, S. A., and Y. W. Kan. 1981. Differentiation of the mRNA transcripts originating from the α1- and α2-globin loci in normals and alpha-thalassemics. J. Clin. Investig. 68:439-446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Liebhaber, S. A., Z. Wang, F. E. Cash, B. Monks, and J. E. Russell. 1996. Developmental silencing of the embryonic ζ-globin gene: concerted action of the promoter and the 3′-flanking region combined with stage-specific silencing by the transcribed segment. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:2637-2646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Makeyev, A. V., and S. A. Liebhaber. 2000. Identification of two novel mammalian genes establishes a subfamily of KH-domain RNA-binding proteins. Genomics 67:301-316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Makeyev, A. V., and S. A. Liebhaber. 2002. The poly(C)-binding proteins: a multiplicity of functions and a search for mechanisms. RNA 8:265-278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Matunis, M. J., W. M. Michael, and G. Dreyfuss. 1992. Characterization and primary structure of the poly(C)-binding heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex K protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12:164-171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Milner, P. F., J. B. Clegg, and D. J. Weatherall. 1971. Haemoglobin-H disease due to a unique haemoglobin variant with an elongated alpha-chain. Lancet i:729-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Morales, J., J. E. Russell, and S. A. Liebhaber. 1997. Destabilization of human alpha-globin mRNA by translation anti-termination is controlled during erythroid differentiation and is paralleled by phased shortening of the poly(A) tail. J. Biol. Chem. 272:6607-6613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ostareck, D. H., A. Ostareck-Lederer, M. Wilm, B. J. Thiele, M. Mann, and M. W. Hentze. 1997. mRNA silencing in erythroid differentiation: hnRNP K and hnRNP E1 regulate 15-lipoxygenase translation from the 3′ end. Cell 89:597-606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ostareck, D. H., A. Ostareck-Lederer, I. N. Shatsky, and M. W. Hentze. 2001. Lipoxygenase mRNA silencing in erythroid differentiation: the 3′UTR regulatory complex controls 60S ribosomal subunit joining. Cell 104:281-290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ostareck-Lederer, A., D. H. Ostareck, N. Standart, and B. J. Thiele. 1994. Translation of 15-lipoxygenase mRNA is inhibited by a protein that binds to a repeated sequence in the 3′ untranslated region. EMBO J. 13:1476-1481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Paulding, W. R., and M. F. Czyzyk-Krzeska. 2000. Hypoxia-induced regulation of mRNA stability. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 475:111-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ross, J. 1995. mRNA stability in mammalian cells. Microbiol. Rev. 59:423-450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Russell, J. E., J. Morales, and S. A. Liebhaber. 1997. The role of mRNA stability in the control of globin gene expression. Prog. Nucleic Acids Res. Mol. Biol. 57:249-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Siomi, H., M. J. Matunis, W. M. Michael, and G. Dreyfuss. 1993. The pre-mRNA binding K protein contains a novel evolutionarily conserved motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 21:1193-1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Stefanovic, B., C. Hellerbrand, M. Holcik, M. A. Briendl, S. A. Liebhaber, and D. A. Brenner. 1997. Posttranscriptional regulation of collagen α1(I) mRNA in hepatic stellate cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:5201-5209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Surdej, P., A. Riedl, and M. Jacobs-Lorena. 1994. Regulation of mRNA stability in development. Annu. Rev. Genet. 28:263-282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Thiele, B. J., H. Andree, M. Hohne, and S. M. Rapoport. 1981. Regulation of the synthesis of lipoxygenase in erythroid cells. Acta Biol. Med. Ger. 40:597-602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Thiele, B. J., H. Andree, M. Hohne, and S. M. Rapoport. 1982. Lipoxygenase mRNA in rabbit reticulocytes. Its isolation, characterization and translational repression. Eur. J. Biochem. 129:133-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang, X., M. Kiledjian, I. M. Weiss, and S. A. Liebhaber. 1995. Detection and characterization of a 3′ untranslated region ribonucleoprotein complex associated with human α-globin mRNA stability. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15:1769-1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wang, Z., N. Day, P. Trifillis, and M. Kiledjian. 1999. An mRNA stability complex functions with poly(A)-binding protein to stabilize mRNA in vitro. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:4552-4560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Weiss, I. M., and S. A. Liebhaber. 1994. Erythroid cell-specific determinants of α-globin mRNA stability. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:8123-8132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Weiss, I. M., and S. A. Liebhaber. 1995. Erythroid cell-specific mRNA stability elements in the α2-globin 3′ nontranslated region. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15:2457-2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Welfle, H., B. Henkel, and H. Bielka. 1976. Ionic interactions in eukaryotic ribosomes: splitting of the subunits of rat liver ribosomes by treatment with monovalent cations. Acta Biol. Med. Ger. 35:401-411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ziemiecki, A., R. G. Muller, X. C. Fu, N. E. Hynes, and S. Kozma. 1990. Oncogenic activation of the human trk proto-oncogene by recombination with the ribosomal large subunit protein L7a. EMBO J. 9:191-196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]