Abstract
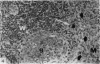
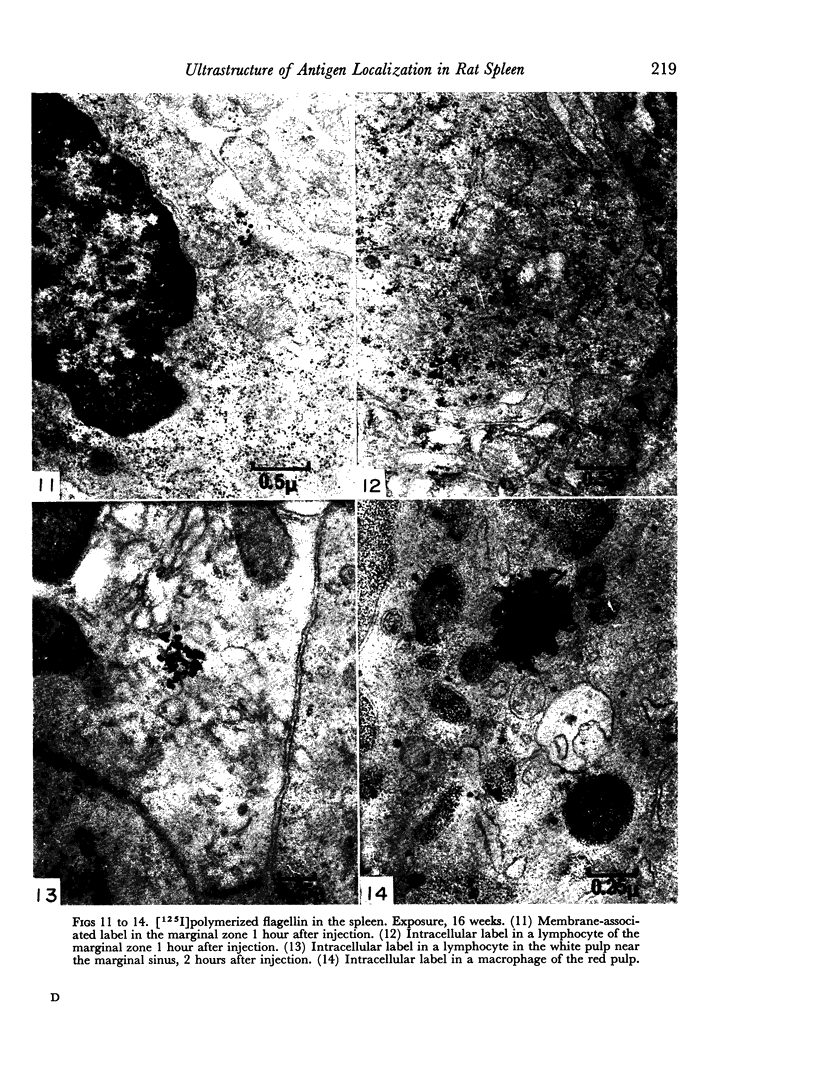
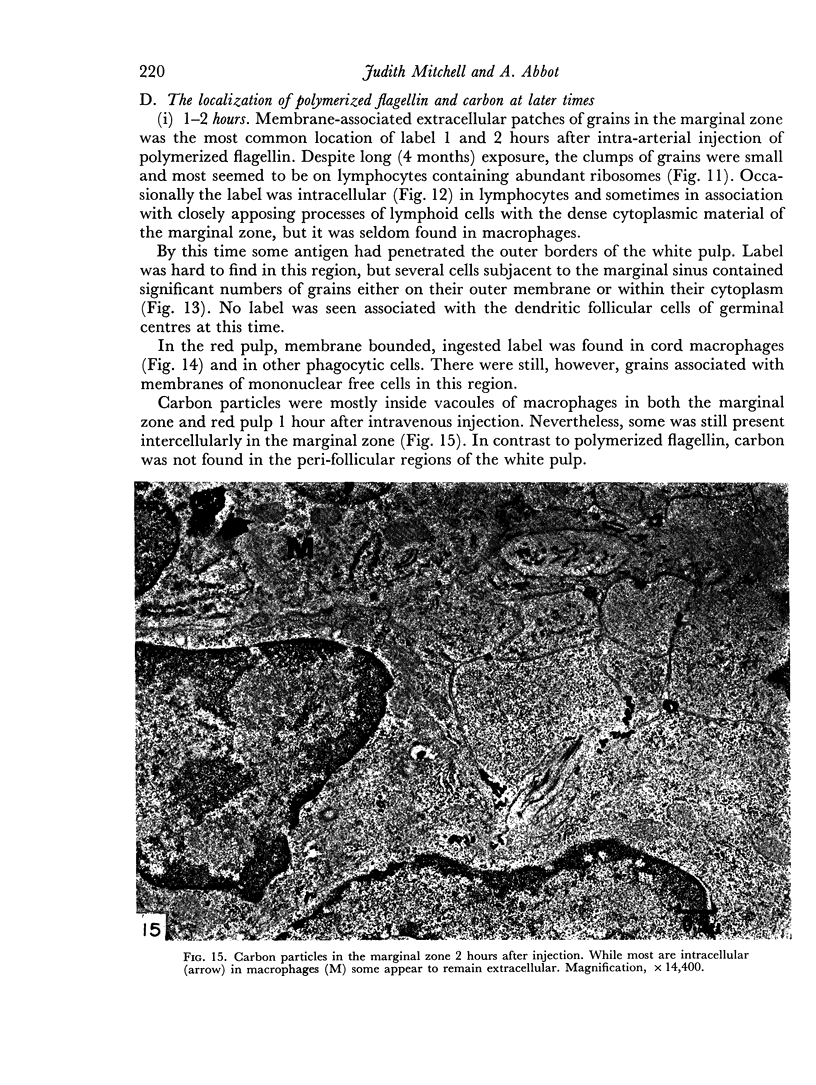
This paper describes the ultrastructural location of labelled antigens and carbon in the spleens of rats from 4 minutes to 5 days after injection. Particular attention was focused on the sites of deposition 4 minutes after intra-arterial injection of microgram quantities of 125I-labelled Salmonella flagellar antigens, crayfish haemocyanin and BSA, using colloidal carbon for comparison. The combination of radioautography with both light and electron microscopy showed the importance of antigen binding by lymphocytes in the marginal zone of the spleen. Macrophage sequestration of antigens was not prominent in the spleen, although it occurred in the liver with the flagellar antigens and haemocyanin.
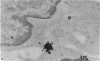
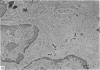
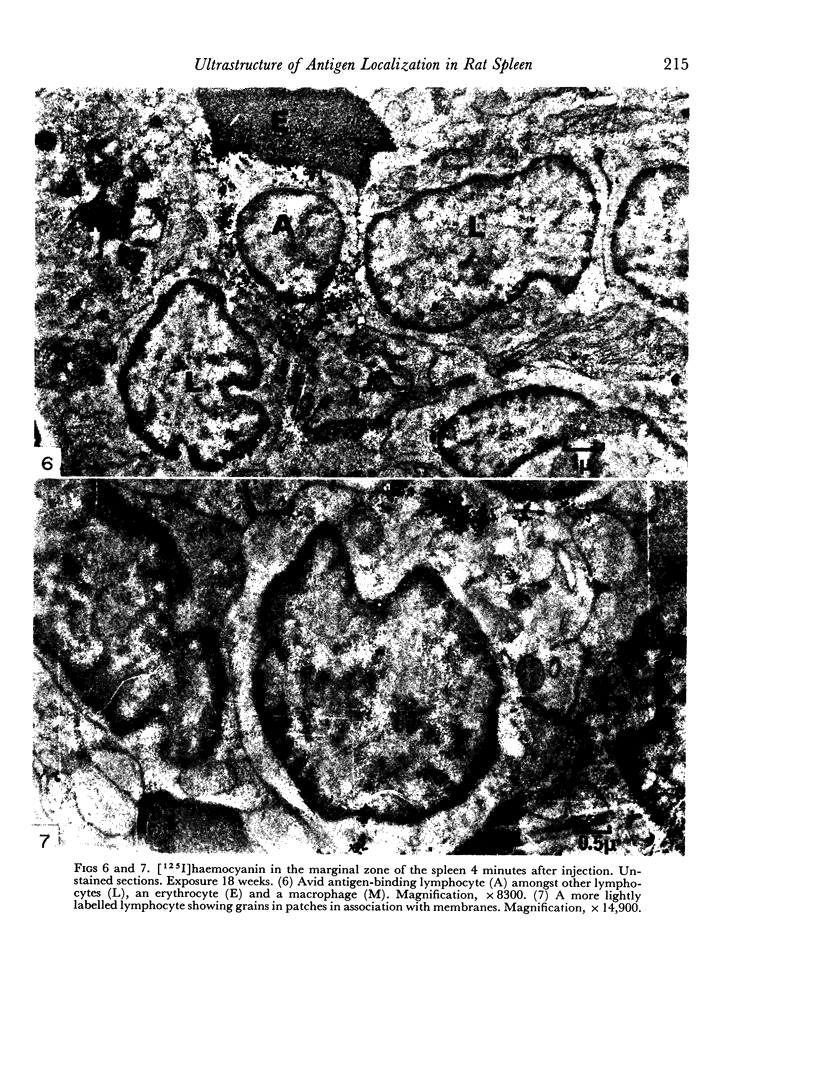
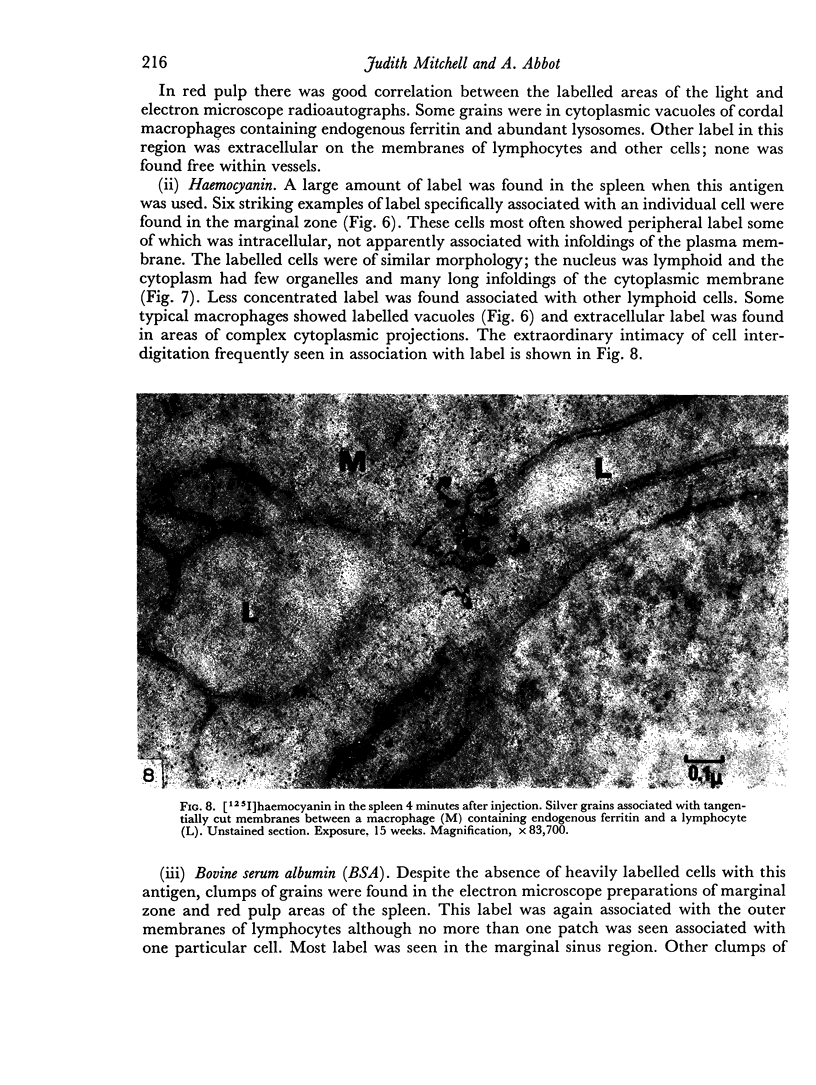
In the spleen marginal zone, avid antigen-binding cells were found in situ 4 minutes after the injection of labelled haemocyanin. These appear to be the counterpart in vivo of antigen-binding lymphocytes prepared in vitro. Such cells also occurred infrequently after the injection of labelled polymerized flagellin, but were not found with either BSA or carbon.
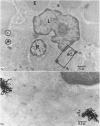
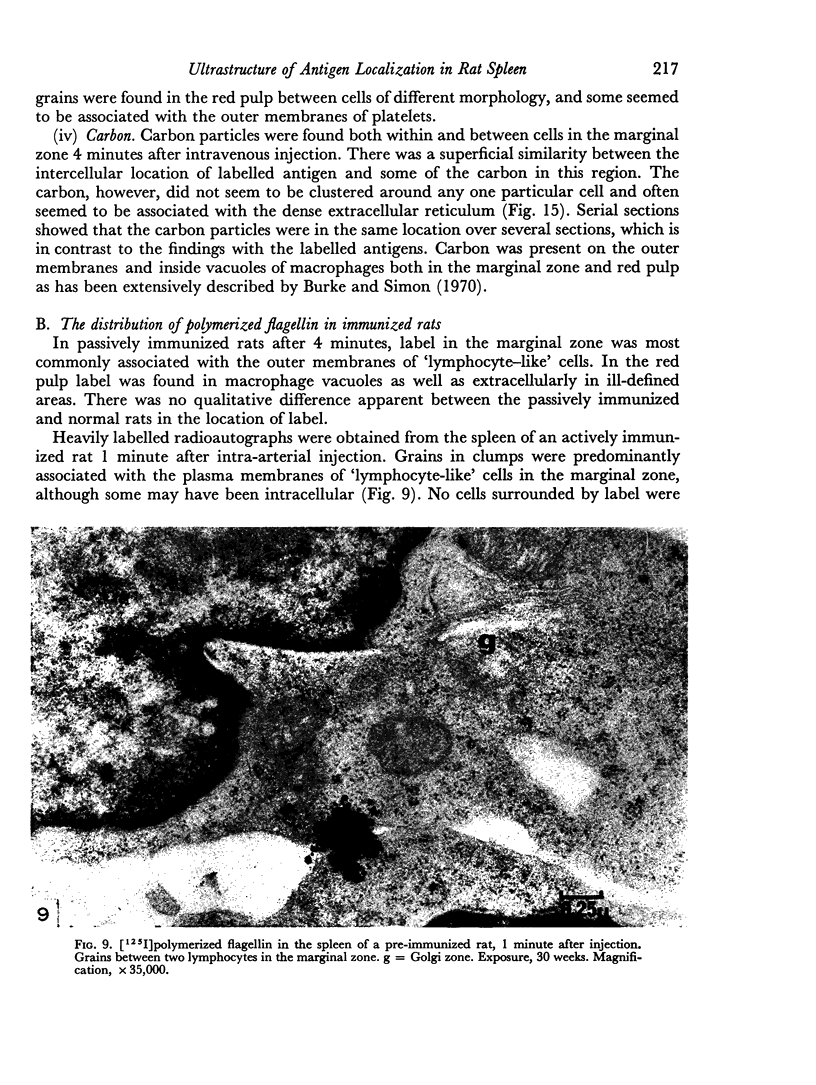
The apparent movement of flagellar antigen from the marginal zone to the white pulp between 1 and 2 hours after injection was seen to involve lymphocyte-associated antigen. The follicular antigen localization occurring from 1 day onwards after injection was on the dendritic reticular cells of germinal centres, as has been described in lymph nodes after subcutaneous injection.
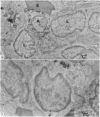
Carbon particles were rapidly sequestered in macrophages of the spleen and liver, although some particles were found between cells in the marginal zone for as long as 2 hours after injection. By 2 and 5 days, however, all the carbon was in phagocytes, even in the white pulp. Differences between the localization of antigens and carbon were clear, even in the ultrastructural sites of their location in tingible body macrophages of germinal centres.
The unexpected emphasis of lymphocyte association with labelled antigens in the spleen marginal zone has allowed a revison of the mechanism previously proposed for the movement of antigens within the microenvironments of the spleen.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., NOSSAL G. J., PYE J., ABBOT A. ANTIGENS IN IMMUNITY. I. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF FLAGELLAR ANTIGENS FROM SALMONELLA ADELAIDE. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Jun;42:267–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADA G. L., NOSSAL G. J., PYE J. ANTIGENS IN IMMUNITY. III. DISTRIBUTION OF IODINATED ANTIGENS FOLLOWING INJECTION INTO RATS VIA THE HIND FOOTPADS. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Jun;42:295–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki T., Hämmerling U., De Harven E., Boyse E. A., Old L. J. Antigenic structure of cell surfaces. An immunoferritin study of the occurrence and topography of H-2' theta, and TL alloantigens on mouse cells. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):979–1001. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. S., Simon G. T. Electron microscopy of the spleen. II. Phagocytosis of colloidal carbon. Am J Pathol. 1970 Jan;58(1):157–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel T., Byrt P., Ada G. L. A morphological examination of antigen reactive cells from mouse spleen and peritoneal cavity. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Nov;58(1):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcuson E. C., Roitt I. M. Immunoglobulin allotypic determinants on rabbit lymphocytes. Nature. 1970 Sep 5;227(5262):1051–1053. doi: 10.1038/2271051a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Abbot A., Mitchell J. Antigens in immunity. XIV. Electron microscopic radioautographic studies of antigen capture in the lymph node medulla. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):263–276. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Abbot A., Mitchell J., Lummus Z. Antigens in immunity. XV. Ultrastructural features of antigen capture in primary and secondary lymphoid follicles. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):277–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Austin C. M., Pye J., Mitchell J. Antigens in immunity. XII. Antigen trapping in the spleen. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(4):368–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALPETER M. M., BACHMANN L. AUTORADIOGRAPHY WITH THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. A PROCEDURE FOR IMPROVING RESOLUTION, SENSITIVITY, AND CONTRAST. J Cell Biol. 1964 Aug;22:469–477. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulitzeanu D., Naor D. The affinity of radioiodinated BSA for lymphoid cells. II. Binding of 125I-BSA to lymphoid cells of normal mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;35(6):564–578. doi: 10.1159/000230210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]